Abstract
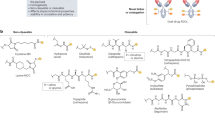
The in vitro potency of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) increases with the drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR); however, ADC plasma clearance also increases with DAR, reducing exposure and in vivo efficacy. Here we show that accelerated clearance arises from ADC hydrophobicity, which can be modulated through drug-linker design. We exemplify this using hydrophilic auristatin drug linkers and PEGylated ADCs that yield uniform, high-DAR ADCs with superior in vivo performance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sievers, E.L. & Senter, P.D. Annu. Rev. Med. 64, 15–29 (2013).
Hamblett, K.J. et al. Clin. Cancer Res. 10, 7063–7070 (2004).
Herbertson, R.A. et al. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 6709–6715 (2009).
Lyon, R.P., Meyer, D.L., Setter, J.R. & Senter, P.D. Methods Enzymol. 502, 123–138 (2012).
Wang, L., Amphlett, G., Blattler, W.A., Lambert, J.M. & Zhang, W. Protein Sci. 14, 2436–2446 (2005).
McDonagh, C.F. et al. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 19, 299–307 (2006).
Junutula, J.R. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 26, 925–932 (2008).
Jeffrey, S.C. et al. Bioconjug. Chem. 24, 1256–1263 (2013).
Strop, P. et al. Chem. Biol. 20, 161–167 (2013).
King, H.D. et al. J. Med. Chem. 45, 4336–4343 (2002).
Miller, M.L. et al. J. Med. Chem. 47, 4802–4805 (2004).
Moon, S.J. et al. J. Med. Chem. 51, 6916–6926 (2008).
Zhao, R.Y. et al. J. Med. Chem. 54, 3606–3623 (2011).
Jeffrey, S.C. et al. Bioconjug. Chem. 17, 831–840 (2006).
Wahl, A.F. et al. Cancer Res. 62, 3736–3742 (2002).
Oflazoglu, E. et al. Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 6171–6180 (2008).
Doronina, S.O. et al. Bioconjug. Chem. 17, 114–124 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We thank our Seattle Genetics colleagues S. Alley for assistance in pharmacokinetic modeling; J. Miyamoto for in vitro cytotoxicity assays; A. Cronkite for competition binding studies; and C. Zapata, C. Balasubramanian and W. Schultz for rat toxicology studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.P.L. designed drug linkers, prepared and characterized ADCs by HIC, designed in vivo studies, performed the pharmacokinetic data fitting and wrote the manuscript; T.D.B. synthesized drug linkers; S.O.D. designed and synthesized drug linkers, P.J.B. designed and synthesized PEGylated drug linkers; J.H.H. performed radiolabeling and quantification for pharmacokinetic studies; H.D.N.-L. designed and interpreted the rat toxicology studies; M.J. performed IHC analysis of ADC uptake by rat liver; M.E.A. performed in vivo work (activity, pharmacokinetics and biodistribution); J.R.S. performed mass spectrometry assays to characterize ADC drug loading and stability, and to quantify MMAE delivery in vivo; P.D.S. directed the synthetic chemistry and co-wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
“All authors are employees of Seattle Genetics, Inc.”
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–9 and Supplementary Note (PDF 1171 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyon, R., Bovee, T., Doronina, S. et al. Reducing hydrophobicity of homogeneous antibody-drug conjugates improves pharmacokinetics and therapeutic index. Nat Biotechnol 33, 733–735 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3212
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3212
This article is cited by
-
Targeted drug delivery using nanobodies to deliver effective molecules to breast cancer cells: the most attractive application of nanobodies
Cancer Cell International (2024)
-
Exploring the next generation of antibody–drug conjugates
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology (2024)
-
Antibody-drug conjugates in cancer therapy: innovations, challenges, and future directions
Archives of Pharmacal Research (2024)
-
Payload diversification: a key step in the development of antibody–drug conjugates
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2023)
-
Understanding the activity of antibody–drug conjugates in primary and secondary brain tumours
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology (2023)