Abstract
Background
Predictive factors that can be routinely used in clinical practice are critically needed for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC).
Objective
To comprehensively analyze the predictive impact of peripheral blood markers and C-reactive protein (CRP) in nivolumab therapy for mRCC.
Methods
Fifty-eight patients were retrospectively evaluated. We evaluated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio (MLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), absolute eosinophil count (AEC), and absolute monocyte count (AMC) as peripheral blood markers as well as serum CRP levels. The primary endpoints were progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) after nivolumab initiation.
Results
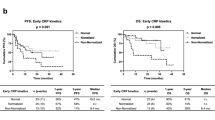
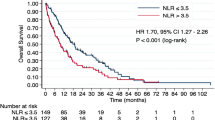
Median PFS was significantly shorter in patients with high NLR (≥ 3) versus low NLR (p = 0.0356), high MLR (≥ 0.3) versus low MLR (p = 0.0013), or high PLR (≥ 160) versus low PLR (p = 0.0073), and median OS was significantly shorter in patients with high NLR versus low NLR (p = 0.0025), high MLR versus low MLR (p = 0.0025), high PLR versus low PLR (p = 0.0256), or high CRP (≥ 1.0 mg/dl) versus low CRP (p = 0.0006). Multivariate analyses showed that MLR (HR 2.65, p = 0.0068) was an independent factor for PFS and that NLR (HR 3.34, p = 0.0218), MLR (HR 3.42, p = 0.0381), and CRP (HR 4.98, p = 0.0108) were independent factors for OS.
Conclusions
The systemic inflammatory factors NLR, MLR, and CRP were predictive factors in nivolumab therapy for mRCC. These easily monitored factors can contribute to effective treatment and follow-up.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y, Bensalah K, Dabestani S, Montes SF, et al. European Association of Urology guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: the 2019 update. Eur Urol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2019.02.011.
George S, Rini BI, Hammers HJ. Emerging role of combination immunotherapy in the first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma: a review. JAMA Oncol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.4604.
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, McDermott DF, George S, Hammers HJ, Srinivas S, et al. Nivolumab versus everolimus in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(19):1803–13. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1510665.
Motzer RJ, Tannir NM, McDermott DF, Aren Frontera O, Melichar B, Choueiri TK, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(14):1277–90. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1712126.
De Giorgi U, Carteni G, Giannarelli D, Basso U, Galli L, Cortesi E, et al. Safety and efficacy of nivolumab for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: real-world results from an expanded access programme. BJU Int. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.14461.
Zahoor H, Barata PC, Jia X, Martin A, Allman KD, Wood LS, et al. Patterns, predictors and subsequent outcomes of disease progression in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated with nivolumab. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6(1):107. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-018-0425-8.
Ishihara H, Takagi T, Kondo T, Tachibana H, Fukuda H, Yoshida K, et al. Correlation between the magnitude of best tumor response and patient survival in nivolumab therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Med Oncol (Northwood, London, England). 2019;36(4):35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-019-1261-5.
Champiat S, Dercle L, Ammari S, Massard C, Hollebecque A, Postel-Vinay S, et al. Hyperprogressive disease is a new pattern of progression in cancer patients treated by anti-PD-1/PD-L1. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(8):1920–8. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-16-1741.
Kato S, Goodman A, Walavalkar V, Barkauskas DA, Sharabi A, Kurzrock R. Hyperprogressors after immunotherapy: analysis of genomic alterations associated with accelerated growth rate. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(15):4242–50. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-16-3133.
Ishihara H, Kondo T, Takagi T, Tachibana H, Fukuda H, Yoshida K, et al. Immediate progressive disease in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with nivolumab: a multi-institution retrospective study. Target Oncol. 2018;13(5):611–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-018-0591-0.
Verma V, Sprave T, Haque W, Simone CB 2nd, Chang JY, Welsh JW, et al. A systematic review of the cost and cost-effectiveness studies of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6(1):128. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-018-0442-7.
Tanaka N, Mizuno R, Yasumizu Y, Ito K, Shirotake S, Masunaga A, et al. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with first-line and subsequent second-line targeted therapy: a proposal of the modified-IMDC risk model. Urol Oncol. 2017;35(2):39.e19–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.10.001.
Teishima J, Kobatake K, Kitano H, Nagamatsu H, Sadahide K, Hieda K, et al. The impact of change in serum C-reactive protein level on the prediction of effects of molecular targeted therapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2016;117(6b):E67–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.13260.
Beuselinck B, Vano YA, Oudard S, Wolter P, De Smet R, Depoorter L, et al. Prognostic impact of baseline serum C-reactive protein in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) treated with sunitinib. BJU Int. 2014;114(1):81–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.12494.
Santoni M, De Giorgi U, Iacovelli R, Conti A, Burattini L, Rossi L, et al. Pre-treatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio may be associated with the outcome in patients treated with everolimus for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2013;109(7):1755–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2013.522.
Keizman D, Ish-Shalom M, Huang P, Eisenberger MA, Pili R, Hammers H, et al. The association of pre-treatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio with response rate, progression free survival and overall survival of patients treated with sunitinib for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer (Oxford, England 1990). 2012;48(2):202–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2011.09.001.
Na N, Yao J, Cheng C, Huang Z, Hong L, Li H, et al. Meta-analysis of the efficacy of the pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of prognosis in renal carcinoma patients receiving tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncotarget. 2016;7(28):44039–46. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.9836.
Ishihara H, Kondo T, Yoshida K, Omae K, Takagi T, Iizuka J, et al. Effect of systemic inflammation on survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma receiving second-line molecular-targeted therapy. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2017;15(4):495–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2017.01.018.
Ishihara H, Kondo T, Omae K, Takagi T, Iizuka J, Kobayashi H, et al. Sarcopenia and the modified glasgow prognostic score are significant predictors of survival among patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who are receiving first-line sunitinib treatment. Target Oncol. 2016;11(5):605–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-016-0430-0.
Nunno VD, Mollica V, Gatto L, Santoni M, Cosmai L, Porta C, et al. Prognostic impact of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Immunotherapy. 2019;11(7):631–43. https://doi.org/10.2217/imt-2018-0175.
Capone M, Giannarelli D, Mallardo D, Madonna G, Festino L, Grimaldi AM, et al. Baseline neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and derived NLR could predict overall survival in patients with advanced melanoma treated with nivolumab. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6(1):74. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-018-0383-1.
Nakamura Y, Tanaka R, Maruyama H, Ishitsuka Y, Okiyama N, Watanabe R, et al. Correlation between blood cell count and outcome of melanoma patients treated with anti-PD-1 antibodies. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyy201.
Bagley SJ, Kothari S, Aggarwal C, Bauml JM, Alley EW, Evans TL, et al. Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a marker of outcomes in nivolumab-treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer (Amsterdam, Netherlands). 2017;106:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.01.013.
Oya Y, Yoshida T, Kuroda H, Mikubo M, Kondo C, Shimizu J, et al. Predictive clinical parameters for the response of nivolumab in pretreated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(61):103117–28. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21602.
Martens A, Wistuba-Hamprecht K, Geukes Foppen M, Yuan J, Postow MA, Wong P, et al. Baseline peripheral blood biomarkers associated with clinical outcome of advanced melanoma patients treated with ipilimumab. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22(12):2908–18. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-15-2412.
Weide B, Martens A, Hassel JC, Berking C, Postow MA, Bisschop K, et al. Baseline biomarkers for outcome of melanoma patients treated with pembrolizumab. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22(22):5487–96. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-16-0127.
Heppt MV, Heinzerling L, Kahler KC, Forschner A, Kirchberger MC, Loquai C, et al. Prognostic factors and outcomes in metastatic uveal melanoma treated with programmed cell death-1 or combined PD-1/cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 inhibition. Eur J Cancer (Oxford, England: 1990). 2017;82:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2017.05.038.
Soyano AE, Dholaria B, Marin-Acevedo JA, Diehl N, Hodge D, Luo Y, et al. Peripheral blood biomarkers correlate with outcomes in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with anti-PD-1 antibodies. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6(1):129. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-018-0447-2.
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer (Oxford, England: 1990). 2009;45(2):228–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026.
Ishihara H, Kondo T, Yoshida K, Omae K, Takagi T, Iizuka J, et al. Time to progression after first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitor predicts survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma receiving second-line molecular-targeted therapy. Urol Oncol. 2017;35(9):542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2017.05.014.
Ishihara H, Takagi T, Kondo T, Tachibana H, Yoshida K, Omae K, et al. Efficacy and safety of third-line molecular-targeted therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma resistant to first-line vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor and second-line therapy. Int J Clin Oncol. 2018;23(3):559–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-018-1241-3.
Boissier R, Campagna J, Branger N, Karsenty G, Lechevallier E. The prognostic value of the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in renal oncology: a review. Urol Oncol. 2017;35(4):135–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2017.01.016.
Chen Z, Shao Y, Yao H, Zhuang Q, Wang K, Xing Z, et al. Preoperative albumin to globulin ratio predicts survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. Oncotarget. 2017;8(29):48291–302. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15162.
Chen Z, Wang K, Lu H, Xue D, Fan M, Zhuang Q, et al. Systemic inflammation response index predicts prognosis in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma: a propensity score-matched analysis. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:909–19. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.s186976.
Wang X, Su S, Guo Y. The clinical use of the platelet to lymphocyte ratio and lymphocyte to monocyte ratio as prognostic factors in renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(48):84506–14. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21108.
Russo A, Franchina T, Ricciardi GRR, Battaglia A, Scimone A, Berenato R, et al. Baseline neutrophilia, derived neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (dNLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and outcome in non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with nivolumab or docetaxel. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(10):6337–43. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26609.
Ramsey S, Lamb GW, Aitchison M, Graham J, McMillan DC. Evaluation of an inflammation-based prognostic score in patients with metastatic renal cancer. Cancer. 2007;109(2):205–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.22400.
Naito S, Kinoshita H, Kondo T, Shinohara N, Kasahara T, Saito K, et al. Prognostic factors of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma with removed metastases: a multicenter study of 556 patients. Urology. 2013;82(4):846–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2013.06.035.
Ko JJ, Xie W, Kroeger N, Lee JL, Rini BI, Knox JJ, et al. The International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium model as a prognostic tool in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma previously treated with first-line targeted therapy: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(3):293–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(14)71222-7.
Bilen MA, Dutcher GMA, Liu Y, Ravindranathan D, Kissick HT, Carthon BC, et al. Association between pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and outcome of patients with metastatic renal-cell carcinoma treated with nivolumab. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2018;16(3):e563–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2017.12.015.
Coussens LM, Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. 2002;420(6917):860–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01322.
Balkwill FR, Mantovani A. Cancer-related inflammation: common themes and therapeutic opportunities. Semin Cancer Biol. 2012;22(1):33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2011.12.005.
Klinger MH, Jelkmann W. Role of blood platelets in infection and inflammation. Journal Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002;22(9):913–22. https://doi.org/10.1089/10799900260286623.
Diem S, Schmid S, Krapf M, Flatz L, Born D, Jochum W, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) as prognostic markers in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with nivolumab. Lung Cancer (Amsterdam, Netherlands). 2017;111:176–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.07.024.
Murray PJ. Immune regulation by monocytes. Semin Immunol. 2018;35:12–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2017.12.005.
Bilen MA, Martini DJ, Liu Y, Lewis C, Collins HH, Shabto JM, et al. The prognostic and predictive impact of inflammatory biomarkers in patients who have advanced-stage cancer treated with immunotherapy. Cancer. 2019;125(1):127–34. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.31778.
De Giorgi U, Procopio G, Giannarelli D, Sabbatini R, Bearz A, Buti S, et al. Association of systemic inflammation index and body mass index with survival in patients with renal cell cancer treated with nivolumab. Clin Cancer Res. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-18-3661.
Simson L, Ellyard JI, Dent LA, Matthaei KI, Rothenberg ME, Foster PS, et al. Regulation of carcinogenesis by IL-5 and CCL11: a potential role for eosinophils in tumor immune surveillance. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md: 1950). 2007;178(7):4222–9.
Carretero R, Sektioglu IM, Garbi N, Salgado OC, Beckhove P, Hammerling GJ. Eosinophils orchestrate cancer rejection by normalizing tumor vessels and enhancing infiltration of CD8(+) T cells. Nat Immunol. 2015;16(6):609–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.3159.
Sasaki A, Nakamura Y, Mishima S, Kawazoe A, Kuboki Y, Bando H, et al. Predictive factors for hyperprogressive disease during nivolumab as anti-PD1 treatment in patients with advanced gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-018-00922-8.
Weber JS, Tang H, Hippeli L, Qian M, Wind-Rotolo M, Larkin JMG, et al. Serum IL-6 and CRP as prognostic factors in melanoma patients receiving single agent and combination checkpoint inhibition. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(15_suppl):100. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2019.37.15_suppl.100.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ms. Nobuko Hata (Department of Urology, Tokyo Women’s Medical University and Department of Urology) for secretarial work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Tsunenori Kondo received honoraria from Ono Pharmaceutical. Hiroki Ishihara, Hidekazu Tachibana, Toshio Takagi, Hironori Fukuda, Kazuhiko Yoshida, Junpei Iizuka, Hirohito Kobayashi, Masayoshi Okumi, Hideki Ishida, and Kazunari Tanabe have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Funding
This study did not receive any funding.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishihara, H., Tachibana, H., Takagi, T. et al. Predictive Impact of Peripheral Blood Markers and C-Reactive Protein in Nivolumab Therapy for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Targ Oncol 14, 453–463 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-019-00660-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-019-00660-6