Abstract.
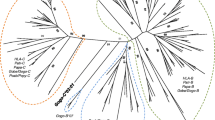
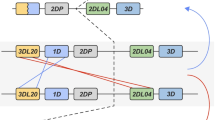
Natural killer (NK) immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) are a family of polymorphic receptors which interact with specific motifs on HLA class I molecules and modulate NK cytolytic activity. In this study, we analyzed a recently sequenced subgenomic region on chromosome 19q13.4 containing eight members of the KIR receptor repertoire. Six members are clustered within a 100-kb continuous sequence. These genes include a previously unpublished member of the KIR gene family 2DS6, as well as 2DL1, 2DL4, 3DL1, 2DS4, 3DL2, from centromere to telomere. Two additional KIR genes, KIRCI and 2DL3, which may be located centromeric of this cluster were also analyzed. We show that the KIR genes have undergone repeated gene duplications. Diversification between the genes has occurred postduplication primarily as a result of retroelement indels and gene truncation. Using pre- and postduplication Alu sequences identified within these genes as evolutionary molecular clocks, the evolution and duplication of this gene cluster is estimated to have occurred 30–45 million years ago, during primate evolution. A proposed model of the duplication history of the KIR gene family leading to their present organization is presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 November 1999 / Revised: 10 January 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, A., Freitas, E., Witt, C. et al. The genomic organization and evolution of the natural killer immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) gene cluster. Immunogenetics 51, 268–280 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002510050620
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002510050620