Abstract
Purpose
Pembrolizumab is an effective front-line treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in patients expressing high levels of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1). However, it is unclear whether first-line pembrolizumab has similar efficacy among elderly (aged ≥ 75 years) and younger patients. This study aimed to investigate the safety and efficacy of front-line pembrolizumab monotherapy in older adults with NSCLC expressing high PD-L1.
Methods
A total of 128 patients with advanced NSCLC expressing high PD-L1, including 47 older adults, received first-line pembrolizumab monotherapy at ten institutions in Japan, between February 2017 and February 2018. Data related to patient characteristics, efficacy of pembrolizumab therapy, and the type and severity of adverse events were recorded.
Results
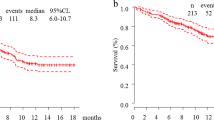
Overall, 47 patients [40 men and 7 women; median age 79 (range 75–88) years] were included in our analysis. In patients who received first-line pembrolizumab monotherapy, overall response, disease control rates, median progression-free survival (PFS), and median overall survival (OS) were 53.1%, 74.4%, 7.0 months, and not reached, respectively. Common adverse events included anorexia, fatigue, skin rash, and hypothyroidism. Two treatment-related deaths were noted, due to pneumonitis and infection. First-line pembrolizumab monotherapy was associated with improved PFS in patients with non-progressive disease (PD). In patients with non-PD and good performance status (PS), pembrolizumab monotherapy improved OS.
Conclusions
Elderly patients with NSCLC expressing high PD-L1 tolerated front-line pembrolizumab monotherapy well. Their survival outcomes were equivalent to those of younger patients. In patients with non-PD, first-line pembrolizumab monotherapy may improve PFS; in conjunction with good PS, it additionally improves OS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alguilar EJ et al (2018) MA04. 05 outcomes in NSCLC patients treated with first-line pembrolizumab and a PD-L1 TPS of 50-74% vs 75-100% or 50-89% vs 90-100%. J Thorac Oncol 13:S367–S368
Alkharabsheh O, Kannarkatt P, Kannarkatt J, Karapetyan L, Laird-Fick HS, Al-Janadi A (2018) An overview of the toxicities of checkpoint inhibitors in older patients with cancer. J Geriatr Oncol 9:451–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgo.2018.02.002
Champiat S et al (2016) Management of immune checkpoint blockade dysimmune toxicities: a collaborative position paper. Ann Oncol 27:559–574. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdv623
Daste A et al (2017) Immune checkpoint inhibitors and elderly people: a review. Eur J Cancer 82:155–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2017.05.044
Davidoff AJ, Tang M, Seal B, Edelman MJ (2010) Chemotherapy and survival benefit in elderly patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:2191–2197. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2009.25.4052
Dudnik E et al (2018) Effectiveness and safety of nivolumab in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: the real-life data. Lung Cancer 126:217–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.11.015
Eisenhauer EA et al (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
Ferlay J et al (2015) Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 136:E359–E386. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29210
Fujimoto D et al (2018) Efficacy and safety of nivolumab in previously treated patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a multicenter retrospective cohort study. Lung Cancer 119:14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.02.017
Gandhi L et al (2018) Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 378:2078–2092. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1801005
Garon EB et al (2015) Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 372:2018–2028. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1501824
Gridelli C et al (2003) Chemotherapy for elderly patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: the Multicenter Italian Lung Cancer in the Elderly Study (MILES) phase III randomized trial. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:362–372
Haratani K et al (2018) Association of immune-related adverse events with nivolumab efficacy in non-small-cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol 4:374–378. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.2925
Hellmann MD et al (2018) Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in lung cancer with a high tumor mutational burden. N Engl J Med 378:2093–2104. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1801946
Herbst RS et al (2016) Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 387:1540–1550. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(15)01281-7
Kudoh S et al (2006) Phase III study of docetaxel compared with vinorelbine in elderly patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results of the West Japan Thoracic Oncology Group Trial (WJTOG 9904). J Clin Oncol 24:3657–3663. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2006.06.1044
Miller KD et al (2016) Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 66:271–289. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21349
Nosaki K et al (2019) Safety and efficacy of pembrolizumab monotherapy in elderly patients with PD-L1-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: pooled analysis from the KEYNOTE-010, KEYNOTE-024, and KEYNOTE-042 studies. Lung Cancer 135:188–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.07.004
Okamoto I et al (2019) Randomized phase III study comparing carboplatin plus pemetrexed followed by pemetrexed versus docetaxel in elderly patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (JCOG1210/WJOG7813L). J Clin Oncol 37 (suppl; abstr 9031)
Owonikoko TK, Ragin CC, Belani CP, Oton AB, Gooding WE, Taioli E, Ramalingam SS (2007) Lung cancer in elderly patients: an analysis of the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database. J Clin Oncol 25:5570–5577. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2007.12.5435
Pang HH et al (2016) Enrollment trends and disparity among patients with lung cancer in National Clinical Trials, 1990 to 2012. J Clin Oncol 34:3992–3999. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2016.67.7088
Poropatich K, Fontanarosa J, Samant S, Sosman JA, Zhang B (2017) Cancer immunotherapies: are they as effective in the elderly? Drugs Aging 34:567–581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40266-017-0479-1
Reck M et al (2016) Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 375:1823–1833. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1606774
Rizvi NA et al (2015) Activity and safety of nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor, for patients with advanced, refractory squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 063): a phase 2, single-arm trial. Lancet Oncol 16:257–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(15)70054-9
Roach C et al (2016) Development of a companion diagnostic PD-L1 immunohistochemistry assay for pembrolizumab therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 24:392–397. https://doi.org/10.1097/pai.0000000000000408
Sacher AG, Le LW, Leighl NB, Coate LE (2013) Elderly patients with advanced NSCLC in phase III clinical trials: are the elderly excluded from practice-changing trials in advanced NSCLC? J Thorac Oncol 8:366–368. https://doi.org/10.1097/jto.0b013e31827e2145
Singh S, Loke YK (2012) Drug safety assessment in clinical trials: methodological challenges and opportunities. Trials 13:138. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6215-13-138
Socinski MA et al (2018) Atezolizumab for first-line treatment of metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC. N Engl J Med 378:2288–2301. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1716948
Solana R, Tarazona R, Gayoso I, Lesur O, Dupuis G, Fulop T (2012) Innate immunosenescence: effect of aging on cells and receptors of the innate immune system in humans. Semin Immunol 24:331–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2012.04.008
Tomihara K, Curiel TJ, Zhang B (2013) Optimization of immunotherapy in elderly cancer patients. Crit Rev Oncog 18:573–583
Townsley CA, Selby R, Siu LL (2005) Systematic review of barriers to the recruitment of older patients with cancer onto clinical trials. J Clin Oncol 23:3112–3124. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2005.00.141
Townsley CA, Chan KK, Pond GR, Marquez C, Siu LL, Straus SE (2006) Understanding the attitudes of the elderly towards enrolment into cancer clinical trials. BMC Cancer 6:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-6-34
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Drs. Takako Mouri, Yoichiro Hamamoto, Norimitsu Kasahara, Shinichi Ishihara, and Ichiro Naruse for their assistance in preparing this manuscript. We would like to thank Editage (http://www.editage.jp) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any financial or personal relationships with people or organizations that could inappropriately influence this work.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee, and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
The need for informed consent was waived by the institutional review boards of the participating institutions owing to the retrospective nature of the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imai, H., Wasamoto, S., Yamaguchi, O. et al. Efficacy and safety of first-line pembrolizumab monotherapy in elderly patients (aged ≥ 75 years) with non-small cell lung cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 146, 457–466 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-03072-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-03072-1