Abstract
Background and Objective
Synthetic TLR7 agonists have been proposed as oral replacements for interferonα (IFNα) therapy in the treatment of hepatitis C virus infection. However, adverse effects, such as lymphopenia and cardiovascular irregularities, have been observed in the clinical following treatment with TLR7 agonists. We wished to understand and characterise the relationship between TLR7 agonism and adverse effects.
Methods
We compared responses to two prototypic TLR7 agonists (Resiquimod: R-848; and PF-04878691) in a mouse model and compared the responses to treatment with IFNα. We measured clinically relevant adverse effects such as lymphopenia and cardiovascular irregularities and related them to plasma drug levels and clinically relevant efficacy biomarkers such as the pro-inflammatory cytokine IP-10, 2’5’OAS and TLR7 receptor expression.
Results
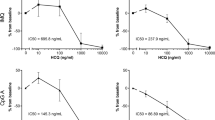
By 2 h post dose all agents had induced a dose-dependent transient lymphopenia. IFNα increased heart rate immediately following dosing, persisting for 5 h, whilst PF-04878691 induced significant reductions in blood pressure. Lymphopenia co-incided with maximum plasma drug levels, raised levels of IP-10 and the auto-induction of TLR7 expression in the blood and lymph nodes. Peak levels of 2’5’OAS occurred at 24 h post-dose and only at doses which also induced lymphopenia.
Conclusions
We conclude that systemic delivery of TLR7 agonists or IFNα induces similar exaggerated pharmacology, consistent with there being a narrow therapeutic window between efficacy and safety. This clinically validated mouse model will help to investigate whether more potent agonists or optimised dosing schedules, will be successful strategies for targeting TLR7 in patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lavanchy D. The global burden of hepatitis C. Liver Int. 2009;29 Suppl 1:74–81.
Thimme R, Lohmann V, Weber F. A target on the move: innate and adaptive immune escape strategies of hepatitis C virus. Antiviral Res. 2006;69(3):129–41.
Keller BC, Johnson CL, Erickson AK, Gale Jr M. Innate immune evasion by hepatitis C virus and West Nile virus. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007;18(5–6):535–44.
Burke KP, Cox AL. Hepatitis C virus evasion of adaptive immune responses: a model for viral persistence. Immunol Res. 2010;47(1–3):216–27. doi:10.1007/s12026-009-8152-3.
Tsubota A, Fujise K, Namiki Y, Tada N. Peginterferon and ribavirin treatment for hepatitis C virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 17(4):419–32.
Manns MP, Wedemeyer H, Cornberg M. Treating viral hepatitis C: efficacy, side effects, and complications. Gut. 2006;55(9):1350–9.
Diebold SS, Kaisho T, Hemmi H, Akira S, Reis e Sousa C. Innate antiviral responses by means of TLR7-mediated recognition of single-stranded RNA. Science. 2004;303(5663):1529–31. doi:10.1126/science.1093616.
Kawai T, Akira S. Innate immune recognition of viral infection. Nat Immunol. 2006;7(2):131–7.
Pockros PJ, Guyader D, Patton H, Tong MJ, Wright T, McHutchison JG, Meng TC. Oral resiquimod in chronic HCV infection: safety and efficacy in 2 placebo-controlled, double-blind phase IIa studies. J Hepatol. 2007;47(2):174–82.
Horsmans Y, Berg T, Desager JP, Mueller T, Schott E, Fletcher SP, Steffy KR, Bauman LA, Kerr BM, Averett DR. Isatoribine, an agonist of TLR7, reduces plasma virus concentration in chronic hepatitis C infection. Hepatology. 2005;42(3):724–31.
Xiang AX, Webber SE, Kerr BM, Rueden EJ, Lennox JR, Haley GJ, Wang T, Ng JS, Herbert MR, Clark DL, Banh VN, Li W, Fletcher SP, Steffy KR, Bartkowski DM, Kirkovsky LI, Bauman LA, Averett DR. Discovery of ANA975: an oral prodrug of the TLR-7 agonist isatoribine. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2007;26(6–7):635–40.
Thomas A, Laxton C, Rodman J, Myangar N, Horscroft N, Parkinson T. Investigating Toll-like receptor agonists for potential to treat hepatitis C virus infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007;51(8):2969–78.
Fletcher S, Steffy K, Averett D. Masked oral prodrugs of toll-like receptor 7 agonists: a new approach for the treatment of infectious disease. Curr Opin Invest Drugs (Thomson Sci). 2006;7(8):702–8.
Averett D. ANA975, An orally administered TLR7 immunotherapeutic under evaluation for treatment of chronic HCV infection SRI Hepatitis conference, March 12th, 2007. 2007.
Harrison LI, Astry C, Kumar S, Yunis C. Pharmacokinetics of 852A, an imidazoquinoline Toll-like receptor 7-specific agonist, following intravenous, subcutaneous, and oral administrations in humans. J Clin Pharmacol. 2007;47(8):962–9.
Dudek AZ, Yunis C, Harrison LI, Kumar S, Hawkinson R, Cooley S, Vasilakos JP, Gorski KS, Miller JS. First in human phase I trial of 852A, a novel systemic toll-like receptor 7 agonist, to activate innate immune responses in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(23):7119–25.
Dummer R, Hauschild A, Becker JC, Grob JJ, Schadendorf D, Tebbs V, Skalsky J, Kaehler KC, Moosbauer S, Clark R, Meng TC, Urosevic M. An exploratory study of systemic administration of the toll-like receptor-7 agonist 852A in patients with refractory metastatic melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(3):856–64.
Geller MA, Cooley S, Argenta PA, Downs LS, Carson LF, Judson PL, Ghebre R, Weigel B, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Curtsinger J, Miller JS. Toll-like receptor-7 agonist administered subcutaneously in a prolonged dosing schedule in heavily pretreated recurrent breast, ovarian, and cervix cancers. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2010;59(12):1877–84.
Fidock MD, Souberbielle BE, Laxton C, Rawal J, Delpuech-Adams O, Corey TP, Colman P, Kumar V, Cheng JB, Wright K, Srinivasan S, Rana K, Craig C, Horscroft N, Perros M, Westby M, Webster R, van der Ryst E. The innate immune response, clinical outcomes, and ex vivo HCV antiviral efficacy of a TLR7 agonist (PF-4878691). Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2011;89(60):821–9.
Kamphuis E, Junt T, Waibler Z, Forster R, Kalinke U. Type I interferons directly regulate lymphocyte recirculation and cause transient blood lymphopenia. Blood. 2006;108(10):3253–61.
Gunzer M, Riemann H, Basoglu Y, Hillmer A, Weishaupt C, Balkow S, Benninghoff B, Ernst B, Steinert M, Scholzen T, Sunderkotter C, Grabbe S. Systemic administration of a TLR7 ligand leads to transient immune incompetence due to peripheral-blood leukocyte depletion. Blood. 2005;106(7):2424–32.
Inglefield JR, Dumitru CD, Alkan SS, Gibson SJ, Lipson KE, Tomai MA, Larson CJ, Vasilakos JP. TLR7 agonist 852A inhibition of tumor cell proliferation is dependent on plasmacytoid dendritic cells and type I IFN. Journal of interferon & cytokine research: the official journal of the International Society for Interferon and Cytokine Research. 2008;28(4):253–63. doi:10.1089/jir.2007.0097.
Baenziger S, Heikenwalder M, Johansen P, Schlaepfer E, Hofer U, Miller RC, Diemand S, Honda K, Kundig TM, Aguzzi A, Speck RF. Triggering TLR7 in mice induces immune activation and lymphoid system disruption, resembling HIV-mediated pathology. Blood. 2009;113(2):377–88.
Soza A, Everhart JE, Ghany MG, Doo E, Heller T, Promrat K, Park Y, Liang TJ, Hoofnagle JH. Neutropenia during combination therapy of interferon alfa and ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2002;36(5):1273–9.
Haining WN, Davies J, Kanzler H, Drury L, Brenn T, Evans J, Angelosanto J, Rivoli S, Russell K, George S, Sims P, Neuberg D, Li X, Kutok J, Morgan J, Wen P, Demetri G, Coffman RL, Nadler LM. CpG oligodeoxynucleotides alter lymphocyte and dendritic cell trafficking in humans. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(17):5626–34.
Cao W, Bover L, Cho M, Wen X, Hanabuchi S, Bao M, Rosen DB, Wang YH, Shaw JL, Du Q, Li C, Arai N, Yao Z, Lanier LL, Liu YJ. Regulation of TLR7/9 responses in plasmacytoid dendritic cells by BST2 and ILT7 receptor interaction. J Exp Med. 2009;206(7):1603–14.
Fukuhara M, Matsumura K, Ohmori S, Yanai T, Tsubota Y, Abe I, Fujishima M. Effects of interferon on circadian changes in blood pressure and heart rate variability in patients with chronic hepatitis. Am J Hypertens. 1999;12(5):519–23.
Shah I, Band J, Samson M, Young J, Robinson R, Bailey B, Lerner AM, Prasad AS. Pharmacokinetics and tolerance of intravenous and intramuscular recombinant alpha 2 interferon in patients with malignancies. Am J Hematol. 1984;17(4):363–71.
Birmachu W, Gleason RM, Bulbulian BJ, Riter CL, Vasilakos JP, Lipson KE, Nikolsky Y. Transcriptional networks in plasmacytoid dendritic cells stimulated with synthetic TLR 7 agonists. BMC Immunol. 2007;8:26.
Lee J, Wu CC, Lee KJ, Chuang TH, Katakura K, Liu YT, Chan M, Tawatao R, Chung M, Shen C, Cottam HB, Lai MM, Raz E, Carson DA. Activation of anti-hepatitis C virus responses via Toll-like receptor 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(6):1828–33.
Chang S, Kodys K, Szabo G. Impaired expression and function of toll-like receptor 7 in hepatitis C virus infection in human hepatoma cells. Hepatology 51(1):35–42.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr Rob Webster and Dr Bernard Souberbielle for helpful discussions. This work was wholly funded by Pfizer Global Research and Development.
Disclosure of Conflict of Interest
All authors are or were fulltime employees of Pfizer Global Research and Development.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hannah Perkins and Tansi Khodai Contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perkins, H., Khodai, T., Mechiche, H. et al. Therapy with TLR7 Agonists Induces Lymphopenia: Correlating Pharmacology to Mechanism in a Mouse Model. J Clin Immunol 32, 1082–1092 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-012-9687-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-012-9687-y