Abstract
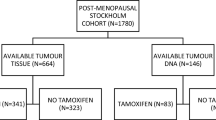
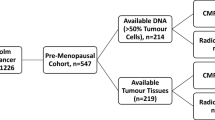
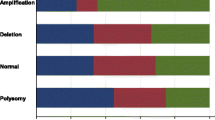
Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease and new clinical markers are needed to individualise disease management and therapy further. Alterations in the PI3K/AKT pathway, mainly PIK3CA mutations, have been shown frequently especially in the luminal breast cancer subtypes, suggesting a cross-talk between ER and PI3K/AKT. Aberrant PI3K/AKT signalling has been connected to poor response to anti-oestrogen therapies. In vitro studies have shown protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 2 (PTPN2) as a previously unknown negative regulator of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Here, we evaluate possible genomic alterations in the PTPN2 gene and its potential as a new prognostic and treatment predictive marker for endocrine therapy benefit in breast cancer. PTPN2 gene copy number was assessed by real-time PCR in 215 tumour samples from a treatment randomised study consisting of postmenopausal patients diagnosed with stage II breast cancer 1976–1990. Corresponding mRNA expression levels of PTPN2 were evaluated in 86 available samples by the same methodology. Gene copy loss of PTPN2 was detected in 16 % (34/215) of the tumours and this was significantly correlated with lower levels of PTPN2 mRNA. PTPN2 gene loss and lower mRNA levels were associated with activation of AKT and a poor prognosis. Furthermore, PTPN2 gene loss was a significant predictive marker of poor benefit from tamoxifen treatment. In conclusion, genomic loss of PTPN2 may be a previously unknown mechanism of PI3K/AKT upregulation in breast cancer. PTPN2 status is a potential new clinical marker of endocrine treatment benefit which could guide further individualised therapies in breast cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AKT:
-
v-AKT murine thymoma viral oncogene homologue
- APP:
-
Amyloid precursor protein
- BCS:
-
Breast cancer-specific survival
- CMF:
-
Cyclophosphamide-methotrexate-5-fluorouracil
- DRFS:
-
Distant recurrence-free survival
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- ER:
-
Oestrogen-receptor
- HER2:
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
- IR:
-
Insulin receptor
- JAK/STAT:
-
Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homologue
- PTPN2:
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 2
- RT:
-
Radiotherapy
References
Hers I, Vincent EE, Tavare JM (2011) Akt signalling in health and disease. Cell Signal 23(10):1515–1527. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.05.004
Fruman DA, Rommel C (2014) PI3K and cancer: lessons, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13(2):140–156. doi:10.1038/nrd4204
Miller TW, Rexer BN, Garrett JT, Arteaga CL (2011) Mutations in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway: role in tumor progression and therapeutic implications in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 13(6):224. doi:10.1186/bcr3039
Miller TW, Balko JM, Arteaga CL (2011) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 29(33):4452–4461. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.34.4879
Klingler-Hoffmann M, Fodero-Tavoletti MT, Mishima K, Narita Y, Cavenee WK, Furnari FB, Huang HJ, Tiganis T (2001) The protein tyrosine phosphatase TCPTP suppresses the tumorigenicity of glioblastoma cells expressing a mutant epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem 276(49):46313–46318. doi:10.1074/jbc.M106571200
Tiganis T, Kemp BE, Tonks NK (1999) The protein-tyrosine phosphatase TCPTP regulates epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent signaling. J Biol Chem 274(39):27768–27775
Climent J, Martinez-Climent JA, Blesa D, Garcia-Barchino MJ, Saez R, Sanchez-Izquierdo D, Azagra P, Lluch A, Garcia-Conde J (2002) Genomic loss of 18p predicts an adverse clinical outcome in patients with high-risk breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 8(12):3863–3869
Addou-Klouche L, Adelaide J, Finetti P, Cervera N, Ferrari A, Bekhouche I, Sircoulomb F, Sotiriou C, Viens P, Moulessehoul S, Bertucci F, Birnbaum D, Chaffanet M (2010) Loss, mutation and deregulation of L3MBTL4 in breast cancers. Mol Cancer 9:213. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-9-213
Rutqvist LE, Johansson H (2006) Long-term follow-up of the Stockholm randomized trials of postoperative radiation therapy versus adjuvant chemotherapy among ‘high risk’ pre- and postmenopausal breast cancer patients. Acta Oncol 45(5):517–527. doi:10.1080/02841860600702068
Rutqvist LE, Johansson H, Stockholm Breast Cancer Study G (2007) Long-term follow-up of the randomized Stockholm trial on adjuvant tamoxifen among postmenopausal patients with early stage breast cancer. Acta Oncol 46(2):133–145. doi:10.1080/02841860601034834
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, Clark GM, Statistics Subcommittee of NCIEWGoCD (2006) REporting recommendations for tumor MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK). Breast Cancer Res Treat 100(2):229–235. doi:10.1007/s10549-006-9242-8
Askmalm MS, Carstensen J, Nordenskjöld B, Olsson B, Rutqvist LE, Skoog L, Stål O (2004) Mutation and accumulation of p53 related to results of adjuvant therapy of postmenopausal breast cancer patients. Acta Oncol 43(3):235–244
Bieche I, Olivi M, Champeme MH, Vidaud D, Lidereau R, Vidaud M (1998) Novel approach to quantitative polymerase chain reaction using real-time detection: application to the detection of gene amplification in breast cancer. Int J Cancer 78(5):661–666
Karlsson E, Waltersson MA, Bostner J, Perez-Tenorio G, Olsson B, Hallbeck AL, Stål O (2011) High-resolution genomic analysis of the 11q13 amplicon in breast cancers identifies synergy with 8p12 amplification, involving the mTOR targets S6K2 and 4EBP1. Genes Chromosom Cancer 50(10):775–787. doi:10.1002/gcc.20900
Khoshnoud MR, Löfdahl B, Fohlin H, Fornander T, Stål O, Skoog L, Bergh J, Nordenskjöld B (2011) Immunohistochemistry compared to cytosol assays for determination of estrogen receptor and prediction of the long-term effect of adjuvant tamoxifen. Breast Cancer Res Treat 126(2):421–430. doi:10.1007/s10549-010-1202-7
Stål O, Sullivan S, Sun XF, Wingren S, Nordenskjöld B (1994) Simultaneous analysis of c-erbB-2 expression and DNA content in breast cancer using flow cytometry. Cytometry 16(2):160–168. doi:10.1002/cyto.990160210
Gunnarsson C, Ahnström M, Kirschner K, Olsson B, Nordenskjöld B, Rutqvist LE, Skoog L, Stål O (2003) Amplification of HSD17B1 and ERBB2 in primary breast cancer. Oncogene 22(1):34–40. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206078
Stål O, Sullivan S, Wingren S, Skoog L, Rutqvist LE, Carstensen JM, Nordenskjöld B (1995) c-erbB-2 expression and benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy of breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 31A(13–14):2185–2190
Perez-Tenorio G, Alkhori L, Olsson B, Waltersson MA, Nordenskjöld B, Rutqvist LE, Skoog L, Stål O (2007) PIK3CA mutations and PTEN loss correlate with similar prognostic factors and are not mutually exclusive in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13(12):3577–3584. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1609
Stål O, Perez-Tenorio G, Åkerberg L, Olsson B, Nordenskjöld B, Skoog L, Rutqvist LE (2003) Akt kinases in breast cancer and the results of adjuvant therapy. Breast Cancer Res 5(2):R37–R44
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ (2011) Strategies for subtypes–dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol 22(8):1736–1747. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdr304
Dube N, Tremblay ML (2005) Involvement of the small protein tyrosine phosphatases TC-PTP and PTP1B in signal transduction and diseases: from diabetes, obesity to cell cycle, and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1754(1–2):108–117. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2005.07.030
Cool DE, Tonks NK, Charbonneau H, Walsh KA, Fischer EH, Krebs EG (1989) cDNA isolated from a human T-cell library encodes a member of the protein-tyrosine-phosphatase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86(14):5257–5261
Johnson CV, Cool DE, Glaccum MB, Green N, Fischer EH, Bruskin A, Hill DE, Lawrence JB (1993) Isolation and mapping of human T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase sequences: localization of genes and pseudogenes discriminated using fluorescence hybridization with genomic versus cDNA probes. Genomics 16(3):619–629. doi:10.1006/geno.1993.1239
Sakaguchi AY, Sylvia VL, Martinez L, Smith EA, Han ES, Lalley PA, Shows TB, Choudhury GG (1992) Assignment of tyrosine-specific T-cell phosphatase to conserved syntenic groups on human chromosome 18 and mouse chromosome 18. Genomics 12(1):151–154
Bussieres-Marmen S, Hutchins AP, Schirbel A, Rebert N, Tiganis T, Fiocchi C, Miranda-Saavedra D, Tremblay ML (2014) Characterization of PTPN2 and its use as a biomarker. Methods 65(2):239–246. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.08.020
Galic S, Hauser C, Kahn BB, Haj FG, Neel BG, Tonks NK, Tiganis T (2005) Coordinated regulation of insulin signaling by the protein tyrosine phosphatases PTP1B and TCPTP. Mol Cell Biol 25(2):819–829. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.2.819-829.2005
Galic S, Klingler-Hoffmann M, Fodero-Tavoletti MT, Puryer MA, Meng TC, Tonks NK, Tiganis T (2003) Regulation of insulin receptor signaling by the protein tyrosine phosphatase TCPTP. Mol Cell Biol 23(6):2096–2108
Mattila E, Auvinen K, Salmi M, Ivaska J (2008) The protein tyrosine phosphatase TCPTP controls VEGFR2 signalling. J Cell Sci 121(Pt 21):3570–3580. doi:10.1242/jcs.031898
Omerovic J, Clague MJ, Prior IA (2010) Phosphatome profiling reveals PTPN2, PTPRJ and PTEN as potent negative regulators of PKB/Akt activation in Ras-mutated cancer cells. Biochem J 426(1):65–72. doi:10.1042/BJ20091413
Tiganis T, Bennett AM, Ravichandran KS, Tonks NK (1998) Epidermal growth factor receptor and the adaptor protein p52Shc are specific substrates of T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase. Mol Cell Biol 18(3):1622–1634
Scharl M, McCole DF, Weber A, Vavricka SR, Frei P, Kellermeier S, Pesch T, Fried M, Rogler G (2011) Protein tyrosine phosphatase N2 regulates TNFalpha-induced signalling and cytokine secretion in human intestinal epithelial cells. Gut 60(2):189–197. doi:10.1136/gut.2010.216606
Scharl M, Rudenko I, McCole DF (2010) Loss of protein tyrosine phosphatase N2 potentiates epidermal growth factor suppression of intestinal epithelial chloride secretion. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 299(4):G935–G945. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00106.2010
Tiganis T (2013) PTP1B and TCPTP–nonredundant phosphatases in insulin signaling and glucose homeostasis. FEBS J 280(2):445–458. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08563.x
Kittiniyom K, Gorse KM, Dalbegue F, Lichy JH, Taubenberger JK, Newsham IF (2001) Allelic loss on chromosome band 18p11.3 occurs early and reveals heterogeneity in breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer Res 3(3):192–198
Lee CF, Ling ZQ, Zhao T, Fang SH, Chang WC, Lee SC, Lee KR (2009) Genomic-wide analysis of lymphatic metastasis-associated genes in human hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 15(3):356–365
Kleppe M, Lahortiga I, El Chaar T, De Keersmaecker K, Mentens N, Graux C, Van Roosbroeck K, Ferrando AA, Langerak AW, Meijerink JP, Sigaux F, Haferlach T, Wlodarska I, Vandenberghe P, Soulier J, Cools J (2010) Deletion of the protein tyrosine phosphatase gene PTPN2 in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat Genet 42(6):530–535. doi:10.1038/ng.587
Kleppe M, Soulier J, Asnafi V, Mentens N, Hornakova T, Knoops L, Constantinescu S, Sigaux F, Meijerink JP, Vandenberghe P, Tartaglia M, Foa R, Macintyre E, Haferlach T, Cools J (2011) PTPN2 negatively regulates oncogenic JAK1 in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 117(26):7090–7098. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-10-314286
Kleppe M, Tousseyn T, Geissinger E, Kalender Atak Z, Aerts S, Rosenwald A, Wlodarska I, Cools J (2011) Mutation analysis of the tyrosine phosphatase PTPN2 in Hodgkin’s lymphoma and T-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Haematologica 96(11):1723–1727. doi:10.3324/haematol.2011.041921
Shields BJ, Court NW, Hauser C, Bukczynska PE, Tiganis T (2008) Cell cycle-dependent regulation of SFK, JAK1 and STAT3 signalling by the protein tyrosine phosphatase TCPTP. Cell Cycle 7(21):3405–3416
Shields BJ, Wiede F, Gurzov EN, Wee K, Hauser C, Zhu HJ, Molloy TJ, O’Toole SA, Daly RJ, Sutherland RL, Mitchell CA, McLean CA, Tiganis T (2013) TCPTP regulates SFK and STAT3 signaling and is lost in triple-negative breast cancers. Mol Cell Biol 33(3):557–570. doi:10.1128/MCB.01016-12
Beelen K, Zwart W, Linn SC (2012) Can predictive biomarkers in breast cancer guide adjuvant endocrine therapy? Nat Rev Clin Oncol 9(9):529–541. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2012.121
Droog M, Beelen K, Linn S, Zwart W (2013) Tamoxifen resistance: from bench to bedside. Eur J Pharmacol 717(1–3):47–57. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.11.071
Schiff R, Massarweh SA, Shou J, Bharwani L, Mohsin SK, Osborne CK (2004) Cross-talk between estrogen receptor and growth factor pathways as a molecular target for overcoming endocrine resistance. Clin Cancer Res 10(1 Pt 2):331S–336S
Beelen K, Opdam M, Severson TM, Koornstra RH, Vincent AD, Wesseling J, Muris JJ, Berns EM, Vermorken JB, van Diest PJ, Linn SC (2014) PIK3CA mutations, phosphatase and tensin homolog, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor and adjuvant tamoxifen resistance in postmenopausal breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res 16(1):R13. doi:10.1186/bcr3606
Beelen K, Opdam M, Severson TM, Koornstra RH, Vincent AD, Wesseling J, Muris JJ, Berns EM, Vermorken JB, van Diest PJ, Linn SC (2014) Phosphorylated p-70S6K predicts tamoxifen resistance in postmenopausal breast cancer patients randomized between adjuvant tamoxifen versus no systemic treatment. Breast Cancer Res 16(1):R6. doi:10.1186/bcr3598
Bostner J, Ahnström Waltersson M, Fornander T, Skoog L, Nordenskjöld B, Stål O (2007) Amplification of CCND1 and PAK1 as predictors of recurrence and tamoxifen resistance in postmenopausal breast cancer. Oncogene 26(49):6997–7005. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210506
Bostner J, Karlsson E, Pandiyan MJ, Westman H, Skoog L, Fornander T, Nordenskjöld B, Stål O (2013) Activation of Akt, mTOR, and the estrogen receptor as a signature to predict tamoxifen treatment benefit. Breast Cancer Res Treat 137(2):397–406. doi:10.1007/s10549-012-2376-y
Karlsson E, Perez-Tenorio G, Amin R, Bostner J, Skoog L, Fornander T, Sgroi DC, Nordenskjöld B, Hallbeck AL, Stål O (2013) The mTOR effectors 4EBP1 and S6K2 are frequently coexpressed, and associated with a poor prognosis and endocrine resistance in breast cancer: a retrospective study including patients from the randomised Stockholm tamoxifen trials. Breast Cancer Res 15(5):R96. doi:10.1186/bcr3557
Perez-Tenorio G, Stål O, Southeast Sweden Breast Cancer G (2002) Activation of AKT/PKB in breast cancer predicts a worse outcome among endocrine treated patients. Br J Cancer 86(4):540–545. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6600126
Mattila E, Marttila H, Sahlberg N, Kohonen P, Tahtinen S, Halonen P, Perala M, Ivaska J (2010) Inhibition of receptor tyrosine kinase signalling by small molecule agonist of T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase. BMC Cancer 10:7. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-10-7
Tiganis T (2002) Protein tyrosine phosphatases: dephosphorylating the epidermal growth factor receptor. IUBMB Life 53(1):3–14. doi:10.1080/15216540210811
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from The Swedish Cancer Society (#13 0435) and The Swedish Research Council (A0346701).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The experiments comply with the current laws of Sweden.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karlsson, E., Veenstra, C., Emin, S. et al. Loss of protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 2 is associated with activation of AKT and tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 153, 31–40 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3516-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3516-y