Abstract
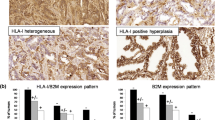
Defects in HLA class I antigen processing machinery (APM) component expression often have a negative impact on the clinical course of tumors and on the response to T cell-based immunotherapy. Since only scant information is available about the frequency and clinical significance of HLA class I APM component abnormalities in prostate cancer, the APM component expression pattern was analyzed in 59 primary prostate carcinoma, adjacent normal tissues, as well as in prostate carcinoma cell lines. The IFN-γ inducible proteasome subunits LMP2 and LMP7, TAP1, TAP2, calnexin, calreticulin, ERp57, and tapasin are strongly expressed in the cytoplasm of normal prostate cells, whereas HLA class I heavy chain (HC) and β2-microglobulin are expressed on the cell surface. Most of the APM components were downregulated in a substantial number of prostate cancers. With the exception of HLA class I HC, TAP2 and ERp57 not detectable in about 0.5% of tumor lesions, all other APM components were not detected in at least 21% of lesions analyzed. These APM component defects were associated with a higher Gleason grade of tumors and an early disease recurrence. Prostate carcinoma cell lines also exhibit a heterogeneous, but reduced constitutive APM component expression pattern associated with lack or reduced HLA class I surface antigens, which could be upregulated by IFN-γ. Our results suggest that HLA class I APM component abnormalities are mainly due to regulatory mechanisms, play a role in the clinical course of prostate cancer and on the outcome of T cell-based immunotherapies.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APM:
-
Antigen processing machinery
- AR:
-
Androgen receptor
- ATCC:
-
American tissue culture collection
- β2-m:
-
β2-Microglobulin
- CTL:
-
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte
- FCS:
-
Fetal calf serum
- HC:
-
Heavy chain
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- LMP:
-
Low molecular weight protein
- mAb:
-
Monoclonal antibody
- MHC:
-
Major histocompatibility complex
- PC:
-
Prostate carcinoma
- PSA:
-
Prostate-specific antigen
- RCC:
-
Renal cell carcinoma
- TA:
-
Tumor antigen
- TAP:
-
Transporter associated with antigen processing
- tpn:
-
Tapasin
- TMA:
-
Tissue microarray
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
References
Epstein JI, Algabe F, Allsbrook WC, Bastacky S (2004) Tumours of the prostate. In: Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA et al (eds) World Health Organization, classification of tumours. Pathology and genetic. Tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs. IARC, Lyon, pp 159–216
Thompson TC (1990) Growth factors and oncogenes in prostate cancer. Cancer cells 2:345–354
Risk M, Corman JM (2009) The role of immunotherapy in prostate cancer: an overview of current approaches in development. Rev Urol 11:16–27
Chakraborty NG, Stevens RL, Mehrotra S, Laska E, Taxel P, Sporn JR, Schauer P, Albertsen PC (2003) Recognition of PSA-derived peptide antigens by T cells from prostate cancer patients without any prior stimulation. Cancer Immunol Immunother 52:497–505
Wang YS, Tsang YW, Chi CH, Cahng CC, Chu RM, Chi KH (2008) Synergistic anti-tumor effect of combination radio- and immunotherapy by electro-gene therapy plus intra-tumor injection of dendritic cells. Cancer Lett 266:275–285
Kiessling A, Füssel S, Wehner R, Bachmann M, Wirth MP, Rieber EP, Schmitz M (2008) Advances in specific immunotherapy for prostate cancer. Eur Urol 53:694–708
Olson WC, Heston WD, Rajasekaran AK (2007) Clinical trials of cancer therapies targeting prostate-specific membrane antigen. Rev Recent Clin Trials 2:182–190
Small EJ, Tchekmedyian NS, Rini BI, Fong L, Lowy I, Allison JP (2007) A pilot trial of CTLA-4 blockade with human anti-CTLA-4 in patients with hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13:1810–1815
Fong L, Kwek SS, O’Brien S, Kavanagh B, McNeel DG, Weinberg V, Lin AM, Rosenberg J, Ryan CJ, Rini BI, Small EJ (2009) Potentiating endogenous antitumor immunity to prostate cancer through combination immunotherapy with CTLA4 blockade and GM-CSF. Cancer Res 69:609–615
Theoret MR, Arlen PM, Pazdur M, Dahut WL, Schlom J, Gulley JL (2007) Phase I trail of an enhanced prostate-specific antigen-based vaccine and anti-CTLA-4 antibody in patients with metastatic androgen-independent prostate cancer. Clin Genitourin Cancer 5:347–350
Slovin SF (2008) Pitfalls or promise in prostate cancer immunotherapy which is winning? Cancer J 14:26–34
Burch PA, Breen JK, Buckner JC, Gastineau DA, Kaur JA, Laus RL, Padley DJ, Peshwa MV, Pitot HC, Richardson RL, Smits BJ, Sopapan P, Strang G, Valone FH, Vuk-Pavlović S (2000) Priming tissue-specific cellular immunity in a phase I trial of autologous dendritic cells for prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 6:2175–2182
Eder JP, Kantoff PW, Roper K, Xu GX, Bubley GJ, Boyden J, Gritz L, Mazzara G, Oh WK, Arlen P, Tsang KY, Panicali D, Schlom J, Kufe DW (2000) A phase I trial of a recombinant vaccina virus expressing prostate-specific antigen in advanced prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 6:1632–1638
Simons JW, Mikhak B, Chang JF, DeMarzo AM, Carducci MA, Lim M, Weber CE, Baccala AA, Goemann MA, Clift SM, Ando DG, Levitsky HI, Cohen LK, Sanda MG, Mulligan RC, Partin AW, Carter HB, Piantadosi S, Marshall FF, Nelson WG (2001) Induction of immunity to prostate cancer antigens: results of a clinical trial of vaccination with irradiated autologous prostate tumor cell engineered to secrete granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor using ex vivo gene transfer. Cancer Res 59:5160–5168
Hammer GE, Kanaseki T, Shastri N (2007) The final touches make perfect the peptide-MHC class I repertoire. Immunity 26:397–406
Jensen PE (2007) Recent advances in antigen processing and presentation. Nat Immunol 8:1041–1048
Aptsiauri N, Cabrera T, Mendez R, Garcia-Lora A, Ruiz-Cabello F, Garrido F (2007) Role of altered expression of HLA class I molecules in cancer progression. Adv Exp Med Biol 601:123–131
Cabrera T, Maleno I, Collado A, Lopez Nevot MA, Tait BD, Garrido F (2007) Analysis of HLA class I alterations in tumors: choosing a strategy based on known patterns of underlying molecular mechanisms. Tissue Antigens 1:264–268
Marincola FM, Jaffee EM, Hicklin DJ, Ferrone S (2000) Escape of human solid tumor from T cell recognition: molecular mechanisms and functional significance. Adv Immunol 74:181–273
Seliger B, Ritz U, Ferrone S (2006) Molecular mechanisms of HLA class I antigen abnormalities following viral infection and transformation. Int J Cancer 118:129–138
Sanda MG, Restifo NP, Walsh JC, Kawakami Y, Nelson WG, Pardoll DM, Simons JW (1995) Molecular characterization of defective antigen processing in human prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 87:280–285
Lee HM, Timme TL, Thompson TC (2000) Resistance to lysis by cytotoxic T cells: a dominant effect in metastatic mouse prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 60:1927–1933
Sharpe JC, Abel PD, Gilbertson JA, Brawn P, Foster CS (1994) Modulated expression of human leukocyte antigen class I and class II determinants in hyperplastic and malignant human prostatic epithelium. Br J Urol 74:609–616
Setiadi AF, David MD, Chen SS, Hiscott J, Jefferies WA (2005) Identification of mechanisms underlying transporter associated with antigen processing deficiency in metastatic murine carcinomas. Cancer Res 65:7485–7492
Kitamura H, Torigoe T, Asanuma H, Honma I, Sato N, Tsukamoto T (2007) Down-regulation of HLA class I antigens in prostate cancer tissues and up-regulation by histone deacetylase inhibition. J Urol 178:692–696
Stolzenburg JU, Rabenalt R, Do M, Kallidonis P, Liatsikos EN (2008) Endoscopic extraperitoneal radical prostatectomy: the University of Leipzig experience of 2000 cases. J Endourol 22:2319–2325
Sobin LH, Wittekind C (1997) TNM classification of malignant tumours. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 172–175
Kasper G, Weiser AA, Rump A, Sparbier K, Dahl E, Hartmann A, Wild P, Schwidetzky U, Castaños-Vélez E, Lehmann K (2005) Expression levels of putative zinc transporter LIV-1 are associated with a better outcome of breast cancer patients. Int J Cancer 117:961–973
van Oers JM, Wild PJ, Burger M, Denzinger S, Stoehr R, Rosskopf E, Hofstaedter F, Steyerberg EW, Klinkhammer-Schalke M, Zwarthoff EC, van der Kwast TH, Hartmann A (2007) FGFR3 mutations and normal CK20 staining pattern define low-grade noninvasive urothelial bladder tumors. Eur Urol 52:760–768
Stam NJ, Spits H, Ploegh HL (1986) Monoclonal antibodies raised against denatured HLA-B locus heavy chains permit biochemical characterization of certain HLA-C locus products. J Immunol 137:2299–2306
Perosa F, Luccarelli G, Prete M, Favoino E, Ferrone S, Dammacco F (2003) Beta 2-microglobulin-free HLA class I heavy chain epitope mimicry by monoclonal antibody HC-10-specific peptide. J Immunol 171:1918–1926
Lampson LA, Fisher CA, Whelan JP (1983) Striking paucity of HLA-A, B, C and beta 2-microglobulin on human neuroblastoma cell lines. J Immunol 30:2471–2478
Bandoh N, Ogino T, Cho HS, Hur SY, Shen J, Wang X, Kato S, Miyokawa N, Harabuchi Y, Ferrone S (2005) Development and characterization of human constitutive proteasome and immunoproteasome subunit-specific monoclonal antibodies. Tissue Antigens 66:185–194
Wang X, Campoli M, Cho HS, Ogino T, Bandoh N, Shen J, Hur SY, Kageshita T, Ferrone S (2005) A method to generate antigen-specific mAb capable of staining formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections. J. Immunol. Methods 299:139–151
Ogino T, Wang X, Kato S, Miyokawa N, Harabuchi Y, Ferrone S (2003) Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone-specific monoclonal antibodies for flow cytometry and immunohistochemical staining. Tissue Antigens 62:382–393
Temponi M, Kageshita T, Perosa F, Ono R, Okada H, Ferrone S (1989) Purification of murine IgG monoclonal antibodies by precipitation with caprylic acid: comparison with other methods of purification. Hybridoma 8:85–95
Norell H, Carlsten M, Ohlum T, Malmberg KJ, Masucci G, Schedvins K, Altermann W, Handke D, Atkins D, Seliger B, Kiessling R (2006) Frequent loss of HLA-A2 expression in metastasizing ovarian carcinomas associated with genomic haplotype loss and HLA-A2-restricted HER-2/neu-specific immunity. Cancer Res 66:6387–6394
Atkins D, Ferrone S, Schmahl GE, Störkel S, Seliger B (2004) Down-regulation of HLA class I antigen processing molecules: an immune escape mechanism of renal cell carcinoma? J Urol 171:885–889
Armes JE, Trute L, White D, Southey MC, Hammet F, Tesoriero A, Hutchins AM, Dite GS, McCredie MR, Giles GG, Hopper JL, Venter DJ (1999) Distinct molecular pathogeneses of early-onset breast cancers in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers: a population-based-study. Cancer Res 59:2011–2017
Seliger B, Atkins D, Bock M, Ritz U, Ferrone S, Huber C, Störkel S (2003) Characterization of human lymphocyte antigen class I antigen-processing machinery defects in renal cell carcinoma lesions with special emphasis on transporter-associated with antigen-processing down-regulation. Clin Cancer Res 95:1721–1727
Blandes RA, Keating PJ, McWilliams LJ, George NJR, Stern PL (1995) Loss of HLA class I expression in prostate cancer: implications for immunotherapy. Urology 46:681–687
Bander NH, Yao D, Liu H, Chen YT, Steiner M, Zuccaro W, Moy P (1997) MHC class I and II expression in prostate carcinoma and modulation by interferon-alpha and -gamma. Prostate 33:233–239
Zhang H, Melamed J, Wei P, Cox K, Frankel W, Bahnson RR, Robinson N, Pyka R, Liu Y, Zheng P (2003) Concordant down-regulation of proto-oncogene PML and major histocompatibility antigen HLA class I expression in high-grade prostate cancer. Cancer Immun 3:2
Chang CC, Ogino T, Mullins DW, Oliver JL, Yamshchikov GV, Bandoh N, Slingluff CL Jr, Ferrone S (2006) Defective human leukocyte antigen class I-associated antigen presentation caused by a novel beta2-microglobulin loss-of-function in melanoma cells. J Biol Chem 281:18763–18773
Momburg F, Koch S (1989) Selective loss of beta 2-microglobulin mRNA in human colon carcinoma. J Exp Med 169:309–314
Vermeulen CF, Jordanova ES, ter Haar NT, Kolkman-Uljee SM, de Miranda NF, Ferrone S, Peters AA, Fleuren GJ (2007) Expression and genetic analysis of transporter associated with antigen processing in cervical carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 105:593–599
Kageshita T, Hirai S, Ono T, Hicklin DJ, Ferrone S (1999) Down-regulation of HLA class I antigen-processing molecules in malignant melanoma: association with disease progression. Am J Pathol 154:745–754
Lou Y, Vitalis TZ, Basha G, Cai B, Chen SS, Choi KB, Jeffries AP, Elliott WM, Atkins D, Seliger B, Jefferies WA (2005) Restoration of the expression of transporters associated with antigen processing in lung carcinoma increases tumor-specific immune responses and survival. Cancer Res 65:7926–7933
Meissner M, Reichert TE, Kunkel M, Gooding W, Whiteside TL, Ferrone S, Seliger B (2005) Defects in the human leucocyte antigen class I antigen-processing machinery in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: association with clinical outcome. Clinical Cancer Res 11:2552–2560
Mehta AM, Jordanova ES, Kenter GG, Ferrone S, Fleuren GJ (2008) Association of antigen processing machinery and HLA class I defects with clinicopathological outcome in cervical carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother 57:197–206
Wright KL, White LC, Kelly A, Beck S, Trowsdale J, Ting JP (1995) Coordinate regulation of the human TAP1 and LMP2 genes from a shared bidirectional promoter. J Exp Med 181:1459–1471
Leys CM, Nomura S, LaFleur BJ, Ferrone S, Kaminishi M, Montgomery E, Goldenring JR (2007) Expression and prognostic significance of prothymosin-alpha and ERp57 in human gastric cancer. Surgery 141:41–50
Obeid M, Tesniere A, Ghiringhelli F, Fimia GM, Apetoh L, Perfettini JL, Castedo M, Mignot G, Panaretakis T, Casares N, Métivier D, Larochette N, van Endert P, Ciccosanti F, Piacentini M, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G (2007) Calreticulin exposure dictates the immunogenicity of cancer cell death. Nat Med 13:54–61
Panaretakis T, Joza N, Modjtahedi N, Tesniere A, Vitale I, Durchschlag M, Fimia GM, Kepp O, Piacentini M, Froehlich KU, van Endert P, Zitvogel L, Madeo F, Kroemer G (2008) The co-translocation of ERp57 and calreticulin determines the immunogenicity of cell death. Cell Death Differ 15:1499–1509
Clarke C, Smyth MJ (2007) Calreticulin exposure increases cancer immunogenicity. Nat Biotechnol 25:192–193
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Rudolf Jung for excellent technical support and Claudia Stoerr and Sylvi Magdeburg for the excellent secretarial help in preparing the manuscript. This work is supported by a grant of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft SE-581/10-1, 2 (BS) and by PHS grants RO1CA110249 awarded by the National Cancer Institute, DHHS and DOD grant 7-01-0096 (SF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seliger, B., Stoehr, R., Handke, D. et al. Association of HLA class I antigen abnormalities with disease progression and early recurrence in prostate cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 59, 529–540 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-009-0769-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-009-0769-5