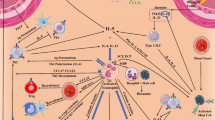
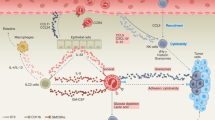
Abstract
Eosinophils are a subset of granulocytes mostly known for their ability to combat parasites and induce allergy. Although they were described to be related to cancer more than 100 years ago, their role in tumors is still undefined. Recent observations revealed that they display regulatory functions towards other immune cell subsets in the tumor microenvironment or direct cytotoxic functions against tumor cells, leading to either antitumor or protumor effects. This paradoxical role of eosinophils was suggested to be dependent on the different factors in the TME. In addition, the clinical relevance of these cells has been recently addressed. In most cases, the accumulation of eosinophils both in the tumor tissue, called tumor-associated tissue eosinophilia, and in the peripheral blood were reported to be prognostic markers for a better outcome of cancer patients. In immunotherapy of cancer, particularly in therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors, eosinophils were even shown to be a potential predictive marker for a beneficial clinical response. A better understanding of their role in cancer progression will help to establish them as prognostic and predictive markers and to design strategies for targeting eosinophils.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AEC:
-
Absolute eosinophil count
- CCL:
-
CC-chemokine ligand
- CCR:
-
CC-chemokine receptor
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- CXCL:
-
C-X-C-chemokine ligand
- DAMPs:
-
Damage-associated molecular patterns
- DFS:
-
Disease-free survival
- DPP4:
-
Dipeptidylpeptidase 4
- ECP:
-
Eosinophil cationic protein
- EDN:
-
Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin
- GI:
-
Gastrointestinal
- HMGB1:
-
High-mobility group box 1 protein
- HPF:
-
High power fields
- ICI:
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitor
- MBP:
-
Major basic protein
- MM:
-
Malignant melanoma
- OSCC:
-
Oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PAMP:
-
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns
- PFS:
-
Progression free survival
- REC:
-
Relative eosinophil count
- Siglec:
-
Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin
- TATE:
-
Tumor-associated tissue eosinophilia
- Th2:
-
Type 2 Th cells
References
Vakkila J, Lotze MT (2004) Inflammation and necrosis promote tumour growth. Nat Rev Immunol 4(8):641–648. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1415
Carretero R, Sektioglu IM, Garbi N, Salgado OC, Beckhove P, Hammerling GJ (2015) Eosinophils orchestrate cancer rejection by normalizing tumor vessels and enhancing infiltration of CD8(+) T cells. Nat Immunol 16(6):609–609+. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.3159
Lucarini V, Ziccheddu G, Macchia I, La Sorsa V, Peschiaroli F, Buccione C, Sistigu A, Sanchez M, Andreone S, D’Urso MT, Spada M, Macchia D, Afferni C, Mattei F, Schiavoni G (2017) IL-33 restricts tumor growth and inhibits pulmonary metastasis in melanoma-bearing mice through eosinophils. Oncoimmunology. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402x.2017.1317420
Legrand F, Driss V, Delbeke M, Loiseau S, Hermann E, Dombrowicz D, Capron M (2010) Human eosinophils exert TNF-alpha and granzyme A-mediated tumoricidal activity toward colon carcinoma cells. J Immunol (Baltim Md 1950) 185(12):7443–7451. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1000446
Rosenberg HF, Dyer KD, Foster PS (2013) Eosinophils: changing perspectives in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 13(1):9–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3341
Rothenberg ME, Hogan SP (2006) The eosinophil. Annu Rev Immunol 24:147–174. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.24.021605.090720
Weller PF, Spencer LA (2017) Functions of tissue-resident eosinophils. Nat Rev Immunol 17(12):746–760. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2017.95
Floyd H, Ni J, Cornish AL, Zeng Z, Liu D, Carter KC, Steel J, Crocker PR (2000) Siglec-8. A novel eosinophil-specific member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. J Biol Chem 275(2):861–866
Dyer KD, Garcia-Crespo KE, Killoran KE, Rosenberg HF (2011) Antigen profiles for the quantitative assessment of eosinophils in mouse tissues by flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods 369(1–2):91–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2011.04.009
Stevens WW, Kim TS, Pujanauski LM, Hao X, Braciale TJ (2007) Detection and quantitation of eosinophils in the murine respiratory tract by flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods 327(1–2):63–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2007.07.011
Gleich GJ, Adolphson CR, Leiferman KM (1993) The biology of the eosinophilic leukocyte. Annu Rev Med 44:85–101. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.me.44.020193.000505
Upadhyaya B, Yin Y, Hill BJ, Douek DC, Prussin C (2011) Hierarchical IL-5 expression defines a subpopulation of highly differentiated human Th2 cells. J Immunol (Baltim Md 1950) 187(6):3111–3120. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1101283
Nussbaum JC, Van Dyken SJ, von Moltke J, Cheng LE, Mohapatra A, Molofsky AB, Thornton EE, Krummel MF, Chawla A, Liang HE, Locksley RM (2013) Type 2 innate lymphoid cells control eosinophil homeostasis. Nature 502(7470):245–248. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12526
Clutterbuck EJ, Hirst EM, Sanderson CJ (1989) Human interleukin-5 (IL-5) regulates the production of eosinophils in human bone marrow cultures: comparison and interaction with IL-1, IL-3, IL-6, and GMCSF. Blood 73(6):1504–1512
Farne HA, Wilson A, Powell C, Bax L, Milan SJ (2017) Anti-IL5 therapies for asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 9:CD010834. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD010834.pub3
Collins PD, Marleau S, Griffiths-Johnson DA, Jose PJ, Williams TJ (1995) Cooperation between interleukin-5 and the chemokine eotaxin to induce eosinophil accumulation in vivo. J Exp Med 182(4):1169–1174
Daugherty BL, Siciliano SJ, DeMartino JA, Malkowitz L, Sirotina A, Springer MS (1996) Cloning, expression, and characterization of the human eosinophil eotaxin receptor. J Exp Med 183(5):2349–2354
Kvarnhammar AM, Cardell LO (2012) Pattern-recognition receptors in human eosinophils. Immunology 136(1):11–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2567.2012.03556.x
Dvorak AM, Estrella P, Ishizaka T (1994) Vesicular transport of peroxidase in human eosinophilic myelocytes. Clin Exp Allergy 24(1):10–18
Domachowske JB, Dyer KD, Bonville CA, Rosenberg HF (1998) Recombinant human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin/RNase 2 functions as an effective antiviral agent against respiratory syncytial virus. J Infect Dis 177(6):1458–1464
Lehrer RI, Szklarek D, Barton A, Ganz T, Hamann KJ, Gleich GJ (1989) Antibacterial properties of eosinophil major basic protein and eosinophil cationic protein. J Immunol (Baltim Md 1950) 142(12):4428–4434
von Kockritz-Blickwede M, Nizet V (2009) Innate immunity turned inside-out: antimicrobial defense by phagocyte extracellular traps. J Mol Med (Berl) 87(8):775–783. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-009-0481-0
Yousefi S, Gold JA, Andina N, Lee JJ, Kelly AM, Kozlowski E, Schmid I, Straumann A, Reichenbach J, Gleich GJ, Simon HU (2008) Catapult-like release of mitochondrial DNA by eosinophils contributes to antibacterial defense. Nat Med 14(9):949–953. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.1855
Jacobsen EA, Ochkur SI, Pero RS, Taranova AG, Protheroe CA, Colbert DC, Lee NA, Lee JJ (2008) Allergic pulmonary inflammation in mice is dependent on eosinophil-induced recruitment of effector T cells. J Exp Med 205(3):699–710. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20071840
Chu VT, Frohlich A, Steinhauser G, Scheel T, Roch T, Fillatreau S, Lee JJ, Lohning M, Berek C (2011) Eosinophils are required for the maintenance of plasma cells in the bone marrow. Nat Immunol 12(2):151–159. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1981
Minai-Fleminger Y, Elishmereni M, Vita F, Soranzo MR, Mankuta D, Zabucchi G, Levi-Schaffer F (2010) Ultrastructural evidence for human mast cell-eosinophil interactions in vitro. Cell Tissue Res 341(3):405–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-010-1010-8
Wen T, Rothenberg ME (2016) The regulatory function of eosinophils. Microbiol Spectr. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.MCHD-0020-2015
Shi HZ, Humbles A, Gerard C, Jin Z, Weller PF (2000) Lymph node trafficking and antigen presentation by endobronchial eosinophils. J Clin Invest 105(7):945–953. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI8945
Huang L, Appleton JA (2016) Eosinophils in Helminth Infection: Defenders and Dupes. Trends Parasitol 32(10):798–807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2016.05.004
Linch SN, Kelly AM, Danielson ET, Pero R, Lee JJ, Gold JA (2009) Mouse eosinophils possess potent antibacterial properties in vivo. Infect Immun 77(11):4976–4982. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00306-09
Phipps S, Lam CE, Mahalingam S, Newhouse M, Ramirez R, Rosenberg HF, Foster PS, Matthaei KI (2007) Eosinophils contribute to innate antiviral immunity and promote clearance of respiratory syncytial virus. Blood 110(5):1578–1586. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-01-071340
Bedoya VI, Boasso A, Hardy AW, Rybak S, Shearer GM, Rugeles MT (2006) Ribonucleases in HIV type 1 inhibition: effect of recombinant RNases on infection of primary T cells and immune activation-induced RNase gene and protein expression. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 22(9):897–907. https://doi.org/10.1089/aid.2006.22.897
Chu VT, Beller A, Rausch S, Strandmark J, Zanker M, Arbach O, Kruglov A, Berek C (2014) Eosinophils promote generation and maintenance of immunoglobulin-A-expressing plasma cells and contribute to gut immune homeostasis. Immunity 40(4):582–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2014.02.014
Throsby M, Herbelin A, Pleau JM, Dardenne M (2000) CD11c + eosinophils in the murine thymus: developmental regulation and recruitment upon MHC class I-restricted thymocyte deletion. J Immunol (Baltim Md 1950) 165(4):1965–1975
Wu D, Molofsky AB, Liang HE, Ricardo-Gonzalez RR, Jouihan HA, Bando JK, Chawla A, Locksley RM (2011) Eosinophils sustain adipose alternatively activated macrophages associated with glucose homeostasis. Science 332(6026):243–247. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1201475
Mazzeo C, Canas JA, Zafra MP, Rojas Marco A, Fernandez-Nieto M, Sanz V, Mittelbrunn M, Izquierdo M, Baixaulli F, Sastre J, Del Pozo V (2015) Exosome secretion by eosinophils: a possible role in asthma pathogenesis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 135(6):1603–1613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2014.11.026
Nair P, Pizzichini MM, Kjarsgaard M, Inman MD, Efthimiadis A, Pizzichini E, Hargreave FE, O’Byrne PM (2009) Mepolizumab for prednisone-dependent asthma with sputum eosinophilia. N Engl J Med 360(10):985–993. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0805435
Gorriz Gil C, Matallana Royo V, Alvarez Montero O, Rodriguez Valiente A, Fernandez Manzano C, Conde Garcia B, Garcia-Berrocal JR (2018) Eosinophilic esophagitis: an underdiagnosed cause of dysphagia and food impaction to be recognized by otolaryngologists. HNO. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00106-018-0516-3
Gotlib J (2017) World Health Organization-defined eosinophilic disorders: 2017 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am J Hematol 92(11):1243–1259. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.24880
Navabi B, Upton JE (2016) Primary immunodeficiencies associated with eosinophilia. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol 12:27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-016-0130-4
Feldbausch F (1900) The occurrence of eosinophilic leukocytes in tumours. Archiv Fur Pathologische Anatomie Physiologie Fur Klinische Medicin 161(1):1–18
Huang M, Wang J, Lee P, Sharma S, Mao JT, Meissner H, Uyemura K, Modlin R, Wollman J, Dubinett SM (1995) Human non-small cell lung cancer cells express a type 2 cytokine pattern. Cancer Res 55(17):3847–3853
Pandit R, Scholnik A, Wulfekuhler L, Dimitrov N (2007) Non-small-cell lung cancer associated with excessive eosinophilia and secretion of interleukin-5 as a paraneoplastic syndrome. Am J Hematol 82(3):234–237. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.200789
Curran CS, Evans MD, Bertics PJ (2011) GM-CSF production by glioblastoma cells has a functional role in eosinophil survival, activation, and growth factor production for enhanced tumor cell proliferation. J Immunol 187(3):1254–1263. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1001965
Tepper RI, Coffman RL, Leder P (1992) An eosinophil-dependent mechanism for the antitumor effect of interleukin-4. Science 257(5069):548–551
Mattes J, Hulett M, Xie W, Hogan S, Rothenberg ME, Foster P, Parish C (2003) Immunotherapy of cytotoxic T cell-resistant tumors by T helper 2 cells: an eotaxin and STAT6-dependent process. J Exp Med 197(3):387–393
Simson L, Ellyard JI, Dent LA, Matthaei KI, Rothenberg ME, Foster PS, Smyth MJ, Parish CR (2007) Regulation of carcinogenesis by IL-5 and CCL11: A potential role for eosinophils in tumor immune surveillance. J Immunol 178(7):4222–4229. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.178.7.4222
Lorena SCM, Oliveira DT, Dorta RG, Landman G, Kowalski LP (2003) Eotaxin expression in oral squamous cell carcinomas with and without tumour associated tissue eosinophilia. Oral Dis 9(6):279–283. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1601-0825.2003.00958.x
Hirai H, Fujishita T, Kurimoto K, Miyachi H, Kitano S, Inamoto S, Itatani Y, Saitou M, Maekawa T, Taketo MM (2014) CCR1-mediated accumulation of myeloid cells in the liver microenvironment promoting mouse colon cancer metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 31(8):977–989. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-014-9684-z
Cormier SA, Taranova AG, Bedient C, Nguyen T, Protheroe C, Pero R, Dimina D, Ochkur SI, O’Neill K, Colbert D, Lombari TR, Constant S, McGarry MP, Lee JJ, Lee NA (2006) Pivotal advance: Eosinophil infiltration of solid tumors is an early and persistent inflammatory host response. J Leukoc Biol 79(6):1131–1139. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0106027
Lotfi R, Herzog GI, DeMarco RA, Beer-Stolz D, Lee JJ, Rubartelli A, Schrezenmeier H, Lotze MT (2009) Eosinophils oxidize damage-associated molecular pattern molecules derived from stressed cells. J Immunol (Baltim Md 1950) 183(8):5023–5031. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0900504
Kobayashi T, Soma T, Noguchi T, Nakagome K, Nakamoto H, Kita H, Nagata M (2015) ATP drives eosinophil effector responses through P2 purinergic receptors. Allergol Int 64(Suppl):S30–S36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alit.2015.04.009
da Silva JM, Queiroz-Junior CM, Batista AC, Rachid MA, Teixeira MM, da Silva TA (2014) Eosinophil depletion protects mice from tongue squamous cell carcinoma induced by 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide. Histol Histopathol 29(3):387–396. https://doi.org/10.14670/hh-29.387
Wong DTW, Bowen SM, Elovic A, Gallagher GT, Weller PF (1999) Eosinophil ablation and tumor development. Oral Oncol 35(5):496–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1368-8375(99)00023-8
O’Flaherty SM, Sutummaporn K, Haggtoft WL, Worrall AP, Rizzo M, Braniste V, Hoglund P, Kadri N, Chambers BJ (2017) TLR-stimulated eosinophils mediate recruitment and activation of NK cells in vivo. Scand J Immunol 85(6):417–424. https://doi.org/10.1111/sji.12554
Lotfi R, Lotze MT (2008) Eosinophils induce DC maturation, regulating immunity. J Leukoc Biol 83(3):456–460. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0607366
Xing Y, Tian Y, Kurosawa T, Matsui S, Touma M, Yanai T, Wu Q, Sugimoto K (2016) CCL11-induced eosinophils inhibit the formation of blood vessels and cause tumor necrosis. Genes Cells 21(6):624–638. https://doi.org/10.1111/gtc.12371
Kubo H, Loegering DA, Adolphson CR, Gleich GJ (1999) Cytotoxic properties of eosinophil granule major basic protein for tumor cells. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 118(2–4):426–428. https://doi.org/10.1159/000024154
Furbert-Harris PM, Smith MA, Law MP, Currie E, Young JM, Gause DP, Vaughn TR, Harris VL, Oredipe OA (2005) Eosinophil granular protein major basic protein combines with tumor necrosis factor alpha to kill prostate multicellular spheroids in vitro. J Immunother 28(6):619–619. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.cji.0000190967.73030.72
Costain DJ, Guha AK, Liwski RS, Lee TDG (2001) Murine hypodense eosinophils induce tumour cell apoptosis by a granzyme B-dependent mechanism. Cancer Immunol Immunother 50(6):293–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/pl00006690
Caruso RA, Parisi A, Quattrocchi E, Scardigno M, Branca G, Parisi C, Luciano R, Paparo D, Fedele F (2011) Ultrastructural descriptions of heterotypic aggregation between eosinophils and tumor cells in human gastric carcinomas. Ultrastruct Pathol 35(4):145–149. https://doi.org/10.3109/01913123.2011.578233
Gatault S, Delbeke M, Driss V, Sarazin A, Dendooven A, Kahn JE, Lefevre G, Capron M (2015) IL-18 Is involved in eosinophil-mediated tumoricidal activity against a colon carcinoma cell line by upregulating LFA-1 and ICAM-1. J Immunol 195(5):2483–2492. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1402914
Zaynagetdinov R, Sherrill TP, Gleaves LA, McLoed AG, Saxon JA, Habermann AC, Connelly L, Dulek D, Peebles RS Jr, Fingleton B, Yull FE, Stathopoulos GT, Blackwell TS (2015) Interleukin-5 facilitates lung metastasis by modulating the immune microenvironment. Cancer Res 75(8):1624–1634. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-2379
Kratochvill F, Neale G, Haverkamp JM, Van de Velde LA, Smith AM, Kawauchi D, McEvoy J, Roussel MF, Dyer MA, Qualls JE, Murray PJ (2015) TNF counterbalances the emergence of M2 tumor macrophages. Cell Rep 12(11):1902–1914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.08.033
Frumento G, Rotondo R, Tonetti M, Damonte G, Benatti U, Ferrara GB (2002) Tryptophan-derived catabolites are responsible for inhibition of T and natural killer cell proliferation induced by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. J Exp Med 196(4):459–468
Astigiano S, Morandi B, Costa R, Mastracci L, D’Agostino A, Ratto GB, Melioli G, Frumento G (2005) Eosinophil granulocytes account for indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-mediated immune escape in human non-small cell lung cancer. Neoplasia 7(4):390–396. https://doi.org/10.1593/neo.04658
Puxeddu I, Berkman N, Nissim Ben Efraim AH, Davies DE, Ribatti D, Gleich GJ, Levi-Schaffer F (2009) The role of eosinophil major basic protein in angiogenesis. Allergy 64(3):368–374. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1398-9995.2008.01822.x
Varricchi G, Galdiero MR, Loffredo S, Lucarini V, Marone G, Mattei F, Marone G, Schiavoni G (2018) Eosinophils: the unsung heroes in cancer? Oncoimmunology 7(2):e1393134. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2017.1393134
Looi LM (1987) Tumor-associated tissue eosinophilia in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. A pathologic study of 422 primary and 138 metastatic tumors. Cancer 59(3):466–470
Dorta RG, Landman G, Kowalski LP, Lauris JRP, Latorre M, Oliveira DT (2002) Tumour-associated tissue eosinophilia as a prognostic factor in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Histopathology 41(2):152–157. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2559.2002.01437.x
Jain D, Tikku G, Bhadana P, Dravid C, Grover RK (2017) The impact of peritumoral retraction clefting & intratumoral eosinophils on overall survival in oral squamous carcinoma patients. Pathol Oncol Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-017-0328-x
Peurala E, Tuominen M, Loyttyniemi E, Syrjanen S, Rautava J (2018) Eosinophilia is a favorable prognostic marker for oral cavity and lip squamous cell carcinoma. APMIS: acta pathologica, microbiologica, et immunologica Scandinavica 126(3):201–207. https://doi.org/10.1111/apm.12809
Oliveira DT, Biassi TP, Faustino SE, Carvalho AL, Landman G, Kowalski LP (2012) Eosinophils may predict occult lymph node metastasis in early oral cancer. Clin Oral Investig 16(6):1523–1528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-011-0651-7
Rakesh N, Devi Y, Majumdar K, Reddy SS, Agarwal K (2015) Tumour associated tissue eosinophilia as a predictor of locoregional recurrence in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Exp Dent 7(1):e1–e6. https://doi.org/10.4317/jced.51610
Alrawi SJ, Tan D, Stoler DL, Dayton M, Anderson GR, Mojica P, Douglas W, Hicks W Jr, Rigual N, Loree T (2005) Tissue eosinophilic infiltration: a useful marker for assessing stromal invasion, survival and locoregional recurrence in head and neck squamous neoplasia. Cancer J 11(3):217–225
Tostes Oliveira D, Tjioe KC, Assao A, Sita Faustino SE, Lopes Carvalho A, Landman G, Kowalski LP (2009) Tissue eosinophilia and its association with tumoral invasion of oral cancer. Int J Surg Pathol 17(3):244–249. https://doi.org/10.1177/1066896909333778
Moezzi J, Gopalswamy N, Haas RJ, Markert RJ, Suryaprasad S, Bhutani MS (2000) Stromal eosinophilia in colonic epithelial neoplasms. Am J Gastroenterol 95(2):520–523
Kiziltas S, Sezgin Ramadan S, Topuzoglu A, Kullu S (2008) Does the severity of tissue eosinophilia of colonic neoplasms reflect their malignancy potential? Turk J Gastroenterol 19(4):239–244
Cho H, Lim SJ, Won KY, Bae GE, Kim GY, Min JW, Noh BJ (2016) Eosinophils in colorectal neoplasms associated with expression of CCL11 and CCL24. J Pathol transl Med 50(1):45–51. https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.10.16
Prizment AE, Vierkant RA, Smyrk TC, Tillmans LS, Lee JJ, Sriramarao P, Nelson HH, Lynch CF, Thibodeau SN, Church TR, Cerhan JR, Anderson KE, Limburg PJ (2016) Tumor eosinophil infiltration and improved survival of colorectal cancer patients: Iowa Women’s Health Study. Mod Pathol 29(5):516–527. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2016.42
Prizment AE, Anderson KE, Visvanathan K, Folsom AR (2011) Inverse association of eosinophil count with colorectal cancer incidence: atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 20 (9):1861–1864. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.Epi-11-0360
Wei Y, Zhang X, Wang G, Zhou Y, Luo M, Wang S, Hong C (2018) The impacts of pretreatment circulating eosinophils and basophils on prognosis of stage - colorectal cancer. Asia Pacific J Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajco.12871
Ownby HE, Roi LD, Isenberg RR, Brennan MJ (1983) Peripheral lymphocyte and eosinophil counts as indicators of prognosis in primary breast-cancer. Cancer 52 (1):126–130. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(19830701)52:1%3C126::Aid-cncr2820520123%3E3.0.Co;2-y
Gunduz S, Goksu SS, Arslan D, Tatli AM, Uysal M, Gunduz UR, Sevinc MM, Coskun HS, Bozcuk H, Mutlu H, Savas B (2015) Factors affecting disease-free survival in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer who receive adjuvant trastuzumab. Mol Clin Oncol 3(5):1109–1112. https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2015.610
Xie F, Liu LB, Shang WQ, Chang KK, Meng YH, Mei J, Yu JJ, Li DJ, Li MQ (2015) The infiltration and functional regulation of eosinophils induced by TSLP promote the proliferation of cervical cancer cell. Cancer Lett 364(2):106–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.04.029
vanDriel WJ, Hogendoorn PCW, Jansen FW, Zwinderman AH, Trimbos JP, Fleuren GJ (1996) Tumor-associated eosinophilic infiltrate of cervical cancer is indicative for ex less effective immune response. Hum Pathol 27(9):904–911. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0046-8177(96)90216-6
Bethwaite PB, Holloway LJ, Yeong ML, Thornton A (1993) Effect of tumor-assoicated tissue eosinophilia on survival of women with stage-IB carcinoma of the uterine cervix. J Clin Pathol 46(11):1016–1020. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.46.11.1016
Iwasaki K, Torisu M, Fujimura T (1986) Malignant-tumor and eosinophils. 1. Prognostic-significance in gastric-cancer. Cancer 58 (6):1321–1327. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(19860915)58:6%3C1321::Aid-cncr2820580623%3E3.0.Co;2-o
Cuschieri A, Talbot I, Weeden S (2002) Influence of pathological tumour variables on long-term survival in resectable gastric cancer. Br J Cancer 86(5):674–679. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6600161
Zhang Y, Ren H, Wang L, Ning Z, Zhuang Y, Gan J, Chen S, Zhou D, Zhu H, Tan D, Zhang H (2014) Clinical impact of tumor-infiltrating inflammatory cells in primary small cell esophageal carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci 15(6):9718–9734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15069718
Ishibashi S, Ohashi Y, Suzuki T, Miyazaki S, Moriya T, Satomi S, Sasano H (2006) Tumor-associated tissue eosinophilia in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res 26(2B):1419–1424
Steel JL, Kim KH, Dew MA, Unruh ML, Antoni MH, Olek MC, Geller DA, Carr BI, Butterfield LH, Gamblin TC (2010) Cancer-related symptom clusters, eosinophils, and survival in hepatobiliary cancer: an exploratory study. J Pain Symptom Manag 39(5):859–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2009.09.019
Wang HK, Wan FN, Gu WJ, Zhu Y, Dai B, Shi GH, Zhang HL, Ye DW (2016) Eosinophil percentage elevation as a prognostic factor for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Oncotarget 7(42):68943–68953. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12126
Huland E, Huland H (1992) Tumor-associated eosinophilia in interleukin-2-treated patients: evidence of toxic eosinophil degranulation on bladder cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 118(6):463–467
Sosman JA, Bartemes K, Offord KP, Kita H, Fisher SG, Kefer C, Ellis TA, Fisher RI, Higgins TJ, Gerald GJ (1995) Evidence for eosinophil activation in cancer patients receiving recombinant interleukin-4: Effects of interleukin-4 alone and following interleukin-2 administration. Clin Cancer Res 1(8):805–812
Bristol JA, Zhu M, Ji H, Mina M, Xie Y, Clarke L, Forry-Schaudies S, Ennist DL (2003) In vitro and in vivo activities of an oncolytic adenoviral vector designed to express GM-CSF. Mol Ther 7(6):755–764
Weide B, Martens A, Hassel JC, Berking C, Postow MA, Bisschop K, Simeone E, Mangana J, Schilling B, Di Giacomo AM, Brenner N, Kahler K, Heinzerling L, Gutzmer R, Bender A, Gebhardt C, Romano E, Meier F, Martus P, Maio M, Blank C, Schadendorf D, Dummer R, Ascierto PA, Hospers G, Garbe C, Wolchok JD (2016) Baseline biomarkers for outcome of melanoma patients treated with pembrolizumab. Clin Cancer Res 22(22):5487–5496. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0127
Gebhardt C, Sevko A, Jiang H, Lichtenberger R, Reith M, Tarnanidis K, Holland-Letz T, Umansky L, Beckhove P, Sucker A, Schadendorf D, Utikal J, Umansky V (2015) Myeloid cells and related chronic inflammatory factors as novel predictive markers in melanoma treatment with ipilimumab. Clin Cancer Res 21(24):5453–5459. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0676
Moreira A, Leisgang W, Schuler G, Heinzerling L (2017) Eosinophilic count as a biomarker for prognosis of melanoma patients and its importance in the response to immunotherapy. Immunotherapy 9(2):115–121. https://doi.org/10.2217/imt-2016-0138
Heppt MV, Heinzerling L, Kahler KC, Forschner A, Kirchberger MC, Loquai C, Meissner M, Meier F, Terheyden P, Schell B, Herbst R, Goppner D, Kiecker F, Rafei-Shamsabadi D, Haferkamp S, Huber MA, Utikal J, Ziemer M, Bumeder I, Pfeiffer C, Schad SG, Schmid-Tannwald C, Tietze JK, Eigentler TK, Berking C (2017) Prognostic factors and outcomes in metastatic uveal melanoma treated with programmed cell death-1 or combined PD-1/cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 inhibition. Eur J Cancer (Oxf Engl 1990) 82:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2017.05.038
Tanizaki J, Haratani K, Hayashi H, Chiba Y, Nakamura Y, Yonesaka K, Kudo K, Kaneda H, Hasegawa Y, Tanaka K, Takeda M, Ito A, Nakagawa K (2018) Peripheral blood biomarkers associated with clinical outcome in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with nivolumab. J Thorac Oncol 13(1):97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2017.10.030
Shelton A, Green RH, Bradding P, Free CM (2010) Peripheral blood eosinophil count correlates with survival in lung cancer. Lung Cancer (Amst Neth) 67:S40–S41. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-5002(10)70123-9
McNeel DG, Gardner TA, Higano CS, Kantoff PW, Small EJ, Wener MH, Sims RB, DeVries T, Sheikh NA, Dreicer R (2014) A transient increase in eosinophils is associated with prolonged survival in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer who receive sipuleucel-T. Cancer Immunol Res 2(10):988–999. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.Cir-14-0073
Legrand F, Klion AD (2015) Biologic therapies targeting eosinophils: current status and future prospects. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 3(2):167–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaip.2015.01.013
Hollande C, da Silva RB, Bondet V, Llibre A, Duffy D, Mallet V, Pol S, Albert M (2017) DPP4 inhibition reveals interleukin-33-dependent eosinophil-mediated tumor immunity in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 66(1):S225–S225. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-8278(17)30748-1
Liu LY, Bates ME, Jarjour NN, Busse WW, Bertics PJ, Kelly EA (2007) Generation of Th1 and Th2 chemokines by human eosinophils: evidence for a critical role of TNF-alpha. J Immunol (Baltim Md 1950) 179(7):4840–4848
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Elisabeth Cordell for editing the manuscript, Xiaoying Hu for designing figure elements, Rebekka Weber and Zeno Riester for helpful advice. The literature search was assisted by Maurizio Grilli from the library for the Medical Faculty of Mannheim, Ruprecht-Karl University of Heidelberg.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the German Research Council (RTG2099) to J. Utikal and V. Umansky and the Cooperation between German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) and Ministry of Science, Technology and Space of Israel (MOST) in Cancer Research (CA181 to V. Umansky). This work was kindly backed by the COST Action BM1404 Mye-EUNITER (http://www.mye-euniter.eu). COST is supported by the EU Framework Program Horizon 2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SCSS: writing, review and revision of the manuscript, preparation and revision of the figure and table. JU: review and revision of the manuscript. VU: writing, review and revision of the manuscript and revision of the table and figure.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simon, S.C.S., Utikal, J. & Umansky, V. Opposing roles of eosinophils in cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 68, 823–833 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-018-2255-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-018-2255-4