Abstract
Focal high-level amplifications of MYC (or MYCC) define a subset of high-risk medulloblastoma patients. However, the prognostic role of MYCN oncogene amplification remains unresolved. We aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of this alteration alone and in combination with biological modifiers in 67 pediatric medulloblastomas with MYCN amplification (MYCN-MB). Twenty-one MYCN-MB were examined using gene expression profiling and array-CGH, whereas for 46 tumors immunohistochemical analysis and FISH were performed. All 67 tumors were further subjected to mutational analyses. We compared molecular, clinical, and prognostic characteristics both within biological MYCN-MB groups and with non-amplified tumors. Transcriptomic analysis revealed SHH-driven tumorigenesis in a subset of MYCN-MBs indicating a biological dichotomy of MYCN-MB. Activation of SHH was accompanied by variant-specific cytogenetic aberrations including deletion of 9q in SHH tumors. Non-SHH MB were associated with gain of 7q and isochromosome 17q/17q gain. Among clinically relevant variables, SHH subtype and 10q loss for non-SHH tumors comprised the most powerful markers of favorable prognosis in MYCN-MB. In conclusion, we demonstrate considerable heterogeneity within MYCN-MB in terms of genetics, tumor biology, and clinical outcome. Thus, assessment of disease group and 10q copy-number status may improve risk stratification of this group and may delineate MYCN-MB with the same dismal prognosis as MYC amplified tumors. Furthermore, based on the enrichment of MYCN and GLI2 amplifications in SHH-driven medulloblastoma, amplification of these downstream signaling intermediates should be taken into account before a patient is enrolled into a clinical trial using a smoothened inhibitor.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldosari N, Bigner SH, Burger PC, Becker L, Kepner JL, Friedman HS, McLendon RE (2002) MYCC and MYCN oncogene amplification in medulloblastoma. A fluorescence in situ hybridization study on paraffin sections from the Children’s Oncology Group. Arch Pathol Lab Med 126(5):540–544
Beauchamp EM, Ringer L, Bulut G, Sajwan KP, Hall MD, Lee YC, Peaceman D, Ozdemirli M, Rodriguez O, Macdonald TJ, Albanese C, Toretsky JA, Uren A (2011) Arsenic trioxide inhibits human cancer cell growth and tumor development in mice by blocking Hedgehog/GLI pathway. J Clin Invest 121(1):148–160. doi:10.1172/JCI4287442874
Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Hallahan AR, Pritchard JI, Eberhart CG, Watkins DN, Chen JK, Cooper MK, Taipale J, Olson JM, Beachy PA (2002) Medulloblastoma growth inhibition by hedgehog pathway blockade. Science 297(5586):1559–1561. doi:10.1126/science.1073733297/5586/1559
Bown N, Cotterill S, Łastowska M, O’Neill S, Pearson ADJ, Plantaz D, Meddeb M, Danglot G, Brinkschmidt C, Christiansen H, Laureys G, Nicholson J, Bernheim A, Betts DR, Vandesompele J, Van Roy N, Speleman F (1999) Gain of chromosome arm 17q and adverse outcome in patients with neuroblastoma. N Engl J Med 340(25):1954–1961. doi:10.1056/NEJM199906243402504
Brunet JP, Tamayo P, Golub TR, Mesirov JP (2004) Metagenes and molecular pattern discovery using matrix factorization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(12):4164–4169. doi:10.1073/pnas.03085311010308531101
Cho YJ, Tsherniak A, Tamayo P, Santagata S, Ligon A, Greulich H, Berhoukim R, Amani V, Goumnerova L, Eberhart CG, Lau CC, Olson JM, Gilbertson RJ, Gajjar A, Delattre O, Kool M, Ligon K, Meyerson M, Mesirov JP, Pomeroy SL (2011) Integrative genomic analysis of medulloblastoma identifies a molecular subgroup that drives poor clinical outcome. J Clin Oncol 29(11):1424–1430. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.28.5148
Eberhart CG, Kratz J, Wang Y, Summers K, Stearns D, Cohen K, Dang CV, Burger PC (2004) Histopathological and molecular prognostic markers in medulloblastoma: c-myc, N-myc, TrkC, and anaplasia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63(5):441–449
Eberhart CG, Kratz JE, Schuster A, Goldthwaite P, Cohen KJ, Perlman EJ, Burger PC (2002) Comparative genomic hybridization detects an increased number of chromosomal alterations in large cell/anaplastic medulloblastomas. Brain Pathol 12(1):36–44
Ellison D (2002) Classifying the medulloblastoma: insights from morphology and molecular genetics. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 28(4):257–282. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2990.2002.00419.x
Ellison DW (2010) Childhood medulloblastoma: novel approaches to the classification of a heterogeneous disease. Acta Neuropathol 120(3):305–316. doi:10.1007/s00401-010-0726-6
Ellison DW, Dalton J, Kocak M, Nicholson SL, Fraga C, Neale G, Kenney AM, Brat DJ, Perry A, Yong WH, Taylor RE, Bailey S, Clifford SC, Gilbertson RJ (2011) Medulloblastoma: clinicopathological correlates of SHH, WNT, and non-SHH/WNT molecular subgroups. Acta Neuropathol 121(3):381–396. doi:10.1007/s00401-011-0800-8
Ellison DW, Kocak M, Dalton J, Megahed H, Lusher ME, Ryan SL, Zhao W, Nicholson SL, Taylor RE, Bailey S, Clifford SC (2011) Definition of disease-risk stratification groups in childhood medulloblastoma using combined clinical, pathologic, and molecular variables. J Clin Oncol 29(11):1400–1407. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.30.2810
Gajjar A, Hernan R, Kocak M, Fuller C, Lee Y, McKinnon PJ, Wallace D, Lau C, Chintagumpala M, Ashley DM, Kellie SJ, Kun L, Gilbertson RJ (2004) Clinical, histopathologic, and molecular markers of prognosis: toward a new disease risk stratification system for medulloblastoma. J Clin Oncol 22(6):984–993. doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.06.032
Goeman JJ, le Cessie S (2006) A goodness-of-fit test for multinomial logistic regression. Biometrics 62(4):980–985. doi:10.1111/j.1541-0420.2006.00581.x
Graf E, Schmoor C, Sauerbrei W, Schumacher M (1999) Assessment and comparison of prognostic classification schemes for survival data. Stat Med 18(17–18):2529–2545. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0258(19990915/30)18:17/18<2529
Grotzer MA, von Hoff K, von Bueren AO, Shalaby T, Hartmann W, Warmuth-Metz M, Emser A, Kortmann RD, Kuehl J, Pietsch T, Rutkowski S (2007) Which clinical and biological tumor markers proved predictive in the prospective multicenter trial HIT’91–implications for investigating childhood medulloblastoma. Klin Padiatr 219(6):312–317. doi:10.1055/s-2007-985843
Katoh Y, Katoh M (2009) Hedgehog target genes: mechanisms of carcinogenesis induced by aberrant hedgehog signaling activation. Curr Mol Med 9(7):873–886
Kenney AM, Cole MD, Rowitch DH (2003) Nmyc upregulation by sonic hedgehog signaling promotes proliferation in developing cerebellar granule neuron precursors. Development 130(1):15–28
Kessler JD, Hasegawa H, Brun SN, Emmenegger BA, Yang ZJ, Dutton JW, Wang F, Wechsler-Reya RJ (2009) N-myc alters the fate of preneoplastic cells in a mouse model of medulloblastoma. Genes Dev 23(2):157–170. doi:10.1101/gad.1759909
Kool M, Koster J, Bunt J, Hasselt NE, Lakeman A, van Sluis P, Troost D, Meeteren NS, Caron HN, Cloos J, Mrsic A, Ylstra B, Grajkowska W, Hartmann W, Pietsch T, Ellison D, Clifford SC, Versteeg R (2008) Integrated genomics identifies five medulloblastoma subtypes with distinct genetic profiles, pathway signatures and clinicopathological features. PLoS One 3(8):e3088. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003088
Korshunov A, Benner A, Remke M, Lichter P, von Deimling A, Pfister S (2008) Accumulation of genomic aberrations during clinical progression of medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol 116(4):383–390. doi:10.1007/s00401-008-0422-y
Korshunov A, Remke M, Werft W, Benner A, Ryzhova M, Witt H, Sturm D, Wittmann A, Schottler A, Felsberg J, Reifenberger G, Rutkowski S, Scheurlen W, Kulozik AE, von Deimling A, Lichter P, Pfister SM (2010) Adult and pediatric medulloblastomas are genetically distinct and require different algorithms for molecular risk stratification. J Clin Oncol 28(18):3054–3060. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.25.7121
Lamont JM, McManamy CS, Pearson AD, Clifford SC, Ellison DW (2004) Combined histopathological and molecular cytogenetic stratification of medulloblastoma patients. Clin Cancer Res 10(16):5482–5493. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-072110/16/5482
Li T, Ding C (2006) The relationships among various nonnegative matrix factorization methods for clustering. Paper presented at the Proceedings of Sixth International Conference on Data Mining
Low JA, de Sauvage FJ (2010) Clinical experience with Hedgehog pathway inhibitors. J Clin Oncol 28(36):5321–5326. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.27.9943
Margolin AA, Nemenman I, Basso K, Wiggins C, Stolovitzky G, Dalla Favera R, Califano A (2006) ARACNE: an algorithm for the reconstruction of gene regulatory networks in a mammalian cellular context. BMC Bioinformatics 7(Suppl 1):S7. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-7-S1-S7
Margolin AA, Wang K, Lim WK, Kustagi M, Nemenman I, Califano A (2006) Reverse engineering cellular networks. Nat Protoc 1(2):662–671. doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.106
Murphy DM, Buckley PG, Bryan K, Watters KM, Koster J, van Sluis P, Molenaar J, Versteeg R, Stallings RL (2011) Dissection of the oncogenic MYCN transcriptional network reveals a large set of clinically relevant cell cycle genes as drivers of neuroblastoma tumorigenesis. Mol Carcinog 50(6):403–411. doi:10.1002/mc.20722
Northcott PA, Fernandez LA, Hagan JP, Ellison DW, Grajkowska W, Gillespie Y, Grundy R, Van Meter T, Rutka JT, Croce CM, Kenney AM, Taylor MD (2009) The miR-17/92 polycistron is up-regulated in sonic hedgehog-driven medulloblastomas and induced by N-myc in sonic hedgehog-treated cerebellar neural precursors. Cancer Res 69(8):3249–3255. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4710
Northcott PA, Korshunov A, Witt H, Hielscher T, Eberhart CG, Mack S, Bouffet E, Clifford SC, Hawkins CE, French P, Rutka JT, Pfister S, Taylor MD (2011) Medulloblastoma comprises four distinct molecular variants. J Clin Oncol 29(11):1408–1414. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.27.4324
Northcott PA, Rutka JT, Taylor MD (2010) Genomics of medulloblastoma: from Giemsa-banding to next-generation sequencing in 20 years. Neurosurg Focus 28(1):E6. doi:10.3171/2009.10.FOCUS09218
Oliver TG, Grasfeder LL, Carroll AL, Kaiser C, Gillingham CL, Lin SM, Wickramasinghe R, Scott MP, Wechsler-Reya RJ (2003) Transcriptional profiling of the Sonic hedgehog response: a critical role for N-myc in proliferation of neuronal precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(12):7331–7336. doi:10.1073/pnas.08323171000832317100
Pession A, Tonelli R (2005) The MYCN oncogene as a specific and selective drug target for peripheral and central nervous system tumors. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 5(4):273–283
Pfaff E, Remke M, Sturm D, Benner A, Witt H, Milde T, von Bueren AO, Wittmann A, Schottler A, Jorch N, Graf N, Kulozik AE, Witt O, Scheurlen W, von Deimling A, Rutkowski S, Taylor MD, Tabori U, Lichter P, Korshunov A, Pfister SM (2010) TP53 mutation is frequently associated with CTNNB1 mutation or MYCN amplification and is compatible with long-term survival in medulloblastoma. J Clin Oncol 28(35):5188–5196. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.31.1670
Pfister S, Remke M, Benner A, Mendrzyk F, Toedt G, Felsberg J, Wittmann A, Devens F, Gerber NU, Joos S, Kulozik A, Reifenberger G, Rutkowski S, Wiestler OD, Radlwimmer B, Scheurlen W, Lichter P, Korshunov A (2009) Outcome prediction in pediatric medulloblastoma based on DNA copy-number aberrations of chromosomes 6q and 17q and the MYC and MYCN loci. J Clin Oncol 27(10):1627–1636. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.17.9432
Pfister SM, Korshunov A, Kool M, Hasselblatt M, Eberhart C, Taylor MD (2010) Molecular diagnostics of CNS embryonal tumors. Acta Neuropathol 120(5):553–566. doi:10.1007/s00401-010-0751-5
Pomeroy SL, Tamayo P, Gaasenbeek M, Sturla LM, Angelo M, McLaughlin ME, Kim JY, Goumnerova LC, Black PM, Lau C, Allen JC, Zagzag D, Olson JM, Curran T, Wetmore C, Biegel JA, Poggio T, Mukherjee S, Rifkin R, Califano A, Stolovitzky G, Louis DN, Mesirov JP, Lander ES, Golub TR (2002) Prediction of central nervous system embryonal tumour outcome based on gene expression. Nature 415(6870):436–442. doi:10.1038/415436a
Qi Q, Zhao Y, Li M, Simon R (2009) Non-negative matrix factorization of gene expression profiles: a plug-in for BRB-ArrayTools. Bioinformatics 25(4):545–547. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp009
Remke M, Hielscher T, Korshunov A, Northcott PA, Bender S, Kool M, Westermann F, Benner A, Cin H, Ryzhova M, Sturm D, Witt H, Haag D, Toedt G, Wittmann A, Schottler A, von Bueren AO, von Deimling A, Rutkowski S, Scheurlen W, Kulozik AE, Taylor MD, Lichter P, Pfister SM (2011) FSTL5 is a marker of poor prognosis in non-WNT/non-SHH medulloblastoma. J Clin Oncol 29(29):3852–3861. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.36.2798
Remke M, Hielscher T, Northcott PA, Witt H, Ryzhova M, Wittmann A, Benner A, von Deimling A, Scheurlen W, Perry A, Croul S, Kulozik AE, Lichter P, Taylor MD, Pfister SM, Korshunov A (2011) Adult medulloblastoma comprises three major molecular variants. J Clin Oncol 29(19):2717–2723. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.34.9373
Rutkowski S, von Bueren A, von Hoff K, Hartmann W, Shalaby T, Deinlein F, Warmuth-Metz M, Soerensen N, Emser A, Bode U, Mittler U, Urban C, Benesch M, Kortmann RD, Schlegel PG, Kuehl J, Pietsch T, Grotzer M (2007) Prognostic relevance of clinical and biological risk factors in childhood medulloblastoma: results of patients treated in the prospective multicenter trial HIT’91. Clin Cancer Res 13(9):2651–2657. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1779
Schwab M, Westermann F, Hero B, Berthold F (2003) Neuroblastoma: biology and molecular and chromosomal pathology. Lancet Oncol 4(8):472–480 (S1470204503011665[pii])
Scott DK, Straughton D, Cole M, Bailey S, Ellison DW, Clifford SC (2006) Identification and analysis of tumor suppressor loci at chromosome 10q23.3-10q25.3 in medulloblastoma. Cell Cycle 5(20):2381–2389 (3360[pii])
Suzuki R, Shimodaira H (2006) Pvclust: an R package for assessing the uncertainty in hierarchical clustering. Bioinformatics 22(12):1540–1542. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btl117
Swartling FJ, Grimmer MR, Hackett CS, Northcott PA, Fan QW, Goldenberg DD, Lau J, Masic S, Nguyen K, Yakovenko S, Zhe XN, Gilmer HC, Collins R, Nagaoka M, Phillips JJ, Jenkins RB, Tihan T, Vandenberg SR, James CD, Tanaka K, Taylor MD, Weiss WA, Chesler L (2010) Pleiotropic role for MYCN in medulloblastoma. Genes Dev 24(10):1059–1072. doi:10.1101/gad.1907510
Taylor RE, Bailey CC, Robinson KJ, Weston CL, Walker DA, Ellison D, Ironside J, Pizer BL, Lashford LS (2005) Outcome for patients with metastatic (M2–3) medulloblastoma treated with SIOP/UKCCSG PNET-3 chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer 41(5):727–734. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2004.12.017
Westermann F, Muth D, Benner A, Bauer T, Henrich KO, Oberthuer A, Brors B, Beissbarth T, Vandesompele J, Pattyn F, Hero B, Konig R, Fischer M, Schwab M (2008) Distinct transcriptional MYCN/c-MYC activities are associated with spontaneous regression or malignant progression in neuroblastomas. Genome Biol 9(10):R150. doi:10.1186/gb-2008-9-10-r150
Zitterbart K, Filkova H, Tomasikova L, Necesalova E, Zambo I, Kantorova D, Slamova I, Vranova V, Zezulkova D, Pesakova M, Pavelka Z, Veselska R, Kuglik P, Sterba J (2010) Low-level copy number changes of MYC genes have a prognostic impact in medulloblastoma. J Neurooncol 102:25–33. doi:10.1007/s11060-010-0289-3
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the Deutsche Kinderkrebsstiftung to S.P., a “Lina Marguerite Siebert” Award, a “Young Investigator Fellowship” of the Medical Faculty of Heidelberg and a grant from the Landesstiftung Baden-Wuerttemberg to M.R., and a guest scientist fellowship of the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) Heidelberg to M.Ry., EU (FP6 and FP7): E.E.T. Pipeline #037260 and ASSET #259348 to F.W..
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
401_2011_918_MOESM2_ESM.eps
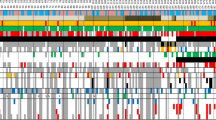
Unsupervised hierarchical clustering from 77 primary medulloblastomas using 300 genes with high standard deviation demonstrates the presence of MYCN amplifications in various subgroups. Molecular characteristics (amplifications of MYCN, MYC (red), and GLI2; 6q loss, gain of chromosome 7, loss of 9q, 10q, and 17p; gain of 17q; disease variant denominations: WNT (blue), SHH (red), group C (yellow), and group D (green)) of the study population are shown below the dendrogram. Molecular alteration present (black). (EPS 4643 kb)
401_2011_918_MOESM3_ESM.docx
a Bootstrapped ARACNE network illustrating the estimated interacting genes in 77 primary medulloblastomas. Limited subnetwork shown to illustrate an estimated direct interaction between MYCN and the SHH-specific gene GLI2. b Expression of GLI2 (left panel) and MYCN (right panel) transcripts derived from transcriptome analysis of primary medulloblastoma, grouped according to the presence of MYCN amplification and/or SHH pathway activation. (DOCX 417 kb)
401_2011_918_MOESM4_ESM.eps
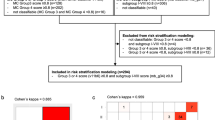
Kaplan-Meier plot of estimated overall survival time (a) and progression-free survival time (b) distributions. The number of patients under risk is indicated for time increments of 12 months. Kaplan-Meier plots according to the presence MYCN amplification in tumors with SHH pathway activation (EPS 1599 kb)
401_2011_918_MOESM5_ESM.eps
Kaplan-Meier plot of estimated overall survival time (a) and progression-free survival time (b) distributions. The number of patients under risk is indicated for time increments of 12 months. Kaplan-Meier plots according to the presence MYCN amplification in non-SHH medulloblastomas (EPS 1947 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korshunov, A., Remke, M., Kool, M. et al. Biological and clinical heterogeneity of MYCN-amplified medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol 123, 515–527 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-011-0918-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-011-0918-8