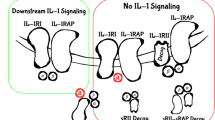
Abstract
While progress has been made in treating primary epithelial tumors, metastatic tumors remain largely incurable and still account for 85–90 % of all cancer-related deaths. Interleukin-4 (IL4), a Th2 cytokine, and the IL4/IL4 receptor (IL4R) interaction have well defined roles in the immune system. Yet, IL4 receptors are over-expressed by many epithelial cancers and could be a promising target for metastatic tumor therapy. The IL4/IL4R signaling axis is a strong promoter of pro-metastatic phenotypes in epithelial cancer cells including enhanced migration, invasion, survival, and proliferation. The promotion of breast cancer growth specifically is also supported in part by IL4-induced glutamine metabolism, and we have shown that IL4 is also capable of inducing glucose metabolism in breast cancer cells. Importantly, there are several types of FDA approved medications for use in asthma patients that inhibit the IL4/IL4R signaling axis. However, these approved medications inhibit both the type I IL4 receptor found on immune cells, and the type II IL4 receptor that is predominantly expressed by some non-hematopoietic cells including epithelial cancer cells. This article reviews existing therapies targeting IL4, IL4R, or IL4/IL4R signaling, and recent findings guiding the creation of novel therapies that specifically inhibit the type II IL4R, while taking into consideration effects on immune cells within the tumor microenvironment. Some of these therapies are currently in clinical trials for cancer patients, and may be exploitable for the treatment of metastatic disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FDA:
-
Food and Drug Administration (U.S.A.)
- γc:
-
Common gamma chain
- IL4:
-
Interleukin 4
- IL4R:
-
Interleukin 4 receptor
- JAK:
-
Janus kinase
- KO:
-
Knockout
- MDSC:
-
Myeloid-derived suppressor cell
- STAT:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription factor
- TAM:
-
Tumor-associated macrophage
- Th2:
-
T-helper type 2
- TME:
-
Tumor microenvironment
- Tc2:
-
Type 2 cytotoxic T cell
- IRS:
-
Insuling receptor substrate protein
- Tyk2:
-
Tyrosine kinase 2
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- AKT:
-
Protein kinase B
- PI3 K:
-
Phosphoinositide-3 kinase
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- pM:
-
Picomolar
- Kd:
-
Dissociation constant
- IL4-DM:
-
IL4 double mutein
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- CML:
-
Chronic myeloid leukemia
- AML:
-
Acute myeloid leukemia
- GBM:
-
Glioblastoma multiforme
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2015) Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 65:5–29. doi:10.3322/caac.21254
Hallett MA, Venmar KT, Fingleton B (2012) Cytokine stimulation of epithelial cancer cells: the similar and divergent functions of IL-4 and IL-13. Cancer Res 72:6338–6343. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3544
Li BH, Yang XZ, Li PD, Yuan Q, Liu XH, Yuan J, Zhang WJ (2008) IL-4/Stat6 activities correlate with apoptosis and metastasis in colon cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 369:554–560. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.02.052
DeNardo DG, Barreto JB, Andreu P, Vasquez L, Tawfik D, Kolhatkar N, Coussens LM (2009) CD4(+) T cells regulate pulmonary metastasis of mammary carcinomas by enhancing protumor properties of macrophages. Cancer Cell 16:91–102. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2009.06.018
Venmar KT, Kimmel DW, Cliffel DE, Fingleton B (2015) IL4 receptor α mediates enhanced glucose and glutamine metabolism to support breast cancer growth. Biochim Biophys Acta 1853:1219–1228. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.02.020
Venmar KT, Carter KJ, Hwang DG, Dozier EA, Fingleton B (2014) IL-4 receptor ILR4α regulates metastatic colonization by mammary tumors through multiple signaling pathways. Cancer Res. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0093
Dufort FJ, Bleiman BF, Gumina MR, Blair D, Wagner DJ, Roberts MF, Abu-Amer Y, Chiles TC (2007) Cutting edge: IL-4-mediated protection of primary B lymphocytes from apoptosis via Stat6-dependent regulation of glycolytic metabolism. J Immunol 179:4953–4957
Wang R, Green DR (2012) Metabolic checkpoints in activated T cells. Nat Immunol 13:907–915. doi:10.1038/ni.2386
Martinez FO, Sica A, Mantovani A, Locati M (2008) Macrophage activation and polarization. Front Biosci 13:453–461
Nelms K, Keegan AD, Zamorano J, Ryan JJ, Paul WE (1999) The IL-4 receptor: signaling mechanisms and biologic functions. Annu Rev Immunol 17:701–738. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.17.1.701
Gallina G, Dolcetti L, Serafini P, De Santo C, Marigo I, Colombo MP, Basso G, Brombacher F, Borrello I, Zanovello P, Bicciato S, Bronte V (2006) Tumors induce a subset of inflammatory monocytes with immunosuppressive activity on CD8+ T cells. J Clin Invest 116:2777–2790. doi:10.1172/JCI28828
Surana R, Wang S, Xu W, Jablonski SA, Weiner LM (2014) IL4 limits the efficacy of tumor-targeted antibody therapy in a murine model. Cancer Immunol Res 2:1103–1112. doi:10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-14-0103
Todaro M, Lombardo Y, Francipane MG, Alea MP, Cammareri P, Iovino F, Di Stefano AB, Di Bernardo C, Agrusa A, Condorelli G, Walczak H, Stassi G (2008) Apoptosis resistance in epithelial tumors is mediated by tumor-cell-derived interleukin-4. Cell Death Differ 15:762–772. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4402305
Mueller TD, Zhang J-L, Sebald W, Duschl A (2002) Structure, binding, and antagonists in the IL-4/IL-13 receptor system. Biochim Biophys Acta 1592:237–250
Kotsimbos TC, Ghaffar O, Minshall EM, Humbert M, Durham SR, Pfister R, Menz G, Kay AB, Hamid QA (1998) Expression of the IL-4 receptor alpha-subunit is increased in bronchial biopsy specimens from atopic and nonatopic asthmatic subjects. J Allergy Clin Immunol 102:859–866
Andrews R, Rosa L, Daines M, Khurana Hershey G (2001) Reconstitution of a functional human type II IL-4/IL-13 receptor in mouse B cells: demonstration of species specificity. J Immunol 166:1716–1722
Dubois GR, Schweizer RC, Versluis C, Bruijnzeel-Koomen CA, Bruijnzeel PL (1998) Human eosinophils constitutively express a functional interleukin-4 receptor: interleukin-4—induced priming of chemotactic responses and induction of PI-3 kinase activity. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 19:691–699. doi:10.1165/ajrcmb.19.4.3208
Doucet C, Brouty-Boyé D, Pottin-Clémenceau C, Canonica GW, Jasmin C, Azzarone B (1998) Interleukin (IL) 4 and IL-13 act on human lung fibroblasts. Implication in asthma. J Clin Invest 101:2129–2139. doi:10.1172/JCI741
Van der Velden VH, Naber BA, Wierenga-Wolf AF, Debets R, Savelkoul HF, Overbeek SE, Hoogsteden HC, Versnel MA (1998) Interleukin 4 receptors on human bronchial epithelial cells. An in vivo and in vitro analysis of expression and function. Cytokine 10:803–813. doi:10.1006/cyto.1998.0365
Siddiqui S, Mistry V, Doe C, Stinson S, Foster M, Brightling C (2010) Airway wall expression of OX40/OX40L and interleukin-4 in asthma. Chest 137:797–804. doi:10.1378/chest.09-1839
Ito T, Suzuki S, Kanaji S, Shiraishi H, Ohta S, Arima K, Tanaka G, Tamada T, Honjo E, Garcia KC, Kuroki R, Izuhara K (2009) Distinct structural requirements for interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-13 binding to the shared IL-13 receptor facilitate cellular tuning of cytokine responsiveness. J Biol Chem 284:24289–24296. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.007286
LaPorte SL, Juo ZS, Vaclavikova J, Colf LA, Qi X, Heller NM, Keegan AD, Garcia KC (2008) Molecular and structural basis of cytokine receptor pleiotropy in the interleukin-4/13 system. Cell 132:259–272. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.030
Obiri NI, Hillman GG, Haas GP, Sud S, Puri RK (1993) Expression of high affinity interleukin-4 receptors on human renal cell carcinoma cells and inhibition of tumor cell growth in vitro by interleukin-4. J Clin Invest 91:88–93. doi:10.1172/JCI116205
Obiri NI, Siegel JP, Varricchio F, Puri RK (1994) Expression of high-affinity IL-4 receptors on human melanoma, ovarian and breast carcinoma cells. Clin Exp Immunol 95:148–155
Leland P, Taguchi J, Husain SR, Kreitman RJ, Pastan I, Puri RK (2000) Human breast carcinoma cells express type II IL-4 receptors and are sensitive to antitumor activity of a chimeric IL-4-Pseudomonas exotoxin fusion protein in vitro and in vivo. Mol Med 6:165–178
Kioi M, Takahashi S, Kawakami M, Kawakami K, Kreitman RJ, Puri RK (2005) Expression and targeting of interleukin-4 receptor for primary and advanced ovarian cancer therapy. Cancer Res 65:8388–8396. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1043
Puri RK, Leland P, Kreitman RJ, Pastan I (1994) Human neurological cancer cells express interleukin-4 (IL-4) receptors which are targets for the toxic effects of IL4-Pseudomonas exotoxin chimeric protein. Int J Cancer 58:574–581
Husain SR, Gill P, Kreitman RJ, Pastan I, Puri RK (1997) Interleukin-4 receptor expression on AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma cells and their targeting by a chimeric protein comprised of circularly permuted interleukin-4 and Pseudomonas exotoxin. Mol Med 3:327–338
Kawakami K, Leland P, Puri RK (2000) Structure, function, and targeting of interleukin 4 receptors on human head and neck cancer cells. Cancer Res 60:2981–2987
Clinicaltrials.gov (2015) https://clinicaltrials.gov. Accessed June 5, 2015
Kasaian MT, Miller DK (2008) IL-13 as a therapeutic target for respiratory disease. Biochem Pharmacol 76:147–155. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2008.04.002
Conticello C, Pedini F, Zeuner A, Patti M, Zerilli M, Stassi G, Messina A, Peschle C, De Maria R (2004) IL-4 protects tumor cells from anti-CD95 and chemotherapeutic agents via up-regulation of antiapoptotic proteins. J Immunol 172:5467–5477
Roca H, Craig MJ, Ying C, Varsos ZS, Czarnieski P, Alva AS, Hernandez J, Fuller D, Daignault S, Healy PN, Pienta KJ (2011) IL-4 induces proliferation in prostate cancer PC3 cells under nutrient-depletion stress through the activation of the JNK-pathway and survivin upregulation. J Cell Biochem 113:1569–1580. doi:10.1002/jcb.24025
Prokopchuk O, Liu Y, Henne-Bruns D, Kornmann M (2005) Interleukin-4 enhances proliferation of human pancreatic cancer cells: evidence for autocrine and paracrine actions. Br J Cancer 92:921–928. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602416
Maes T, Joos GF, Brusselle GG (2012) Targeting interleukin-4 in asthma: lost in translation? Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 47:261–270. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2012-0080TR
Kuperman DA, Schleimer RP (2008) Interleukin-4, interleukin-13, signal transducer and activator of transcription factor 6, and allergic asthma. Curr Mol Med 8:384–392
Oh CK, Geba GP, Molfino N (2010) Investigational therapeutics targeting the IL-4/IL-13/STAT-6 pathway for the treatment of asthma. Eur Respir Rev 19:46–54. doi:10.1183/09059180.00007609
Murata T, Noguchi PD, Puri RK (1995) Receptors for interleukin (IL)-4 do not associate with the common chain, and IL-4 induces the phosphorylation of JAK2 tyrosine kinase in human colon carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 270:30829–30836. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.51.30829
Delgoffe GM, Kole TP, Zheng Y, Zarek PE, Matthews KL, Xiao B, Worley PF, Kozma SC, Powell JD (2009) The mTOR kinase differentially regulates effector and regulatory T cell lineage commitment. Immunity 30:832–844. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2009.04.014
Miklossy G, Hilliard TS, Turkson J (2013) Therapeutic modulators of STAT signalling for human diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:611–629. doi:10.1038/nrd4088
Aaronson DS, Horvath CM (2002) A road map for those who don’t know JAK-STAT. Science 296:1653–1655. doi:10.1126/science.1071545
Li BH, Yang XZ, Li PD, Yuan Q, Liu XH, Yuan J, Zhang WJ (2008) IL-4/Stat6 activities correlate with apoptosis and metastasis in colon cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 369:554–560. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.02.052
Siemasko KF, Chong AS, Williams JW, Bremer EG, Finnegan A (1996) Regulation of B cell function by the immunosuppressive agent leflunomide. Transplantation 61:635–642
Cherwinski HM, Byars N, Ballaron SJ, Nakano GM, Young JM, Ransom JT (1995) Leflunomide interferes with pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis. Inflamm Res 44:317–322
Mattar T, Kochhar K, Bartlett R, Bremer EG, Finnegan A (1993) Inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase activity by leflunomide. FEBS Lett 334:161–164
Friedman Ohana R, Kirkland TA, Woodroofe CC, Levin S, Uyeda HT, Otto P, Hurst R, Robers MB, Zimmerman K, Encell LP, Wood KV (2015) Deciphering the cellular targets of bioactive compounds using a chloroalkane capture tag. ACS Chem Biol. doi:10.1021/acschembio.5b00351
Gibeon D, Menzies-Gow AN (2012) Targeting interleukins to treat severe asthma. Expert Rev Respir Med 6:423–439. doi:10.1586/ers.12.38
Ohara J, Paul WE (1985) Production of a monoclonal antibody to and molecular characterization of B-cell stimulatory factor-1. Nature 315:333–336
Umansky V, Sevko A (2013) Tumor microenvironment and myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cancer Microenviron 6:169–177. doi:10.1007/s12307-012-0126-7
Leen AM, Sukumaran S, Watanabe N, Mohammed S, Keirnan J, Yanagisawa R, Anurathapan U, Rendon D, Heslop HE, Rooney CM, Brenner MK, Vera JF (2014) Reversal of tumor immune inhibition using a chimeric cytokine receptor. Mol Ther 22:1211–1220. doi:10.1038/mt.2014.47
Wang H-W, Joyce JA (2010) Alternative activation of tumor-associated macrophages by IL-4: priming for protumoral functions. Cell Cycle 9:4824–4835
Qian B-Z, Pollard JW (2010) Macrophage diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell 141:39–51. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.014
Roth F, De La Fuente AC, Vella JL, Zoso A, Inverardi L, Serafini P (2012) Aptamer-mediated blockade of IL4Rα triggers apoptosis of MDSCs and limits tumor progression. Cancer Res 72:1373–1383. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2772
Beck LA, Thaçi D, Hamilton JD, Graham NM, Bieber T, Rocklin R, Ming JE, Ren H, Kao R, Simpson E, Ardeleanu M, Weinstein SP, Pirozzi G, Guttman-Yassky E, Suárez-Fariñas M, Hager MD, Stahl N, Yancopoulos GD, Radin AR (2014) Dupilumab treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med 371:130–139. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1314768
Wenzel S, Ford L, Pearlman D, Spector S, Sher L, Skobieranda F, Wang L, Kirkesseli S, Rocklin R, Bock B, Hamilton J, Ming JE, Radin A, Stahl N, Yancopoulos GD, Graham N, Pirozzi G (2013) Dupilumab in persistent asthma with elevated eosinophil levels. N Engl J Med 368:2455–2466. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1304048
Duppatla V, Gjorgjevikj M, Schmitz W, Hermanns HM, Schäfer CM, Kottmair M, Müller T, Sebald W (2014) IL-4 analogues with site-specific chemical modification at position 121 inhibit IL-4 and IL-13 biological activities. Bioconjugate Chem 25:52–62. doi:10.1021/bc400307k
Todaro M, Alea MP, Di Stefano AB, Cammareri P, Vermeulen L, Iovino F, Tripodo C, Russo A, Gulotta G, Medema JP, Stassi G (2007) Colon cancer stem cells dictate tumor growth and resist cell death by production of interleukin-4. Cell Stem Cell 1:389–402. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2007.08.001
Gandhi H, Worch R, Kurgonaite K, Hintersteiner M, Schwille P, Bökel C, Weidemann T (2014) Dynamics and interaction of interleukin-4 receptor subunits in living cells. Biophys J 107:2515–2527. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2014.07.077
Kruse N, Tony HP, Sebald W (1992) Conversion of human interleukin-4 into a high affinity antagonist by a single amino acid replacement. EMBO J 11:3237–3244
Kruse N, Tony HP, Sebald W (1992) Conversion of human interleukin-4 into a high affinity antagonist by a single amino acid replacement. EMBO J 11:3237–3244
Zhang J-L, Buehner M, Sebald W (2002) Functional epitope of common gamma chain for interleukin-4 binding. Eur J Biochem 269:1490–1499
Junttila IS, Creusot RJ, Moraga I, Bates DL, Wong MT, Alonso MN, Suhoski MM, Lupardus P, Meier-Schellersheim M, Engleman EG, Utz PJ, Fathman CG, Paul WE, Garcia KC (2012) Redirecting cell-type specific cytokine responses with engineered interleukin-4 superkines. Nat Chem Biol 8:990–998. doi:10.1038/nchembio.1096
Medicenna Therapeutics Inc. https://medicenna.com. Accessed June 5, 2015
Kienzle N, Olver S, Buttigieg K, Groves P, Janas ML, Baz A, Kelso A (2005) Progressive differentiation and commitment of CD8+ T cells to a poorly cytolytic CD8 low phenotype in the presence of IL-4. J Immunol 174:2021–2029
Kienzle N, Buttigieg K, Groves P, Kawula T, Kelso A (2002) A clonal culture system demonstrates that IL-4 induces a subpopulation of noncytolytic T cells with low CD8, perforin, and granzyme expression. J Immunol 168:1672–1681
Helmich BK, Dutton RW (2001) The role of adoptively transferred CD8 T cells and host cells in the control of the growth of the EG7 thymoma: factors that determine the relative effectiveness and homing properties of Tc1 and Tc2 effectors. J Immunol 166:6500–6508
Kemp RA, Ronchese F (2001) Tumor-specific Tc1, but not Tc2, cells deliver protective antitumor immunity. J Immunol 167:6497–6502
Yang L, DeBusk LM, Fukuda K, Fingleton B, Green-Jarvis B, Shyr Y, Matrisian LM, Carbone DP, Lin PC (2004) Expansion of myeloid immune suppressor Gr + CD11b + cells in tumor-bearing host directly promotes tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 6:409–421. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2004.08.031
Van Kempen LCL, Coussens LM (2002) MMP9 potentiates pulmonary metastasis formation. Cancer Cell 2:251–252
Gabrilovich DI, Nagaraj S (2009) Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 9:162–174. doi:10.1038/nri2506
Pollard JW (2004) Tumour-educated macrophages promote tumour progression and metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 4:71–78. doi:10.1038/nrc1256
Srabovici N, Mujagic Z, Mujanovic-Mustedanagic J, Muminovic Z, Softic A, Begic L (2011) Interleukin 13 expression in the primary breast cancer tumour tissue. Biochem medica 21:131–138
Gabitass RF, Annels NE, Stocken DD, Pandha HA, Middleton GW (2011) Elevated myeloid-derived suppressor cells in pancreatic, esophageal and gastric cancer are an independent prognostic factor and are associated with significant elevation of the Th2 cytokine interleukin-13. Cancer Immunol Immunother 60:1419–1430. doi:10.1007/s00262-011-1028-0
Ostojic A, Vrhovac R, Verstovsek S (2011) Ruxolitinib: a new JAK1/2 inhibitor that offers promising options for treatment of myelofibrosis. Future Oncol 7:1035–1043. doi:10.2217/fon.11.81
Borish LC, Nelson HS, Lanz MJ, Claussen L, Whitmore JB, Agosti JM, Garrison L (1999) Interleukin-4 receptor in moderate atopic asthma. A phase I/II randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 160:1816–1823. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.160.6.9808146
Hart TK, Blackburn MN, Brigham-Burke M, Dede K, Al-Mahdi N, Zia-Amirhosseini P, Cook RM (2002) Preclinical efficacy and safety of pascolizumab (SB 240683): a humanized anti-interleukin-4 antibody with therapeutic potential in asthma. Clin Exp Immunol 130:93–100
Acknowledgments
This work was supported R01 CA157781 awarded to BF, and by F31 CA183539 awarded to KVB. Both awards were made by the U.S. National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
No conflicts of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bankaitis, K.V., Fingleton, B. Targeting IL4/IL4R for the treatment of epithelial cancer metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 32, 847–856 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-015-9747-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-015-9747-9