Abstract
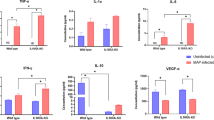
The pathogenesis of tuberculosis-causing Mycobacterium bovis is largely due to its ability to enter and survive in alveolar macrophages. Its mechanism of entry, mediated by proteins encoded by mammalian cell entry (mce) genes, is important for its pathogenesis. Here we focussed on the role of the Mce4A protein in the pathogenesis of M. bovis in cattle. Cell livability decreased in a dosage-dependent manner when Mce4A proteins were used to stimulate alveolar macrophages, which suggested that the recombinant Mce4A protein significantly inhibited alveolar macrophage activity. To test whether Mce4A modulates the gene expression profile of alveolar macrophages, alveolar macrophages were stimulated by Mce4A protein and other proteins/ligands (such as MtbPPD, MbPPD, and BCG), followed by real-time RT-PCR assay for the mRNA expression level of TNF-α, iNOS, IL-6, and IL-12. The results showed that the expression of TNF-α, iNOS, and IL-6 in alveolar macrophages was up-regulated by stimulation with the recombinant Mce4A protein of M. bovis; in contrast, expression of IL-12 was unaffected. MbPPD and BCG up-regulated the mRNA expression of TNF-α, iNOS, IL-6, and IL-12 (P < 0.05), whereas MtbPPD stimulated the mRNA expression of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-12 with no effect on iNOS. This study suggests that Mce4A proteins may induce the body’s inflammation response to M. bovis and therefore may play an important role in the immune response.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raviglione MC (2003) The TB epidemic from 1992 to 2002. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 83:4–14
Kidane D, Olobo JO, Habte A, Negesse Y, Aseffa A, Abate G, Yassin MA, Bereda K, Harboe M (2002) Identification of the causative organism of tuberculous lymphadenitis in ethiopia by PCR. J Clin Microbiol 40:4230–4234
Grange JM (2001) Mycobacterium bovis infection in human beings. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 81:71–77
Liu SG, Wang CL, Zhang XH, Guo SP, Guo Y, Shao ML (2005) Epidemiology and ecology of bovine tuberculosis. China Anim Husb Vet Med 32:60–62
Aderem A, Underhill DM (1999) Mechanisms of phagocytosis in macrophages. Annu Rev Immunol 17:593–623
Tiruviluamala PRL (2002) Tuberculosis. Annu Rev Public Health 2002 23:403–426
Arruda S, Bomfim G, Knights R, Huima-Byron T, Riley LW (1993) Cloning of an M. tuberculosis DNA fragment associated with entry and survival inside cells. Science 261:1454–1457
Flesselles B, Anand NN, Remani J, Loosmore SM, Klein MH (1999) Disruption of the mycobacterial cell entry gene of Mycobacterium bovis BCG results in a mutant that exhibits a reduced invasiveness for epithelial cells. FEMS Microbiol Lett 177:237–242
Cole ST, Brosch R, Parkhill J, Garnier T, Churcher C, Harris D, Gordon SV, Eiglmeier K, Gas S, Barry CE III, Tekaia F, Badcock K, Basham D, Brown D, Chillingworth T, Connor R, Davies R, Devlin K, Feltwell T, Gentles S, Hamlin N, Holroyd S, Hornsby T, Jagels K, Krogh A, McLean J, Moule S, Murphy L, Oliver K, Osborne J, Quail MA, Rajandream MA, Rogers J, Rutter S, Seeger K, Skelton J, Squares R, Squares S, Sulston JE, Taylor K, Whitehead S, Barrell BG (1998) Deciphering the biology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the complete genome sequence. Nature 393:537–544
Gioffre A, Infante E, Aguilar D, De la Paz Santangelo M, Klepp L, Amadio A, Meikle V, Etchechoury I, Romano MI, Cataldi A, Hernandez RP, Bigi F (2005) Mutation in mce operons attenuates Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence. Microbes Infect 7:325–334
Graham JE, Clark-Curtiss JE (1999) Identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis RNAs synthesized in response to phagocytosis by human macrophages by selective capture of transcribed sequences (SCOTS). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:11554–11559
Kumar A, Chandolia A, Chaudhry U, Brahmachari V, Bose M (2005) Comparison of mammalian cell entry operons of mycobacteria: in silico analysis and expression profiling. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 43:185–195
Kumar A, Bose M, Brahmachari V (2003) Analysis of expression profile of mammalian cell entry (mce) operons of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun 71:6083–6087
Harboe M, Christensen A, Haile Y, Ulvund G, Ahmad S, Mustafa AS, Wiker HG (1999) Demonstration of expression of six proteins of the mammalian cell entry (mce1) operon of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by anti-peptide antibodies, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Scand J Immunol 50:519–527
Ahmad S, El-Shazly S, Mustafa AS, Al-Attiyah R (2004) Mammalian cell-entry proteins encoded by the mce3 operon of Mycobacterium tuberculosis are expressed during natural infection in humans. Scand J Immunol 60:382–391
Brosch R, Gordon SV, Marmiesse M, Brodin P, Buchrieser C, Eiglmeier K, Garnier T, Gutierrez C, Hewinson G, Kremer K, Parsons LM, Pym AS, Samper S, van Soolingen D, Cole ST (2002) A new evolutionary scenario for the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:3684–3689
Zumarraga M, Bigi F, Alito A, Romano MI, Cataldi A (1999) A 12.7 kb fragment of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis genome is not present in Mycobacterium bovis. Microbiology 145(Pt 4): 893–897
van Embden JD, Cave MD, Crawford JT, Dale JW, Eisenach KD, Gicquel B, Hermans P, Martin C, McAdam R, Shinnick TM (1993) Strain identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by DNA fingerprinting: recommendations for a standardized methodology. J Clin Microbiol 31:406–409
Ning ZY, Zhao DM, Liu HX, Yang JM, Han CX, Cui YL, Meng LP, Wu CD, Liu ML, Zhang TX (2005) Altered expression of the prion gene in rat astrocyte and neuron cultures treated with prion Peptide 106–126. Cell Mol Neurobiol 25:1171–1183
Chen M, Gan H, Remold HG (2006) A mechanism of virulence: virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain H37Rv, but not attenuated H37Ra, causes significant mitochondrial inner membrane disruption in macrophages leading to necrosis. J Immunol 176:3707–3716
Keane J, Remold HG, Kornfeld H (2000) Virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains evade apoptosis of infected alveolar macrophages. J Immunol 164:2016–2020
Sedgwick JD, Riminton DS, Cyster JG, Korner H (2000) Tumor necrosis factor: a master-regulator of leukocyte movement. Immunol Today 21:110–113
Roach DR, Briscoe H, Baumgart K, Rathjen DA, Britton WJ (1999) Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and a TNF-mimetic peptide modulate the granulomatous response to Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection in vivo. Infect Immun 67:5473–5476
McDermott MF (2001) TNF and TNFR biology in health and disease. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 47:619–635
Kaneko H, Yamada H, Mizuno S, Udagawa T, Kazumi Y, Sekikawa K, Sugawara I (1999) Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in Mycobacterium-induced granuloma formation in tumor necrosis factor-alpha-deficient mice. Lab Invest 79:379–386
Shimono N, Morici L, Casali N, Cantrell S, Sidders B, Ehrt S, Riley LW (2003) Hypervirulent mutant of Mycobacterium tuberculosis resulting from disruption of the mce1 operon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:15918–15923
Xue LJ, Cao MM, Luan J, Ren H, Pan X, Cao J, Qi ZT (2007) Mammalian cell entry protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces the proinflammatory response in RAW 264.7 murine macrophage-like cells. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 87(3):185–192
Moncada S, Palmer RM, Higgs EA (1991) Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev 43:109–142
Sherman MP, Ganz T (1992) Host defense in pulmonary alveoli. Annu Rev Physiol 54:331–350
Liew FY, Cox FE (1991) Nonspecific defence mechanism: the role of nitric oxide. Immunol Today 12:A17–A21
Nathan C (1992) Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. Faseb J 6:3051–3054
Nathan CF, Hibbs JB Jr. (1991) Role of nitric oxide synthesis in macrophage antimicrobial activity. Curr Opin Immunol 3:65–70
Van Snick J, Vink A, Cayphas S, Uyttenhove C (1987) Interleukin-HP1, a T cell-derived hybridoma growth factor that supports the in vitro growth of murine plasmacytomas. J Exp Med 165:641–649
Hirano T, Taga T, Nakano N, Yasukawa K, Kashiwamura S, Shimizu K, Nakajima K, Pyun KH, Kishimoto T (1985) Purification to homogeneity and characterization of human B-cell differentiation factor (BCDF or BSFp-2). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 82:5490–5494
Corbel C, Melchers F (1984) The synergism of accessory cells and of soluble alpha-factors derived from them in the activation of B cells to proliferation. Immunol Rev 78:51–74
Weissenbach J, Chernajovsky Y, Zeevi M, Shulman L, Soreq H, Nir U, Wallach D, Perricaudet M, Tiollais P, Revel M (1980) Two interferon mRNAs in human fibroblasts: in vitro translation and Escherichia coli cloning studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 77:7152–7156
Leal IS, Smedegard B, Andersen P, Appelberg R (1999) Interleukin-6 and interleukin-12 participate in induction of a type 1 protective T-cell response during vaccination with a tuberculosis subunit vaccine. Infect Immun 67:5747–5754
Pasare C, Medzhitov R (2003) Toll pathway-dependent blockade of CD4 + CD25 + T cell-mediated suppression by dendritic cells. Science 299:1033–1036
Aldwell FE, Wedlock DN, Buddle BM (1996) Bacterial metabolism, cytokine mRNA transcription and viability of bovine alveolar macrophages infected with Mycobacterium bovis BCG or virulent M. bovis. Immunol Cell Biol 74:45–51
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Mao at China Institute of Veterinary Drug Control and Dr. Wan at Chinese center for disease control and prevention for support PPD and M. bovis. This work was supported by the 973 Project [No. 2005CB523000), and Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 30500371, Project No. 30571399).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, G., Li, Y., Yang, J. et al. Effect of recombinant Mce4A protein of Mycobacterium bovis on expression of TNF-α, iNOS, IL-6, and IL-12 in bovine alveolar macrophages. Mol Cell Biochem 302, 1–7 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9395-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9395-0