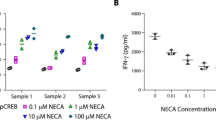
Abstract
Previous studies document that PGE2 and adenosine suppress production of inflammatory cytokines. The present study demonstrates for the first time that (1) PGE2 and 2-chloroadenosine (CADO; a stable analog of adenosine) directly inhibit the cytolytic function of human tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs); (2) the combination PGE2 and CADO have additive suppressive effects; and (3) the cooperative immunosuppressive actions of PGE2 and CADO are mediated via EP2 receptors (EP2Rs) and A2A receptors (A2ARs) and are due to amplification of cAMP production, activation of protein kinase A (PKA) and T cell receptor (TCR) inhibitor Csk leading to inhibition of Lck, ZAP-70 and Akt phosphorylation. (4) During ex vivo expansion, TILs undergo three stages of differentiation converting from TILs with high cytotoxic activity and relative resistance to combined EP2R/A2AR suppression (stage I) to TILs retaining high cytotoxicity and gaining sensitivity to combined suppression (stage II) and then to TILS that are less cytotoxic and very sensitive to combined suppression (stage III). (5) Finally, we find that pretreatment of TILs with non-inhibitory concentrations of EP2R agonists (such as PGE2 or butaprost) or A2AR agonists (such as CADO or CGS21680) increases their cytotoxic activity and induces resistance to EP2R and A2AR inhibitory signaling (cross-resistance) due to homologous and heterologous desensitization and internalization of EP2Rs and A2ARs, thus preventing their inhibitory signaling. We conclude that inducing resistance of TILs to the suppressive effects of PGE2 and adenosine in the tumor microenvironment could represent a novel strategy for improving the efficacy of adoptive immunotherapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosenberg SA, Dudley ME (2009) Adoptive cell therapy for the treatment of patients with metastatic melanoma. Curr Opin Immunol 21:233–240
Rosenberg SA, Yang JC, Restifo NP (2004) Cancer immunotherapy: moving beyond current vaccines. Nat Med 10:909–915
Ahmadzadeh M, Johnson LA, Heemskerk B, Wunderlich JR, Dudley ME, White DE, Rosenberg SA (2009) Tumor antigen-specific CD8 T cells infiltrating the tumor express high levels of PD-1 and are functionally impaired. Blood 114:1537–1544
Gabrilovich DI (2007) Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic reversal of immune suppression in cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 7:1
Gajewski TF, Meng Y, Blank C, Brown I, Kacha A, Kline J, Harlin H (2006) Immune resistance orchestrated by the tumor microenvironment. Immunol Rev 213:131–145
Gorelik L, Flavell RA (2001) Immune-mediated eradication of tumors through the blockade of transforming growth factor-beta signaling in T cells. Nat Med 7:1118–1122
Rosenberg SA, Sherry RM, Morton KE, Scharfman WJ, Yang JC, Topalian SL, Royal RE, Kammula U, Restifo NP, Hughes MS, Schwartzentruber D, Berman DM, Schwarz SL, Ngo LT, Mavroukakis SA, White DE, Steinberg SM (2005) Tumor progression can occur despite the induction of very high levels of self/tumor antigen-specific CD8 + T cells in patients with melanoma. J Immunol 175:6169–6176
Cronstein BN (1994) Adenosine, an endogenous anti-inflammatory agent. J Appl Physiol 76:5–13
Harris SG, Padilla J, Koumas L, Ray D, Phipps RP (2002) Prostaglandins as modulators of immunity. Trends Immunol 23:144–150
Hasko G, Cronstein BN (2004) Adenosine: an endogenous regulator of innate immunity. Trends Immunol 25:33–39
Hata AN, Breyer RM (2004) Pharmacology and signaling of prostaglandin receptors: multiple roles in inflammation and immune modulation. Pharmacol Ther 103:147–166
Sitkovsky MV, Lukashev D, Apasov S, Kojima H, Koshiba M, Caldwell C, Ohta A, Thiel M (2004) Physiological control of immune response and inflammatory tissue damage by hypoxia-inducible factors and adenosine A2A receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 22:657–682
Sitkovsky MV, Ohta A (2005) The ‘danger’ sensors that STOP the immune response: the A2 adenosine receptors? Trends Immunol 26:299–304
Fredholm BB, Chern Y, Franco R, Sitkovsky M (2007) Aspects of the general biology of adenosine A2A signaling. Prog Neurobiol 83:263–276
Kundu N, Walser TC, Ma X, Fulton AM (2005) Cyclooxygenase inhibitors modulate NK activities that control metastatic disease. Cancer Immunol Immunother 54:981–987
Raskovalova T, Huang X, Sitkovsky M, Zacharia LC, Jackson EK, Gorelik E (2005) Gs protein-coupled adenosine receptor signaling and lytic function of activated NK cells. J Immunol 175:4383–4391
Su Y, Huang X, Raskovalova T, Zacharia L, Lokshin A, Jackson E, Gorelik E (2008) Cooperation of adenosine and prostaglandin E(2) (PGE (2)) in amplification of cAMP-PKA signaling and immunosuppression. Cancer Immunol Immunother 57:1611–1623
Blay J, White TD, Hoskin DW (1997) The extracellular fluid of solid carcinomas contains immunosuppressive concentrations of adenosine. Cancer Res 57:2602–2605
Dannenberg AJ, Subbaramaiah K (2003) Targeting cyclooxygenase-2 in human neoplasia: rationale and promise. Cancer Cell 4:431–436
Ohta A, Gorelik E, Prasad SJ, Ronchese F, Lukashev D, Wong MK, Huang X, Caldwell S, Liu K, Smith P, Chen JF, Jackson EK, Apasov S, Abrams S, Sitkovsky M (2006) A2A adenosine receptor protects tumors from antitumor T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:13132–13137
Koshiba M, Kojima H, Huang S, Apasov S, Sitkovsky MV (1997) Memory of extracellular adenosine A2A purinergic receptor-mediated signaling in murine T cells. J Biol Chem 272:25881–25889
Raskovalova T, Lokshin A, Huang X, Su Y, Mandic M, Zarour HM, Jackson EK, Gorelik E (2007) Inhibition of cytokine production and cytotoxic activity of human antimelanoma specific CD8 + and CD4 + T lymphocytes by adenosine-protein kinase A type I signaling. Cancer Res 67:5949–5956
Armstrong JM, Chen JF, Schwarzschild MA, Apasov S, Smith PT, Caldwell C, Chen P, Figler H, Sullivan G, Fink S, Linden J, Sitkovsky M (2001) Gene dose effect reveals no Gs-coupled A2A adenosine receptor reserve in murine T-lymphocytes: studies of cells from A2A-receptor-gene-deficient mice. Biochem J 354:123–130
Desai S, April H, Nwaneshiudu C, Ashby B (2000) Comparison of agonist-induced internalization of the human EP2 and EP4 prostaglandin receptors: role of the carboxyl terminus in EP4 receptor sequestration. Mol Pharmacol 58:1279–1286
Ferguson SS (2001) Evolving concepts in G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis: the role in receptor desensitization and signaling. Pharmacol Rev 53:1–24
Klaasse EC, Ijzerman AP, de Grip WJ, Beukers MW (2008) Internalization and desensitization of adenosine receptors. Purinergic Signal 4:21–37
Bender AT, Beavo JA (2006) Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: molecular regulation to clinical use. Pharmacol Rev 58:488–520
Schmedt C, Saijo K, Niidome T, Kuhn R, Aizawa S, Tarakhovsky A (1998) Csk controls antigen receptor-mediated development and selection of T-lineage cells. Nature 394:901–904
Tasken K, Ruppelt A (2006) Negative regulation of T-cell receptor activation by the cAMP-PKA-Csk signalling pathway in T-cell lipid rafts. Front Biosci 11:2929–2939
Torgersen KM, Vang T, Abrahamsen H, Yaqub S, Horejsi V, Schraven B, Rolstad B, Mustelin T, Tasken K (2001) Release from tonic inhibition of T cell activation through transient displacement of C-terminal Src kinase (Csk) from lipid rafts. J Biol Chem 276:29313–29318
Vang T, Abrahamsen H, Myklebust S, Enserink J, Prydz H, Mustelin T, Amarzguioui M, Tasken K (2004) Knockdown of C-terminal Src kinase by siRNA-mediated RNA interference augments T cell receptor signaling in mature T cells. Eur J Immunol 34:2191–2199
Vang T, Abrahamsen H, Myklebust S, Horejsi V, Tasken K (2003) Combined spatial and enzymatic regulation of Csk by cAMP and protein kinase A inhibits T cell receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 278:17597–17600
Smith-Garvin JE, Koretzky GA, Jordan MS (2009) T cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol 27:591–619
Fuller CL, Ravichandran KS, Braciale VL (1999) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent and -independent cytolytic effector functions. J Immunol 162:6337–6340
Okkenhaug K, Vanhaesebroeck B (2003) PI3K in lymphocyte development, differentiation and activation. Nat Rev Immunol 3:317–330
Sugiyama H, Chen P, Hunter M, Taffs R, Sitkovsky M (1992) The dual role of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase C alpha subunit in T-cell receptor-triggered T-lymphocytes effector functions. J Biol Chem 267:25256–25263
Takayama H, Trenn G, Sitkovsky MV (1988) Locus of inhibitory action of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in the antigen receptor-triggered cytotoxic T lymphocyte activation pathway. J Biol Chem 263:2330–2336
Torgersen KM, Vaage JT, Levy FO, Hansson V, Rolstad B, Tasken K (1997) Selective activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase type I inhibits rat natural killer cell cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem 272:5495–5500
Vang T, Torgersen KM, Sundvold V, Saxena M, Levy FO, Skalhegg BS, Hansson V, Mustelin T, Tasken K (2001) Activation of the COOH-terminal Src kinase (Csk) by cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits signaling through the T cell receptor. J Exp Med 193:497–507
Huang J, Kerstann KW, Ahmadzadeh M, Li YF, El-Gamil M, Rosenberg SA, Robbins PF (2006) Modulation by IL-2 of CD70 and CD27 expression on CD8 + T cells: importance for the therapeutic effectiveness of cell transfer immunotherapy. J Immunol 176:7726–7735
Powell DJ Jr, Dudley ME, Robbins PF, Rosenberg SA (2005) Transition of late-stage effector T cells to CD27 + CD28 + tumor-reactive effector memory T cells in humans after adoptive cell transfer therapy. Blood 105:241–250
Sitkovsky M, Lukashev D, Deaglio S, Dwyer K, Robson SC, Ohta A (2008) Adenosine A2A receptor antagonists: blockade of adenosinergic effects and T regulatory cells. Br J Pharmacol 153(Suppl 1):457–464
Ohta A, Kjaergaard J, Sharma S, Mohsin M, Goel N, Madasu M, Fradkov E, Sitkovsky M (2009) In vitro induction of T cells that are resistant to A2 adenosine receptor-mediated immunosuppression. Br J Pharmacol 156:297–306
Dudley ME, Wunderlich JR, Robbins PF, Yang JC, Hwu P, Schwartzentruber DJ, Topalian SL, Sherry R, Restifo NP, Hubicki AM, Robinson MR, Raffeld M, Duray P, Seipp CA, Rogers-Freezer L, Morton KE, Mavroukakis SA, White DE, Rosenberg SA (2002) Cancer regression and autoimmunity in patients after clonal repopulation with antitumor lymphocytes. Science 298:850–854
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Steven Rosenberg and Dr. John Wonderlich for generously providing samples of TILs for these studies. This work was supported by the DOD, Award BC051720, and Hillman Foundation (E.G.), NIH grants DK68575 and DK79307 (EKJ).
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, Y., Jackson, E.K. & Gorelik, E. Receptor desensitization and blockade of the suppressive effects of prostaglandin E2 and adenosine on the cytotoxic activity of human melanoma-infiltrating T lymphocytes. Cancer Immunol Immunother 60, 111–122 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-010-0924-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-010-0924-z