Abstract
Purpose
Inhibition of angiogenesis is an important new treatment modality for malignancies, including gliomas. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) have been investigated as potent mediators of tumor angiogenesis. We investigated whether four major chemotherapeutic agents (ACNU, cisplatin, etoposide, and SN38) showed an angiosuppressive effect in vitro.
Method
The effects of ACNU, cisplatin, etoposide, and SN38 for endothelial cells were assessed by cell growth inhibition assay (WST-8 assay) and vessel formation assay (angiogenesis kit). The inhibitory effects of the HIF-1α and VEGF expression of glioma cells after SN38 treatment were assessed by real-time RT-PCR, Western blot, and ELISA.
Results
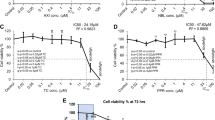
SN38, but not other chemotherapeutic agents, selectively inhibited endothelial cell proliferation and three-dimensional tube formations at the 0.01 μM. Furthermore, SN38 significantly decreased the HIF-1α and VEGF expression of glioma cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. SN38 has dual angiosuppressive actions, including both the inhibition of endothelial proliferation and tube formation, and the inhibition of the angiogenic cascade in glioma cells.
Conclusion
SN38 is an attractive agent as both a direct and indirect angiogenesis inhibitor and provides the anti-glioma agents with an angiosuppressive function.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allegrini G, Goulette AF, Darnowski WJ, Calabresi P (2004) Thrombospondin-1 plus irinotecan: a novel antiangiogenenis-chemotherapeutic combination that inhibits the growth of advanced human colon tumor xenografts in mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 3:261–266
Arthur TW, Vernon ER, Sage EH, Reed JM (1998) Growth factors reverse the impaired sprouting of microvessels from aged mice. Microvasc Res 55:260–270
Ashby LS, Shapiro WR (2001) Intra-arterial cisplatin plus oral etoposide for the treatment of recurrent malignant glioma: a phase II study. J Neurooncol 51:67–86
Bacher M, Schrader J, Thompson N, Kuschela K, Gemsa D, Waeber G, Schlegel J (2003) Up-regulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor gene and protein expression in glial tumor cells during hypoxic and hypoglycemic stress indicates a critical role for angiogenesis in glioblastoma multiforme. Am J Pathol 162:11–17
Bisacchi D, Bebelli R, Vanzetto C, Ferrari N, Tosetti F, Albini A (2003) Anti-angiogenesis and angioprevention: mechanisms, problems and perspectives. Cancer Detect Prev 27:229–238
Brwoder T, Butterfield CE, Kraling BM, Shi B, Marshall B, O’Reilly MS, Folkman J (2000) Antiangiogenic scheduling of chemotherapy improves efficacy against experimental drug-resistant cancer. Cancer Res 60:1878–1886
Buckner JC, Reid JM, Wright K, Kaufmann SH, Erlichman C, Ames M, Cha S, O’Fallon JR, Schaaf LJ, Miller LL (2003) Irinotecan in the treatment of glioma patients: current and future studies of the North Central Cancer Treatment Group. Cancer 97:2352–2358
Carmeliet P, Rakesh JK (2000) Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 14:249–257
Christopher WP, Peter JR (2003) Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia: role of the HIF system. Nat Med 9:677–684
Clements KM, Jones BC, Cumming M, Daoud SS (1999) Antiangiogenic potential of camptothecin and topotecan. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 44:411–416
Folkman J (2003) Angiogenesis and proteins of the hemostatic system. J Thromb Haemost 1:1681–1682
Gasparini G (1999) The rationale and future potential of angiogenesis inhibitors in neoplasia. Drugs 58:17–38
Hanahan D, Beregers G, Bergsland E (2000) Less is more, regularly: metronomic dosing of cytotoxic drugs can target tumor angiogenesis in mice. J Clin Invest 105:1045–1047
Harris AL (2002) Hypoxia—a key regulatory factor in tumor growth. Nat Rev Cancer 2:38–47
Hayot C, Farinelle S, De Decker R, Decaestecker C, Darro F, Kiss R, Van Damme M (2002) In vitro pharmacological characterizations of the anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor cell migration properties mediated by microtubule-affecting drugs, with special emphasis on the organization of the actin cytoskeleton. Int J Oncol 21:417–425
Kerbel R, Folkman J (2002) Clinical translation of angiogenesis inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer 2:727–739
Klement G, Baruchel S, Rak J, Man S, Clark K, Hicklin DJ, Bohlen P, Kerbel RS (2000) Continuous low-dose therapy with vinblastin and VEGF receptor-2 antibody induces sustained tumor regression without overt toxicity. J Clin Invest 105:R15-R24
Kobayashi M, Kondo M, Mitsui Y (1991) Establishment of human endothelial cell lines in a serum-free culture and its application for expression of transfected prepro endothelin gene. Human Cell 4:296–304
Lee JW, Bae SH, Jeong JW, Kim SH, Kim KW (2004) Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1)α: its protein stability and biological functions. Exp Mol Med 36:1–12
Man S, Bocci G, Francia G, Green SK, Jothy S, Hanahan D, Bohlen P, Hicklin DJ, Bergers G, Kerbel RS (2002) Antitumor effects in mice of low-dose (metronomic) cyclophosphamide administered continuously through the drinking water. Cancer Res 62:2731–2735
McCrudden KW, Yokoi A, Thosani A, Soffer SZ, Kim ES, Huang J, Manley C, O’toole K, Yamashiro DJ, Kandel JJ, Middlesworth W (2002) Topotecan is anti-angiogenic in experimental hepatoblastoma. J Pediatr Surg 37:857–861
Nakashio A, Fujita N, Tsuruo T (2002) Topotecan inhibits VEGF- and bFGF-induced vascular endothelial cell migration via downregulation of the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Int J Cancer 98:36–41
O’Leary J, Muggia MF (1998) Camptothecins: a review of development and schedules of administration. Eur J Cancer 34:1500–1508
O’Leary J, Shapiro RL, Ren CJ, Chuang N, Cohen HW, Potmesil M (1999) Antiangiogenic effects of camptothecin analogues 9-amino-20(S)-camptothecin, topotecan, and CPT-11 studied in the mouse cornea model. Clin Cancer Res 5:181–187
Parker JR, Fryehauf PJ, Mehta R, Filka E, Cloughesy T (2004) A prospective blinded study of the predictive value of an extreme drug resistance assay in patients receiving CPT-11 for recurrent glioma. J Neurooncol 66:365–375
Parney IF, Chang SM (2003) Current chemotherapy for glioblastoma. Cancer J 9:149–156
Petrangolini G, Pratesi G, De Cesare M, Supino R, Pisano C, Marcellini M, Giordano V, Laccabue D, Lanzi C, Zunino F (2003) Antiangiogenic effects of the novel camptothecin ST1481 (Gimatecan) in human tumor xenografts. Mol Cancer Res 1:863–870
Pili R, Donehower RC (2003) Is HIF-1α a valid therapeutic target?. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:498–499
Rapisarda A, Uranchimeg B, Scudiero DA, Selby M, Sausville EA, Shoemaker RH, Melillo G (2002) Identification of small molecule inhibitors of Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 transcriptional activation pathway. Cancer Res 62:4316–4324
Rapisarda A, Uranchimeg B, Sordet O, Pommier Y, Shoemaker RH, Malillo G (2004) Topoisomerase I-mediated inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor 1: mechanism and therapeutic implications. Cancer Res 64:1475–1482
Reardon DA, Friedman HS, Powell JB Jr, Gilbert M, Yung WK (2003) Irinotecan: promising activity in the treatment of malignant glioma. Oncology (Huntingt) 17:9–14
Safran M, Kaelin WG Jr (2003) HIF hydroxylation and the mammalian oxygen-sensing pathway. J Clin Invest 111:779–783
Schirner M (2000) Antiangiogenic chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Metastasis Rev 19:67–73
Semenza GL (2003) Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 3:721–732
Soffer SZ, Kim E, Moore JT, Huang J, Yokoi A, Manley C, O’Toole K, Middlesworth W, Stolar C, Yamashiro D, Kandel J (2001) Novel use of an established agent: topotecan is anti-angiogenic in experimental Wilms tumor. J Pediatr Surg 36:1781–1784
Sun X, Kanwar JR, Leung E, Lehnert K, Wang D, Krissansen GW (2001) Gene transfer of antisense hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha enhances the therapeutic efficacy of cancer immunotherapy. Gene Ther 8:638–645
Takano S, Gately S, Neville ME, Herblin WF, Gross JL, Engelhard H, Perricone M, Eidsvoog K, Brem S (1994) Suramin, an anticancer and angiosuppressive agent, inhibits endothelial cell binding of basic fibroblast growth factor, migration, proliferation, and induction of urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Cancer Res 54:2654–2660
Takano S, Yoshii Y, Kondo S, Suzuki H, Maruno T, Shirai S, Nose T (1996) Concentration of vascular endothelial growth factor in the serum and tumor tissue of brain tumor patients. Cancer Res 56:2185–2190
Takano S, Tsuboi K, Matsumura A, Nose T (2003) Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody and nimustine as combined therapy: effects on tumor growth and angiogenesis in human glioblastoma xenografts. Neuro-oncol 5:1–7
Tanaka M, Tanaka T, Harata M, Suzuki T, Mitsui Y (1998) Triplet repeat-containing ribosomal protein L14 gene in immortalized human endothelial cell line (t-HUE4). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 243:531–537
Unruh A, Ressel A, Mohamed HG, Johnson RS, Nadrowitz R, Richter E, Katschinski DM, Wenger RH (2003) The hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha is a negative factor for tumor therapy. Oncogene 22:3213–3220
Xiao D, Tan W, Li M, Ding J (2001) Antiangiogenic potential of 10-hydroxycamptothecin. Life Sci 69:1619–1628
Yabushita H, Shimizu M, Noguchi M, Kishida T, Narumiya H, Sawaguchi K, Noguchi M (2003) Vascular endothelial growth factor activating matrix metalloproteinase in ascitic fluid during peritoneal dissemination of ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep 10:89–95
Yeo EJ, Chun YS, Cho YS, Kim J, Lee JC, Kim MS, Park JW (2003) YC1: a potential anticancer drug targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:516–525
Yoshida J, Kajita Y, Wakabayashi T, Sugita K (1994) Long-term follow-up results of 175 patients with malignant glioma: importance of radical tumor resection and postoperative adjuvant therapy with interferon, ACNU and radiation. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 127:55–59
Zagzag D (1995) Angiogenic growth factors in neural embryogenesis and neoplasia. Am J Pathol 146:293–309
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge Dr. Youji Mitsui, (Laboratory of Physiological Chemistry, Tokushima Bunri University), Dr. Hiroshi Kanma (Laboratory of Cellular Pathology, University of Tsukuba), and Dr. Kazumasa Isobe (Laboratory of Clinical Pathology, University of Tsukuba) for useful discussion, and Ms. Makiko Miyakawa and Yoshiko Tsukada for their excellent technical assistance
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from Japanese Ministry of Education, Science, and Culture and by a grant provided by the Tsukuba Advanced Research Alliance
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamiyama, H., Takano, S., Tsuboi, K. et al. Anti-angiogenic effects of SN38 (active metabolite of irinotecan): inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α)/vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression of glioma and growth of endothelial cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 131, 205–213 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-004-0642-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-004-0642-z