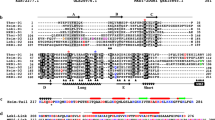
Abstract
Gelsolin is representative of a class of actin-modulating proteins found in lower eukaryotes to mammals, which sever actin filaments1. Gelsolin found in the cytoplasm of cells is functionally similar to a mammalian plasma protein of similar size, originally called ADF or brevin. Human plasma and rabbit macrophage gelsolins differ by the presence of a 25-amino-acid residue extension on plasma gelsolin which appears to account for the difference in relative molecular mass (Mr) between the proteins as assessed by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE), 93,000 (93K) and 90K, respectively2. Here we report the isolation of full-length human plasma gelsolin complementary DNA clones from a HepG2 library. The inferred amino-acid sequence reveals the presence of a signal peptide, a long tandem repeat that matches the actin-binding domains of gelsolin, a tetrapeptide present in actin and extended regions of identical sequence with rabbit macrophage gelsolin. Southern blot analysis indicates that a single gene in the haploid genome encodes both protein forms.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stossel, T. P. et al. A. Rev. Cell Biol. 1, 323–402 (1985).
Yin, H. L., Kwiatkowski, D. J., Mole, J. E. & Cole, F. S. J. biol. chem. 259, 5271–5276 (1984).
Kozak, M. Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 857–872 (1984).
Wickner, W. T. & Lodish, H. F. Science 230, 400–407 (1985).
Yin, H. L. & Stossel, T. P. J. biol. Chem. 255, 9490–9493 (1980).
Soua, Z., Porte, F., Harricane, M-C., Feinberg, J. & Capony, J.-P. Eur. J. Biochem. 153, 275–287 (1985).
Chaponnier, C., Janmey, P. A. & Yin, H. L. J. Cell Biol. (in the press).
Bryan, J. & Hwo, S. J.Cell Biol. 102, 1439–1446 (1986).
Kwiatkowski, D. J., Janmey, P. A., Mole, J. E. & Yin, H. L. J. biol. Chem. 260, 15323–15328 (1985).
Kretsinger, R. H. CRC crit. Rev. Biochem. 8, 119–174 (1980).
Kanehisa, M. Nucleic Acids Res. 10, 183–196 (1982).
Dayhoff, M. O., Schwartz, R. M. & Orcutt, B. C. Atlas of Protein Sequence and Structure Vol. 5 Suppl. 3, 353–358 (Natn. Biomed. Res. Fdn, Silver Spring, 1978).
Robine, S. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 8488–8492 (1985).
Glenney, J. R. & Weber, K. Proc. natn Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 2810–2814 (1981).
Matsudaira, P. T. & Burgess, D. R. J. Cell Biol. 92, 648–656 (1982).
Matsudaira, P., Jakes, R. & Walker, J. E. Nature 315, 248–250 (1985).
Hesterberg, L. K. & Weber, K. J. biol. Chem. 258, 365–369 (1983).
Sutoh, K. Biochemistry 23, 1942–1946 (1984).
Gubler, U. & Hoffman, B. J. Gene 25, 263–279 (1983).
Ginsburg, D. et al. scince 228, 1401–1406 (1985).
Dale, R. M. K., McClure, B. A. & Houchins, J. P. Plasmid 13, 31–40 (1985).
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. & Coulson, A. R. Proc. natn Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5463–5469 (1977).
Feinberg, A.P. & Vogelstein, B. Analyt. Biochem. 137, 266–267 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwiatkowski, D., Stossel, T., Orkin, S. et al. Plasma and cytoplasmic gelsolins are encoded by a single gene and contain a duplicated actin-binding domain. Nature 323, 455–458 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/323455a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/323455a0
This article is cited by
-
Characterization and prognostic impact of ACTBL2-positive tumor-infiltrating leukocytes in epithelial ovarian cancer
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
The exosome-mediated autocrine and paracrine actions of plasma gelsolin in ovarian cancer chemoresistance
Oncogene (2020)
-
Gelsolin of insect vectors negatively regulates actin-based tubule motility of plant reoviruses
Phytopathology Research (2019)
-
Pre-operative Circulating Plasma Gelsolin Predicts Residual Disease and Detects Early Stage Ovarian Cancer
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Interaction Between a Gelsolin from Dendrorhynchus zhejiangensis with Three Gelsolin-Like Domains and Actin In Vitro
The Protein Journal (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.