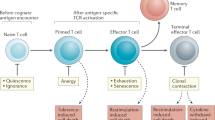
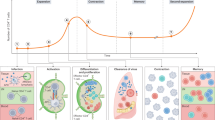
Abstract
Homeostasis in the immune system encompasses the mechanisms governing maintenance of a functional and diverse pool of lymphocytes, thus guaranteeing immunity to pathogens while remaining self-tolerant. Antigen-naïve T cells rely on survival signals through contact with self-peptide-loaded major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules plus interleukin (IL)-7. Conversely, antigen-experienced (memory) T cells are typically MHC-independent and they survive and undergo periodic homeostatic proliferation through contact with both IL-7 and IL-15. Also, non-conventional γδ T cells rely on a mix of IL-7 and IL-15 for their homeostasis, whereas natural killer cells are mainly dependent on contact with IL-15. Homeostasis of CD4+ T regulatory cells is different in being chiefly regulated by contact with IL-2. Notably, increased levels of these cytokines cause expansion of responsive lymphocytes, such as found in lymphopenic hosts or following cytokine injection, whereas reduced cytokine levels cause a decline in cell numbers.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APC:
-
Antigen-presenting cell
- Blimp-1:
-
B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein 1
- BTLA:
-
B and T lymphocyte attenuator
- Foxo1:
-
Forkhead box o1
- Foxp3:
-
Forkhead box p3
- GABPα:
-
GA binding protein α
- Gfi-1:
-
Growth factor independence 1
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- Jak:
-
Janus kinase
- KLF2:
-
Kruppel-like factor 2
- KLRG1:
-
Killer cell lectin-like receptor G1
- LCMV:
-
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus
- LN:
-
Lymph node
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- MHC:
-
Major histocompatibility complex
- MP:
-
Memory-phenotype
- NK:
-
Natural killer
- RAG:
-
Recombinase-activating gene
- S1P1 :
-
Sphingosine 1 phosphate receptor 1
- SOCS-1:
-
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1
- STAT5:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5
- TCF-1:
-
T cell factor 1
- TCR:
-
T cell receptor
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor-β
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- Treg:
-
T regulatory cell
- TSLP:
-
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin
- γc :
-
Common γ chain
References
Hogquist KA, Baldwin TA, Jameson SC (2005) Central tolerance: learning self-control in the thymus. Nat Rev Immunol 5(10):772–782
Ahmed R, Gray D (1996) Immunological memory and protective immunity: understanding their relation. Science 272(5258):54–60
Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A, Araki K, Ahmed R (2010) From vaccines to memory and back. Immunity 33(4):451–463
Sallusto F, Geginat J, Lanzavecchia A (2004) Central memory and effector memory T cell subsets: function, generation, and maintenance. Annu Rev Immunol 22:745–763
Masopust D, Vezys V, Marzo AL, Lefrancois L (2001) Preferential localization of effector memory cells in nonlymphoid tissue. Science 291(5512):2413–2417
Reinhardt RL, Khoruts A, Merica R, Zell T, Jenkins MK (2001) Visualizing the generation of memory CD4 T cells in the whole body. Nature 410(6824):101–105
Sprent J, Surh CD (2011) Normal T cell homeostasis: the conversion of naive cells into memory-phenotype cells. Nat Immunol 12(6):478–484
Takeda S, Rodewald HR, Arakawa H, Bluethmann H, Shimizu T (1996) MHC class II molecules are not required for survival of newly generated CD4+ T cells, but affect their long-term life span. Immunity 5(3):217–228
Labrecque N, Whitfield LS, Obst R, Waltzinger C, Benoist C, Mathis D (2001) How much TCR does a T cell need? Immunity 15(1):71–82
Polic B, Kunkel D, Scheffold A, Rajewsky K (2001) How alpha beta T cells deal with induced TCR alpha ablation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(15):8744–8749
Martin B, Becourt C, Bienvenu B, Lucas B (2006) Self-recognition is crucial for maintaining the peripheral CD4+ T-cell pool in a nonlymphopenic environment. Blood 108(1):270–277
Takada K, Jameson SC (2009) Self-class I MHC molecules support survival of naive CD8 T cells, but depress their functional sensitivity through regulation of CD8 expression levels. J Exp Med 206(10):2253–2269
Hataye J, Moon JJ, Khoruts A, Reilly C, Jenkins MK (2006) Naive and memory CD4+ T cell survival controlled by clonal abundance. Science 312(5770):114–116
Takada K, Jameson SC (2009) Naive T cell homeostasis: from awareness of space to a sense of place. Nat Rev Immunol 9(12):823–832
Boyman O, Letourneau S, Krieg C, Sprent J (2009) Homeostatic proliferation and survival of naive and memory T cells. Eur J Immunol 39(8):2088–2094
Brocker T (1997) Survival of mature CD4 T lymphocytes is dependent on major histocompatibility complex class II-expressing dendritic cells. J Exp Med 186(8):1223–1232
Link A, Vogt TK, Favre S, Britschgi MR, Acha-Orbea H, Hinz B, Cyster JG, Luther SA (2007) Fibroblastic reticular cells in lymph nodes regulate the homeostasis of naive T cells. Nat Immunol 8(11):1255–1265
Jung YW, Rutishauser RL, Joshi NS, Haberman AM, Kaech SM (2010) Differential localization of effector and memory CD8 T cell subsets in lymphoid organs during acute viral infection. J Immunol 185(9):5315–5325
Carlson CM, Endrizzi BT, Wu J, Ding X, Weinreich MA, Walsh ER, Wani MA, Lingrel JB, Hogquist KA, Jameson SC (2006) Kruppel-like factor 2 regulates thymocyte and T-cell migration. Nature 442(7100):299–302
Kerdiles YM, Beisner DR, Tinoco R, Dejean AS, Castrillon DH, DePinho RA, Hedrick SM (2009) Foxo1 links homing and survival of naive T cells by regulating l-selectin, CCR7 and interleukin 7 receptor. Nat Immunol 10(2):176–184
Ouyang W, Beckett O, Flavell RA, Li MO (2009) An essential role of the Forkhead-box transcription factor Foxo1 in control of T cell homeostasis and tolerance. Immunity 30(3):358–371
Swain SL, Hu H, Huston G (1999) Class II-independent generation of CD4 memory T cells from effectors. Science 286(5443):1381–1383
Murali-Krishna K, Lau LL, Sambhara S, Lemonnier F, Altman J, Ahmed R (1999) Persistence of memory CD8 T cells in MHC class I-deficient mice. Science 286(5443):1377–1381
Leignadier J, Hardy MP, Cloutier M, Rooney J, Labrecque N (2008) Memory T-lymphocyte survival does not require T-cell receptor expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(51):20440–20445
Surh CD, Boyman O, Purton JF, Sprent J (2006) Homeostasis of memory T cells. Immunol Rev 211:154–163
Shin H, Blackburn SD, Blattman JN, Wherry EJ (2007) Viral antigen and extensive division maintain virus-specific CD8 T cells during chronic infection. J Exp Med 204(4):941–949
Bensinger SJ, Bandeira A, Jordan MS, Caton AJ, Laufer TM (2001) Major histocompatibility complex class II-positive cortical epithelium mediates the selection of CD4(+)25(+) immunoregulatory T cells. J Exp Med 194(4):427–438
Kim JK, Klinger M, Benjamin J, Xiao Y, Erle DJ, Littman DR, Killeen N (2009) Impact of the TCR signal on regulatory T cell homeostasis, function, and trafficking. PLoS One 4(8):e6580
Rochman Y, Spolski R, Leonard WJ (2009) New insights into the regulation of T cells by gamma(c) family cytokines. Nat Rev Immunol 9(7):480–490
Hildeman D, Jorgensen T, Kappler J, Marrack P (2007) Apoptosis and the homeostatic control of immune responses. Curr Opin Immunol 19(5):516–521
Letourneau S, Krieg C, Pantaleo G, Boyman O (2009) IL-2- and CD25-dependent immunoregulatory mechanisms in the homeostasis of T-cell subsets. J Allergy Clin Immunol 123(4):758–762
Tokoyoda K, Zehentmeier S, Hegazy AN, Albrecht I, Grun JR, Lohning M, Radbruch A (2009) Professional memory CD4+ T lymphocytes preferentially reside and rest in the bone marrow. Immunity 30(5):721–730
Sawa Y, Arima Y, Ogura H, Kitabayashi C, Jiang JJ, Fukushima T, Kamimura D, Hirano T, Murakami M (2009) Hepatic interleukin-7 expression regulates T cell responses. Immunity 30(3):447–457
Fry TJ, Mackall CL (2005) The many faces of IL-7: from lymphopoiesis to peripheral T cell maintenance. J Immunol 174(11):6571–6576
Zhang X, Sun S, Hwang I, Tough DF, Sprent J (1998) Potent and selective stimulation of memory-phenotype CD8+ T cells in vivo by IL-15. Immunity 8(5):591–599
Boyman O (2010) Bystander activation of CD4+ T cells. Eur J Immunol 40(4):936–939
Dubois S, Mariner J, Waldmann TA, Tagaya Y (2002) IL-15Ralpha recycles and presents IL-15 in trans to neighboring cells. Immunity 17(5):537–547
Boyman O, Purton JF, Surh CD, Sprent J (2007) Cytokines and T-cell homeostasis. Curr Opin Immunol 19(3):320–326
Malek TR, Castro I (2010) Interleukin-2 receptor signaling: at the interface between tolerance and immunity. Immunity 33(2):153–165
Fontenot JD, Rasmussen JP, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY (2005) A function for interleukin 2 in Foxp3-expressing regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol 6(11):1142–1151
Malek TR, Yu A, Vincek V, Scibelli P, Kong L (2002) CD4 regulatory T cells prevent lethal autoimmunity in IL-2Rbeta-deficient mice. Implications for the nonredundant function of IL-2. Immunity 17(2):167–178
Rubtsov YP, Niec RE, Josefowicz S, Li L, Darce J, Mathis D, Benoist C, Rudensky AY (2010) Stability of the regulatory T cell lineage in vivo. Science 329(5999):1667–1671
Barron L, Dooms H, Hoyer KK, Kuswanto W, Hofmann J, O’Gorman WE, Abbas AK (2010) Cutting edge: mechanisms of IL-2-dependent maintenance of functional regulatory T cells. J Immunol 185(11):6426–6430
Boyman O, Kovar M, Rubinstein MP, Surh CD, Sprent J (2006) Selective stimulation of T cell subsets with antibody–cytokine immune complexes. Science 311(5769):1924–1927
Webster KE, Walters S, Kohler RE, Mrkvan T, Boyman O, Surh CD, Grey ST, Sprent J (2009) In vivo expansion of T reg cells with IL-2-mAb complexes: induction of resistance to EAE and long-term acceptance of islet allografts without immunosuppression. J Exp Med 206(4):751–760
Pandiyan P, Zheng L, Ishihara S, Reed J, Lenardo MJ (2007) CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells induce cytokine deprivation-mediated apoptosis of effector CD4+ T cells. Nat Immunol 8(12):1353–1362
Letourneau S, van Leeuwen EM, Krieg C, Martin C, Pantaleo G, Sprent J, Surh CD, Boyman O (2010) IL-2/anti-IL-2 antibody complexes show strong biological activity by avoiding interaction with IL-2 receptor alpha subunit CD25. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(5):2171–2176
Boyman O, Cho JH, Sprent J (2010) The role of interleukin-2 in memory CD8 cell differentiation. Adv Exp Med Biol 684:28–41
Mantel PY, Kuipers H, Boyman O, Rhyner C, Ouaked N, Ruckert B, Karagiannidis C, Lambrecht BN, Hendriks RW, Crameri R, Akdis CA, Blaser K, Schmidt-Weber CB (2007) GATA3-driven Th2 responses inhibit TGF-beta1-induced FOXP3 expression and the formation of regulatory T cells. PLoS Biol 5(12):e329
Dooms H, Wolslegel K, Lin P, Abbas AK (2007) Interleukin-2 enhances CD4+ T cell memory by promoting the generation of IL-7R alpha-expressing cells. J Exp Med 204(3):547–557
Pipkin ME, Sacks JA, Cruz-Guilloty F, Lichtenheld MG, Bevan MJ, Rao A (2010) Interleukin-2 and inflammation induce distinct transcriptional programs that promote the differentiation of effector cytolytic T cells. Immunity 32(1):79–90
Williams MA, Tyznik AJ, Bevan MJ (2006) Interleukin-2 signals during priming are required for secondary expansion of CD8+ memory T cells. Nature 441(7095):890–893
Bachmann MF, Wolint P, Walton S, Schwarz K, Oxenius A (2007) Differential role of IL-2R signaling for CD8+ T cell responses in acute and chronic viral infections. Eur J Immunol 37(6):1502–1512
Kalia V, Sarkar S, Subramaniam S, Haining WN, Smith KA, Ahmed R (2010) Prolonged interleukin-2Ralpha expression on virus-specific CD8+ T cells favors terminal-effector differentiation in vivo. Immunity 32(1):91–103
Blattman JN, Grayson JM, Wherry EJ, Kaech SM, Smith KA, Ahmed R (2003) Therapeutic use of IL-2 to enhance antiviral T-cell responses in vivo. Nat Med 9(5):540–547
Lenz DC, Kurz SK, Lemmens E, Schoenberger SP, Sprent J, Oldstone MB, Homann D (2004) IL-7 regulates basal homeostatic proliferation of antiviral CD4+ T cell memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(25):9357–9362
Krieg C, Letourneau S, Pantaleo G, Boyman O (2010) Improved IL-2 immunotherapy by selective stimulation of IL-2 receptors on lymphocytes and endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(26):11906–11911
Krieg C, Han P, Stone R, Goularte OD, Kaye J (2005) Functional analysis of B and T lymphocyte attenuator engagement on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. J Immunol 175(10):6420–6427
Krieg C, Boyman O, Fu YX, Kaye J (2007) B and T lymphocyte attenuator regulates CD8+ T cell-intrinsic homeostasis and memory cell generation. Nat Immunol 8(2):162–171
Schluns KS, Kieper WC, Jameson SC, Lefrancois L (2000) Interleukin-7 mediates the homeostasis of naive and memory CD8 T cells in vivo. Nat Immunol 1(5):426–432
Tan JT, Dudl E, LeRoy E, Murray R, Sprent J, Weinberg KI, Surh CD (2001) IL-7 is critical for homeostatic proliferation and survival of naive T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(15):8732–8737
Kaech SM, Tan JT, Wherry EJ, Konieczny BT, Surh CD, Ahmed R (2003) Selective expression of the interleukin 7 receptor identifies effector CD8 T cells that give rise to long-lived memory cells. Nat Immunol 4(12):1191–1198
Huster KM, Busch V, Schiemann M, Linkemann K, Kerksiek KM, Wagner H, Busch DH (2004) Selective expression of IL-7 receptor on memory T cells identifies early CD40L-dependent generation of distinct CD8+ memory T cell subsets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:5610–5615
Park JH, Yu Q, Erman B, Appelbaum JS, Montoya-Durango D, Grimes HL, Singer A (2004) Suppression of IL7Ralpha transcription by IL-7 and other prosurvival cytokines: a novel mechanism for maximizing IL-7-dependent T cell survival. Immunity 21(2):289–302
Boyman O, Ramsey C, Kim DM, Sprent J, Surh CD (2008) IL-7/anti-IL-7 mAb complexes restore T cell development and induce homeostatic T cell expansion without lymphopenia. J Immunol 180(11):7265–7275
Klonowski KD, Williams KJ, Marzo AL, Lefrancois L (2006) Cutting edge: IL-7-independent regulation of IL-7 receptor alpha expression and memory CD8 T cell development. J Immunol 177(7):4247–4251
DeKoter RP, Lee HJ, Singh H (2002) PU.1 regulates expression of the interleukin-7 receptor in lymphoid progenitors. Immunity 16(2):297–309
Xue HH, Bollenbacher J, Rovella V, Tripuraneni R, Du YB, Liu CY, Williams A, McCoy JP, Leonard WJ (2004) GA binding protein regulates interleukin 7 receptor alpha-chain gene expression in T cells. Nat Immunol 5(10):1036–1044
Chandele A, Joshi NS, Zhu J, Paul WE, Leonard WJ, Kaech SM (2008) Formation of IL-7Ralphahigh and IL-7Ralphalow CD8 T cells during infection is regulated by the opposing functions of GABPalpha and Gfi-1. J Immunol 180(8):5309–5319
Luther SA, Ansel KM, Cyster JG (2003) Overlapping roles of CXCL13, interleukin 7 receptor alpha, and CCR7 ligands in lymph node development. J Exp Med 197(9):1191–1198
Meier D, Bornmann C, Chappaz S, Schmutz S, Otten LA, Ceredig R, Acha-Orbea H, Finke D (2007) Ectopic lymphoid-organ development occurs through interleukin 7-mediated enhanced survival of lymphoid-tissue-inducer cells. Immunity 26(5):643–654
Schmutz S, Bosco N, Chappaz S, Boyman O, Acha-Orbea H, Ceredig R, Rolink AG, Finke D (2009) Cutting edge: IL-7 regulates the peripheral pool of adult RORgamma + lymphoid tissue inducer cells. J Immunol 183(4):2217–2221
Intlekofer AM, Takemoto N, Wherry EJ, Longworth SA, Northrup JT, Palanivel VR, Mullen AC, Gasink CR, Kaech SM, Miller JD, Gapin L, Ryan K, Russ AP, Lindsten T, Orange JS, Goldrath AW, Ahmed R, Reiner SL (2005) Effector and memory CD8+ T cell fate coupled by T-bet and eomesodermin. Nat Immunol 6(12):1236–1244
Banerjee A, Gordon SM, Intlekofer AM, Paley MA, Mooney EC, Lindsten T, Wherry EJ, Reiner SL (2010) Cutting edge: The transcription factor eomesodermin enables CD8+ T cells to compete for the memory cell niche. J Immunol 185(9):4988–4992
Zhou X, Yu S, Zhao DM, Harty JT, Badovinac VP, Xue HH (2010) Differentiation and persistence of memory CD8(+) T cells depend on T cell factor 1. Immunity 33(2):229–240
Jeannet G, Boudousquie C, Gardiol N, Kang J, Huelsken J, Held W (2010) Essential role of the Wnt pathway effector Tcf-1 for the establishment of functional CD8 T cell memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(21):9777–9782
Decaluwe H, Taillardet M, Corcuff E, Munitic I, Law HK, Rocha B, Riviere Y, Di Santo JP (2010) Gamma(c) deficiency precludes CD8+ T cell memory despite formation of potent T cell effectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(20):9311–9316
Joshi NS, Cui W, Chandele A, Lee HK, Urso DR, Hagman J, Gapin L, Kaech SM (2007) Inflammation directs memory precursor and short-lived effector CD8(+) T cell fates via the graded expression of T-bet transcription factor. Immunity 27(2):281–295
Takemoto N, Intlekofer AM, Northrup JT, Wherry EJ, Reiner SL (2006) Cutting Edge: IL-12 inversely regulates T-bet and eomesodermin expression during pathogen-induced CD8+ T cell differentiation. J Immunol 177(11):7515–7519
Kallies A, Xin A, Belz GT, Nutt SL (2009) Blimp-1 transcription factor is required for the differentiation of effector CD8(+) T cells and memory responses. Immunity 31(2):283–295
Rutishauser RL, Martins GA, Kalachikov S, Chandele A, Parish IA, Meffre E, Jacob J, Calame K, Kaech SM (2009) Transcriptional repressor Blimp-1 promotes CD8(+) T cell terminal differentiation and represses the acquisition of central memory T cell properties. Immunity 31(2):296–308
Becker TC, Wherry EJ, Boone D, Murali-Krishna K, Antia R, Ma A, Ahmed R (2002) Interleukin 15 is required for proliferative renewal of virus-specific memory CD8 T cells. J Exp Med 195(12):1541–1548
Judge AD, Zhang X, Fujii H, Surh CD, Sprent J (2002) Interleukin 15 controls both proliferation and survival of a subset of memory-phenotype CD8(+) T cells. J Exp Med 196(7):935–946
Ma A, Koka R, Burkett P (2006) Diverse functions of IL-2, IL-15, and IL-7 in lymphoid homeostasis. Annu Rev Immunol 24:657–679
Becker TC, Coley SM, Wherry EJ, Ahmed R (2005) Bone marrow is a preferred site for homeostatic proliferation of memory CD8 T cells. J Immunol 174(3):1269–1273
Parretta E, Cassese G, Barba P, Santoni A, Guardiola J, Di Rosa F (2005) CD8 cell division maintaining cytotoxic memory occurs predominantly in the bone marrow. J Immunol 174(12):7654–7664
Su YC, Lee CC, Kung JT (2010) Effector function-deficient memory CD8+ T cells clonally expand in the liver and give rise to peripheral memory CD8+ T cells. J Immunol 185(12):7498–7506
Goldrath AW, Sivakumar PV, Glaccum M, Kennedy MK, Bevan MJ, Benoist C, Mathis D, Butz EA (2002) Cytokine requirements for acute and Basal homeostatic proliferation of naive and memory CD8+ T cells. J Exp Med 195(12):1515–1522
Kennedy MK, Glaccum M, Brown SN, Butz EA, Viney JL, Embers M, Matsuki N, Charrier K, Sedger L, Willis CR, Brasel K, Morrissey PJ, Stocking K, Schuh JC, Joyce S, Peschon JJ (2000) Reversible defects in natural killer and memory CD8 T cell lineages in interleukin 15-deficient mice. J Exp Med 191(5):771–780
Lodolce JP, Boone DL, Chai S, Swain RE, Dassopoulos T, Trettin S, Ma A (1998) IL-15 receptor maintains lymphoid homeostasis by supporting lymphocyte homing and proliferation. Immunity 9(5):669–676
Rubinstein MP, Kovar M, Purton JF, Cho JH, Boyman O, Surh CD, Sprent J (2006) Converting IL-15 to a superagonist by binding to soluble IL-15R{alpha}. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(24):9166–9171
Stoklasek TA, Schluns KS, Lefrancois L (2006) Combined IL-15/IL-15Ralpha immunotherapy maximizes IL-15 activity in vivo. J Immunol 177(9):6072–6080
Nishimura H, Yajima T, Naiki Y, Tsunobuchi H, Umemura M, Itano K, Matsuguchi T, Suzuki M, Ohashi PS, Yoshikai Y (2000) Differential roles of interleukin 15 mRNA isoforms generated by alternative splicing in immune responses in vivo. J Exp Med 191(1):157–170
Marks-Konczalik J, Dubois S, Losi JM, Sabzevari H, Yamada N, Feigenbaum L, Waldmann TA, Tagaya Y (2000) IL-2-induced activation-induced cell death is inhibited in IL-15 transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(21):11445–11450
Fehniger TA, Suzuki K, Ponnappan A, VanDeusen JB, Cooper MA, Florea SM, Freud AG, Robinson ML, Durbin J, Caligiuri MA (2001) Fatal leukemia in interleukin 15 transgenic mice follows early expansions in natural killer and memory phenotype CD8+ T cells. J Exp Med 193(2):219–231
Yajima T, Yoshihara K, Nakazato K, Kumabe S, Koyasu S, Sad S, Shen H, Kuwano H, Yoshikai Y (2006) IL-15 regulates CD8+ T cell contraction during primary infection. J Immunol 176(1):507–515
Moroz A, Eppolito C, Li Q, Tao J, Clegg CH, Shrikant PA (2004) IL-21 enhances and sustains CD8+ T cell responses to achieve durable tumor immunity: comparative evaluation of IL-2, IL-15, and IL-21. J Immunol 173(2):900–909
Zeng R, Spolski R, Finkelstein SE, Oh S, Kovanen PE, Hinrichs CS, Pise-Masison CA, Radonovich MF, Brady JN, Restifo NP, Berzofsky JA, Leonard WJ (2005) Synergy of IL-21 and IL-15 in regulating CD8+ T cell expansion and function. J Exp Med 201(1):139–148
Allard EL, Hardy MP, Leignadier J, Marquis M, Rooney J, Lehoux D, Labrecque N (2007) Overexpression of IL-21 promotes massive CD8+ memory T cell accumulation. Eur J Immunol 37(11):3069–3077
Novy P, Huang X, Leonard WJ, Yang Y (2011) Intrinsic IL-21 signaling is critical for CD8 T Cell survival and memory formation in response to vaccinia viral infection. J Immunol 186(5):2729–2738
Elsaesser H, Sauer K, Brooks DG (2009) IL-21 is required to control chronic viral infection. Science 324(5934):1569–1572
Yi JS, Du M, Zajac AJ (2009) A vital role for interleukin-21 in the control of a chronic viral infection. Science 324(5934):1572–1576
Frohlich A, Kisielow J, Schmitz I, Freigang S, Shamshiev AT, Weber J, Marsland BJ, Oxenius A, Kopf M (2009) IL-21R on T cells is critical for sustained functionality and control of chronic viral infection. Science 324(5934):1576–1580
Kieper WC, Tan JT, Bondi-Boyd B, Gapin L, Sprent J, Ceredig R, Surh CD (2002) Overexpression of interleukin (IL)-7 leads to IL-15-independent generation of memory phenotype CD8+ T cells. J Exp Med 195(12):1533–1539
Chappaz S, Flueck L, Farr AG, Rolink AG, Finke D (2007) Increased TSLP availability restores T- and B-cell compartments in adult IL-7 deficient mice. Blood 110(12):3862–3870
Rochman Y, Leonard WJ (2008) The role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in CD8+ T cell homeostasis. J Immunol 181(11):7699–7705
Min B, McHugh R, Sempowski GD, Mackall C, Foucras G, Paul WE (2003) Neonates support lymphopenia-induced proliferation. Immunity 18(1):131–140
Guimond M, Veenstra RG, Grindler DJ, Zhang H, Cui Y, Murphy RD, Kim SY, Na R, Hennighausen L, Kurtulus S, Erman B, Matzinger P, Merchant MS, Mackall CL (2009) Interleukin 7 signaling in dendritic cells regulates the homeostatic proliferation and niche size of CD4+ T cells. Nat Immunol 10(2):149–157
Ernst B, Lee DS, Chang JM, Sprent J, Surh CD (1999) The peptide ligands mediating positive selection in the thymus control T cell survival and homeostatic proliferation in the periphery. Immunity 11(2):173–181
Goldrath AW, Bevan MJ (1999) Low-affinity ligands for the TCR drive proliferation of mature CD8+ T cells in lymphopenic hosts. Immunity 11(2):183–190
Kieper WC, Jameson SC (1999) Homeostatic expansion and phenotypic conversion of naive T cells in response to self peptide/MHC ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(23):13306–13311
Almeida AR, Rocha B, Freitas AA, Tanchot C (2005) Homeostasis of T cell numbers: from thymus production to peripheral compartmentalization and the indexation of regulatory T cells. Semin Immunol 17(3):239–249
Hamilton SE, Wolkers MC, Schoenberger SP, Jameson SC (2006) The generation of protective memory-like CD8+ T cells during homeostatic proliferation requires CD4+ T cells. Nat Immunol 7(5):475–481
Haluszczak C, Akue AD, Hamilton SE, Johnson LD, Pujanauski L, Teodorovic L, Jameson SC, Kedl RM (2009) The antigen-specific CD8+ T cell repertoire in unimmunized mice includes memory phenotype cells bearing markers of homeostatic expansion. J Exp Med 206(2):435–448
Davey GM, Starr R, Cornish AL, Burghardt JT, Alexander WS, Carbone FR, Surh CD, Heath WR (2005) SOCS-1 regulates IL-15-driven homeostatic proliferation of antigen-naive CD8 T cells, limiting their autoimmune potential. J Exp Med 202(8):1099–1108
Ramanathan S, Gagnon J, Leblanc C, Rottapel R, Ilangumaran S (2006) Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 stringently regulates distinct functions of IL-7 and IL-15 in vivo during T lymphocyte development and homeostasis. J Immunol 176(7):4029–4041
Cho JH, Boyman O, Kim HO, Hahm B, Rubinstein MP, Ramsey C, Kim DM, Surh CD, Sprent J (2007) An intense form of homeostatic proliferation of naive CD8+ cells driven by IL-2. J Exp Med 204(8):1787–1801
Workman CJ, Vignali DA (2005) Negative regulation of T cell homeostasis by lymphocyte activation gene-3 (CD223). J Immunol 174(2):688–695
Posevitz V, Arndt B, Krieger T, Warnecke N, Schraven B, Simeoni L (2008) Regulation of T cell homeostasis by the transmembrane adaptor protein SIT. J Immunol 180(3):1634–1642
Li O, Zheng P, Liu Y (2004) CD24 expression on T cells is required for optimal T cell proliferation in lymphopenic host. J Exp Med 200(8):1083–1089
Kolumam GA, Thomas S, Thompson LJ, Sprent J, Murali-Krishna K (2005) Type I interferons act directly on CD8 T cells to allow clonal expansion and memory formation in response to viral infection. J Exp Med 202(5):637–650
Havenar-Daughton C, Kolumam GA, Murali-Krishna K (2006) Cutting Edge: The direct action of type I IFN on CD4 T cells is critical for sustaining clonal expansion in response to a viral but not a bacterial infection. J Immunol 176(6):3315–3319
Xiao Z, Casey KA, Jameson SC, Curtsinger JM, Mescher MF (2009) Programming for CD8 T cell memory development requires IL-12 or type I IFN. J Immunol 182(5):2786–2794
Bahl K, Kim SK, Calcagno C, Ghersi D, Puzone R, Celada F, Selin LK, Welsh RM (2006) IFN-induced attrition of CD8 T cells in the presence or absence of cognate antigen during the early stages of viral infections. J Immunol 176(7):4284–4295
Whitmire JK, Tan JT, Whitton JL (2005) Interferon-gamma acts directly on CD8+ T cells to increase their abundance during virus infection. J Exp Med 201(7):1053–1059
Whitmire JK, Benning N, Whitton JL (2005) Cutting edge: early IFN-gamma signaling directly enhances primary antiviral CD4+ T cell responses. J Immunol 175(9):5624–5628
O’Shea JJ, Paul WE (2010) Mechanisms underlying lineage commitment and plasticity of helper CD4+ T cells. Science 327(5969):1098–1102
Foulds KE, Rotte MJ, Seder RA (2006) IL-10 is required for optimal CD8 T cell memory following Listeria monocytogenes infection. J Immunol 177(4):2565–2574
Kang SS, Allen PM (2005) Priming in the presence of IL-10 results in direct enhancement of CD8+ T cell primary responses and inhibition of secondary responses. J Immunol 174(9):5382–5389
Brooks DG, Trifilo MJ, Edelmann KH, Teyton L, McGavern DB, Oldstone MB (2006) Interleukin-10 determines viral clearance or persistence in vivo. Nat Med 12(11):1301–1309
Ejrnaes M, Filippi CM, Martinic MM, Ling EM, Togher LM, Crotty S, von Herrath MG (2006) Resolution of a chronic viral infection after interleukin-10 receptor blockade. J Exp Med 203(11):2461–2472
Li MO, Sanjabi S, Flavell RA (2006) Transforming growth factor-beta controls development, homeostasis, and tolerance of T cells by regulatory T cell-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Immunity 25(3):455–471
Tinoco R, Alcalde V, Yang Y, Sauer K, Zuniga EI (2009) Cell-intrinsic transforming growth factor-beta signaling mediates virus-specific CD8+ T cell deletion and viral persistence in vivo. Immunity 31(1):145–157
Bonneville M, O’Brien RL, Born WK (2010) Gammadelta T cell effector functions: a blend of innate programming and acquired plasticity. Nat Rev Immunol 10(7):467–478
Jameson J, Havran WL (2007) Skin gammadelta T-cell functions in homeostasis and wound healing. Immunol Rev 215:114–122
Laky K, Lewis JM, Tigelaar RE, Puddington L (2003) Distinct requirements for IL-7 in development of TCR gamma delta cells during fetal and adult life. J Immunol 170(8):4087–4094
De Creus A, Van Beneden K, Stevenaert F, Debacker V, Plum J, Leclercq G (2002) Developmental and functional defects of thymic and epidermal V gamma 3 cells in IL-15-deficient and IFN regulatory factor-1-deficient mice. J Immunol 168(12):6486–6493
Schluns KS, Nowak EC, Cabrera-Hernandez A, Puddington L, Lefrancois L, Aguila HL (2004) Distinct cell types control lymphoid subset development by means of IL-15 and IL-15 receptor alpha expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(15):5616–5621
Yu Q, Tang C, Xun S, Yajima T, Takeda K, Yoshikai Y (2006) MyD88-dependent signaling for IL-15 production plays an important role in maintenance of CD8 alpha alpha TCR alpha beta and TCR gamma delta intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. J Immunol 176(10):6180–6185
Baccala R, Witherden D, Gonzalez-Quintial R, Dummer W, Surh CD, Havran WL, Theofilopoulos AN (2005) Gamma delta T cell homeostasis is controlled by IL-7 and IL-15 together with subset-specific factors. J Immunol 174(8):4606–4612
French JD, Roark CL, Born WK, O’Brien RL (2005) gamma}{delta T cell homeostasis is established in competition with alpha}{beta T cells and NK cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(41):14741–14746
French JD, Roark CL, Born WK, O’Brien RL (2009) Gammadelta T lymphocyte homeostasis is negatively regulated by beta2-microglobulin. J Immunol 182(4):1892–1900
Boyman O, Surh CD, Sprent J (2006) Potential use of IL-2/anti-IL-2 antibody immune complexes for the treatment of cancer and autoimmune disease. Expert Opin Biol Ther 6(12):1001–1009
Prlic M, Blazar BR, Farrar MA, Jameson SC (2003) In vivo survival and homeostatic proliferation of natural killer cells. J Exp Med 197(8):967–976
Vosshenrich CA, Ranson T, Samson SI, Corcuff E, Colucci F, Rosmaraki EE, Di Santo JP (2005) Roles for common cytokine receptor gamma-chain-dependent cytokines in the generation, differentiation, and maturation of NK cell precursors and peripheral NK cells in vivo. J Immunol 174(3):1213–1221
Kasaian MT, Whitters MJ, Carter LL, Lowe LD, Jussif JM, Deng B, Johnson KA, Witek JS, Senices M, Konz RF, Wurster AL, Donaldson DD, Collins M, Young DA, Grusby MJ (2002) IL-21 limits NK cell responses and promotes antigen-specific T cell activation: a mediator of the transition from innate to adaptive immunity. Immunity 16(4):559–569
Sun JC, Beilke JN, Bezman NA, Lanier LL (2010) Homeostatic proliferation generates long-lived natural killer cells that respond against viral infection. J Exp Med 208(2):357–368
Huntington ND, Tabarias H, Fairfax K, Brady J, Hayakawa Y, Degli-Esposti MA, Smyth MJ, Tarlinton DM, Nutt SL (2007) NK cell maturation and peripheral homeostasis is associated with KLRG1 up-regulation. J Immunol 178(8):4764–4770
Jamieson AM, Isnard P, Dorfman JR, Coles MC, Raulet DH (2004) Turnover and proliferation of NK cells in steady state and lymphopenic conditions. J Immunol 172(2):864–870
Purton JF, Tan JT, Rubinstein MP, Kim DM, Sprent J, Surh CD (2007) Antiviral CD4+ memory T cells are IL-15 dependent. J Exp Med 204(4):951–961
Homann D, Teyton L, Oldstone MB (2001) Differential regulation of antiviral T-cell immunity results in stable CD8 + but declining CD4+ T-cell memory. Nat Med 7(8):913–919
Schiemann M, Busch V, Linkemann K, Huster KM, Busch DH (2003) Differences in maintenance of CD8+ and CD4+ bacteria-specific effector-memory T cell populations. Eur J Immunol 33(10):2875–2885
Imamichi H, Sereti I, Lane HC (2008) IL-15 acts as a potent inducer of CD4(+)CD25(hi) cells expressing FOXP3. Eur J Immunol 38(6):1621–1630
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boyman, O., Krieg, C., Homann, D. et al. Homeostatic maintenance of T cells and natural killer cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 69, 1597–1608 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-0968-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-0968-7