Abstract
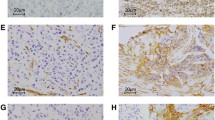
The aim of this study was to investigate expression of CD147 and MMP-9 in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) so as to determine whether these two proteins may be correlated with poor prognosis of TNBC patients. We examined the expression levels of the CD147 and MMP-9 in 127 patients with TNBC and 30 patients with mammary gland fibroma using immunohistochemical staining before any treatments. Furthermore, we analyzed the correlation between the expression of these two proteins and various clinicopathologic factors including survival status of patients with TNBC. Positive stain of CD147 and MMP-9 was observed in all samples of TNBC. A statistically positive correlation was observed between the expression levels of CD147 and MMP-9 in TNBC tissues. The incidences of high expression were 48.0 % for CD147 and 53.5 % for MMP-9 in 127 TNBC tissues, respectively. High expression of either CD147 or MMP-9 was significantly correlated with clinical feature and shorter progression-free survival (PFS) (PCD147 = 0.039; PMMP-9 = 0.017) and overall survival (OS) (PCD147 = 0.037; PMMP-9 = 0.023). The expression levels of CD147 and MMP-9 are positively correlated with invasion, metastasis and shorter PFS/OS of TNBC. Patients with high expression of CD147 and MMP-9 had poor prognosis than TNBC patients with low expression.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumors. Nature. 2000;406:747–52.
Kreike B, van Kouwenhove M, Horlings H, Weigelt B, Peterse H, Bartelink H, et al. Gene expression profiling and histopathological characterization of triple-negative/basal-like breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res. 2007;9:R65.
Reis-Filho JS, Tutt AN. Triple negative tumors: a critical review. Histopathology. 2008;52:108–18.
Kang SP, Martel M, Harris LN. Triple negative breast cancer: current understanding of biology and treatment options. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2008;20:40–6.
Bauer KR, Brown M, Cress RD, Parise CA, Caggiano V. Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor (ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative phenotype: a population-based study from the California cancer Registry. Cancer. 2007;109:1721–8.
Tang Yi, Nakada Marian T, Kesavan Prabakaran, et al. Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer stimulates tumor angiogenesis by elevating vascular endothelial cell growth factor and matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Res. 2005;65:3193–9.
Toole BP. Emmprin (CD147), a cell surface regulator of matrix metalloproteinase production and function. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2003;54:371–89.
Zheng HC, Takahashi H, Murai Y, et al. Upregulated EMM-PRIN/CD147 might contribute to growth and angiogenesis of gastric carcinoma: a good marker for local invasion and prognosis. Br J Cancer. 2006;95:1371–8.
Li Z, Ren Y, Wu QC, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor enhances neoplastic cell invasion by inducing the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 and inter-leukin-8 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines. Chin Med J. 2004;117:107–14.
HymowitzM Zucker, Rollo EE, et al. Tumorigenic potential of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer. Am J Pathol. 2001;158:1921–8.
Mira E, Lacalle RA, Buesa JM, et al. Secreted MMP9 promotes angiogenesis more efficiently than constitutive active MMP9 bound to the tumor cell surface. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:1847–57.
Yu WW, Liu JH, Xiong XL, et al. Expression of MMP-9 and CD147 in invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix and their implication. Pathol Res Pract. 2009;205:709–15.
Tang J, Zhou HW, Jiang JL, et al. ßig-h3 is involved in the HAb18G/CD147-mediated metastasis process in human hepatoma cells. Exp Biol Med. 2007;232:344–52.
Davidson B, Goldberg I, Berner A, et al. EMMPRIN (extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer) is a novel marker of poor outcome in serous ovarian carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2003;20:161–9.
Ramos-DeSimone N, Hahn-Dantona E, Sipley J, et al. Activation of matrix metalloprotease-9 (MMP-9) via converting plasmin/stromelysin-1 cascade enhances tumor cell invasion. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:13066–76.
Alizadeh AA, Ross DT, Perou CM, Ven de Rijn M. Towards a novel classification of human malignancies based on gene expression patterns. J Pathol. 2010;195:41–52.
Kashiwagi S, et al. Significance of E-cadherin expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:249–55.
Liu Z, Li L, Yang ZX, et al. Research article Increased expression of MMP9 is correlated with poor prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:270–5.
Wang S, Zhou J, Wang XY, et al. Down-regulated expression of SATB2 is associated with metastasis and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. J Pathol. 2009;219:114–22.
Masunaga R, Kohno H, Dhar DK, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression correlates with tumor neovascularization and prognosis in human colorectal carcinoma patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:4064–8.
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29.
Li Y, Shang P, Qian AR, et al. Inhibitory effects of antisense RNA of HAb18G/CD147 on invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro. World J Gastroenterol. 2003;9:2174–7.
Reimers N, Za frakas K, Assmann V, et al. Expression of extracellular matrix metalloproteases inducer on micrometastatic and primary mammary carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:3422–8.
Chakraborti S, Mandal M, Das S, et al. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases: an overview. Mol Cell Biochem. 2003;253:269–85.
Opdenakker G, Van den Steen PE, Van Damme J, Gelatinase B. A tuner and amplifier of immune functions. Trends Immunol. 2001;22:571–9.
Opdenakker G, Van den Steen PE, Dubois B, et al. Gelatinase B functions as regulator and effector in leukocyte biology. J Leukoc Biol. 2001;69:851–9.
Matache C, Stefanescu M, Dragomir C, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 and its natural inhibitor TIMP-1 expressed or secreted by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun. 2003;20:323–31.
Li Y, Jing X, Li C, et al. HAb18G (CD147), a cancer-associated biomarker and its role in cancer detection. Histopathology. 2009;54:677–87.
Piao S, Zhao S, Guo F, et al. Increased expression of CD147 and MMP-9 is correlated with poor prognosis of salivary duct carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012;138:627–35.
Ju XZ, Yang JM, Zhou XY, et al. EMMPRIN expression as a prognostic factor in radiotherapy of cervical cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:494–501.
Chen X, Lin J, Kanekura T, et al. A small interfering CD147-targeting RNA inhibited the proliferation, invasiveness, and metastatic activity of malignant melanoma. Cancer Res. 2006;66:11323–30.
Rao JS, Ra C, Gondi C, et al. Inhibition of invasion, angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis by adenovirus-mediated transfer of antisense uPAR and MMP-9 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005;4:1399–408.
Acknowledgments
This experiment was finished in the Oncobiology Key Lab of the Heilongjiang Province Common Institution of Higher Learning. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number 81071889] and Harbin science and technology innovation young talents research funds [grant number 2007RFQXS086].
Conflict of interest
All authors declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shu Zhao and Wenjie Ma contributed equally to the work and should be considered co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, S., Ma, W., Zhang, M. et al. High expression of CD147 and MMP-9 is correlated with poor prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) patients. Med Oncol 30, 335 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0335-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0335-4