Abstract
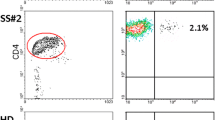
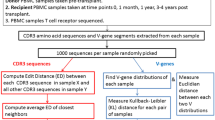
In advanced stages, cutaneous T cell lymphomas (CTCL) are associated with increased mortality from infections and also increased susceptibility to skin malignancies. In this study, we analyzed the complexity of the peripheral blood T cell repertoire with a sensitive b-variable (BV) complementarity-determining region 3 (CDR3) spectratyping analysis and flow cytometry in three-stage IV CTCL/Sezary syndrome patients who achieved complete clinical remission after therapy. The T cell repertoire of peripheral blood T cells before treatment was profoundly abnormal across multiple BV subfamilies. Following treatment, CDR3 spectratype patterns showed dramatic restoration of normal diversity and complexity. However, absolute CD4 counts across multiple BV families remained low for many months, even after identifiable circulating malignant T cell populations were eliminated. These data suggest that the diversity of the T cell repertoire can be recovered after successful treatment of even advanced CTCL.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CTCL:
-
Cutaneous T cell lymphoma
- TREC:
-
T cell receptor excision circle
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- T reg:
-
Regulatory T cell
- BV:
-
b-Variable
- CDR3:
-
Complementarity-determining region 3
- ECP:
-
Extracorporeal photopheresis
- IFN:
-
Interferon
References
Asadullah K, Haeussler A, Friedrich M, Siegling A, Olaizola-Horn S, Trefzer U, Volk HD, Sterry W (1996) IL-7 mRNA is not overexpressed in mycosis fungoides and pleomorphic T-cell lymphoma and is likely to be an autocrine growth factor in vivo. Arch Dermatol Res 289:9–13
Axelrod PI, Lorber B, Vonderheid EC (1992) Infections complicating mycosis fungoides and Sezary syndrome. JAMA 267:1354–1358
Berger CL, Tigelaar R, Cohen J, Mariwalla K, Trinh J, Wang N, Edelson RL (2005) Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: malignant proliferation of T-regulatory cells. Blood 105:1640–1647
Brenchley JM, Schacker TW, Ruff LE, Price DA, Taylor JH, Beilman GJ, Nguyen PL, Khoruts A, Larson M, Haase AT, Douek DC (2004) CD4+ T cell depletion during all stages of HIV disease occurs predominantly in the gastrointestinal tract. J Exp Med 200:749–759
Brownell I, Etzel CJ, Yang DJ, Taylor SH, Duvic M (2008) Increased malignancy risk in the cutaneous T-cell lymphoma patient population. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma 8:100–105
Dummer R, Heald PW, Nestle FO, Ludwig E, Laine E, Hemmi S, Burg G (1996) Sezary syndrome T-cell clones display T-helper 2 cytokines and express the accessory factor-1 (interferon-gamma receptor beta-chain). Blood 88:1383–1389
Ehrhard S, Wernli M, Kaufmann G, Pantaleo G, Rizzardi GP, Gudat F, Erb P, Battegay M (2008) Effect of antiretroviral therapy on apoptosis markers and morphology in peripheral lymph nodes of HIV-infected individuals. Infection 36:120–129
Evans a V, Scarisbrick JJ, Child FJ, Acland KM, Whittaker SJ, Russell-Jones R (2004) Cutaneous malignant melanoma in association with mycosis fungoides. J Am Acad Dermatol 50:701–705
Ferenczi K, Mckee P, Kupper TS (2000) Cutaneous lymphoma. Atlas of clinical oncology. BC Decker, Hamilton, ON, pp 85–117
Ferenczi K, Yawalkar N, Jones D, Kupper TS (2003) Monitoring the decrease of circulating malignant T cells in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma during photopheresis and interferon therapy. Arch Dermatol 139:909–913
Goldgeier MH, Cohen SR, Braverman IM, Stenn KS (1981) An unusual and fatal case of disseminated cutaneous herpes simplex. Infection in a patient with cutaneous T cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides). J Am Acad Dermatol 4:176–180
Hochberg EP, Chillemi AC, Wu CJ, Neuberg D, Canning C, Hartman K, Alyea EP, Soiffer RJ, Kalams SA, Ritz J (2001) Quantitation of T-cell neogenesis in vivo after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in adults. Blood 98:1116–1121
Kim EJ, Hess S, Richardson SK, Newton S, Showe LC, Benoit BM, Ubriani R, Vittorio CC, Junkins-Hopkins JM, Wysocka M, Rook AH (2005) Immunopathogenesis and therapy of cutaneous T cell lymphoma. J Clin Invest 115:798–812
Mukai H, Noguchi T, Kamimura K, Nishioka K, Nishiyama S (1990) Significance of elevated serum LDH (lactate dehydrogenase) activity in atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol 17:477–481
Nguyen V, Huggins RH, Lertsburapa T, Bauer K, Rademaker A, Gerami P, Guitart J (2008) Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and Staphylococcus aureus colonization. J Am Acad Dermatol 59:949–952
Pielop JA, Brownell I, Duvic M (2003) Mycosis fungoides associated with malignant melanoma and dysplastic nevus syndrome. Int J Dermatol 42:116–122
Poznansky MC, Evans RH, Foxall RB, Olszak IT, Piascik AH, Hartman KE, Brander C, Meyer TH, Pykett MJ, Chabner KT, Kalams SA, Rosenzweig M, Scadden DT (2000) Efficient generation of human T cells from a tissue-engineered thymic organoid. Nat Biotechnol 18:729–734
Raaphorst FM, Schelonka RL, Rusnak J, Infante AJ, Teale JM (2002) TCRBV CDR3 diversity of CD4+ and CD8+ T-lymphocytes in HIV-infected individuals. Hum Immunol 63:51–60
Resino S, Correa R, Bellon JM, Munoz-Fernandez MA (2003) Preserved immune system in long-term asymptomatic vertically HIV-1 infected children. Clin Exp Immunol 132:105–112
Ruiz-Mateos E, De La Rosa R, Franco JM, Martinez-Moya M, Rubio A, Soriano N, Sanchez-Quijano A, Lissen E, Leal M (2003) Endogenous IL-7 is associated with increased thymic volume in adult HIV-infected patients under highly active antiretroviral therapy. Aids 17:947–954
Schelonka RL, Raaphorst FM, Infante D, Kraig E, Teale JM, Infante AJ (1998) T cell receptor repertoire diversity and clonal expansion in human neonates. Pediatr Res 43:396–402
Thomas JM, Newton-Bishop J, A’hern R, Coombes G, Timmons M, Evans J, Cook M, Theaker J, Fallowfield M, O’neill T, Ruka W, Bliss JM (2004) Excision margins in high-risk malignant melanoma. N Engl J Med 350:757–766
Van Grevenynghe J, Halwani R, Chomont N, Ancuta P, Peretz Y, Tanel A, Procopio FA, Shi Y, Said EA, Haddad EK, Sekaly RP (2008) Lymph node architecture collapse and consequent modulation of FOXO3a pathway on memory T- and B-cells during HIV infection. Semin Immunol 20:196–203
Vowels BR, Cassin M, Vonderheid EC, Rook AH (1992) Aberrant cytokine production by Sezary syndrome patients: cytokine secretion pattern resembles murine Th2 cells. J Invest Dermatol 99:90–94
Wu CJ, Chillemi A, Alyea EP, Orsini E, Neuberg D, Soiffer RJ, Ritz J (2000) Reconstitution of T-cell receptor repertoire diversity following T-cell depleted allogeneic bone marrow transplantation is related to hematopoietic chimerism. Blood 95:352–359
Yamanaka K, Clark R, Dowgiert R, Hurwitz D, Shibata M, Rich BE, Hirahara K, Jones DA, Eapen S, Mizutani H, Kupper TS (2006) Expression of interleukin-18 and caspase-1 in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 12:376–382
Yamanaka K, Clark R, Rich B, Dowgiert R, Hirahara K, Hurwitz D, Shibata M, Mirchandani N, Jones DA, Goddard DS, Eapen S, Mizutani H, Kupper TS (2006) Skin-derived interleukin-7 contributes to the proliferation of lymphocytes in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Blood 107:2440–2445
Yamanaka K, Yawalkar N, Jones DA, Hurwitz D, Ferenczi K, Eapen S, Kupper TS (2005) Decreased T-cell receptor excision circles in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 11:5748–5755
Yawalkar N, Ferenczi K, Jones DA, Yamanaka K, Suh KY, Sadat S, Kupper TS (2003) Profound loss of T-cell receptor repertoire complexity in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Blood 102:4059–4066
Yoo EK, Cassin M, Lessin SR, Rook AH (2001) Complete molecular remission during biologic response modifier therapy for Sezary syndrome is associated with enhanced helper T type 1 cytokine production and natural killer cell activity. J Am Acad Dermatol 45:208–216
Yoshimoto T, Mizutani H, Tsutsui H, Noben-Trauth N, Yamanaka K, Tanaka M, Izumi S, Okamura H, Paul WE, Nakanishi K (2000) IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4+ T cells, IL-4 and STAT6. Nat Immunol 1:132–137
Acknowledgment
Grant support: SPORE in Skin Cancer from the NCI/NIH.
Conflicts of interest statement
None identified.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
403_2009_1023_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary material 1 (pdf 122 kb) Analysis of Patient B shows a markedly reduced spectratype complexity (Panel a) and an expandedmalignant clone (BV 14, Panel c). Analysis of the same patient after CR shows improved CDR3spectratype (Panel b) with the restriction of diverse T cells in the peripheral blood (Panel d)
403_2009_1023_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Supplementary material 2 (pdf 115 kb) Analysis of Patient C shows a markedly reduced spectratype complexity (Panel a), but dominantclones were undetectable with our panel of TCR BV antibodies (Panel c). Analysis of the patient Cafter CR shows improved CDR3 spectratype (Panel b) with the restriction of diverse T cells in theperipheral blood (Panel d)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamanaka, Ki., Fuhlbrigge, R.C., Mizutani, H. et al. Restoration of peripheral blood T cell repertoire complexity during remission in advanced cutaneous T cell lymphoma. Arch Dermatol Res 302, 453–459 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-009-1023-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-009-1023-x