Abstract
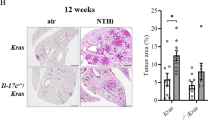
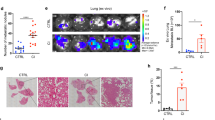
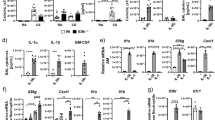
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is associated with an increased risk for lung cancer and an aberrant microbiota of the lung. Microbial colonization contributes to chronic neutrophilic inflammation in COPD. Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi) is frequently found in lungs of stable COPD patients and is the major pathogen triggering exacerbations. The epithelial cytokine interleukin-17C (IL-17C) promotes the recruitment of neutrophils into inflamed tissues. The purpose of this study was to investigate the function of IL-17C in the pulmonary tumor microenvironment. We subjected mice deficient for IL-17C (IL-17C−/−) and mice double deficient for Toll-like receptor 2 and 4 (TLR-2/4−/−) to a metastatic lung cancer model. Tumor proliferation and growth as well as the number of tumor-associated neutrophils was significantly decreased in IL-17C−/− and TLR-2/4−/− mice exposed to NTHi. The NTHi-induced pulmonary expression of IL-17C was dependent on TLR-2/4. In vitro, IL-17C increased the NTHi- and tumor necrosis factor-α-induced expression of the neutrophil chemokines keratinocyte-derived chemokine and macrophage inflammatory protein 2 in lung cancer cells but did not affect proliferation. Human lung cancer samples stained positive for IL-17C, and in non-small cell lung cancer patients with lymph node metastasis, IL-17C was identified as a negative prognostic factor. Our data indicate that epithelial IL-17C promotes neutrophilic inflammation in the tumor microenvironment and suggest that IL-17C links a pathologic microbiota, as present in COPD patients, with enhanced tumor growth.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adcock IM, Caramori G, Barnes PJ . Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and lung cancer: new molecular insights. Respiration 2011; 81: 265–284.
Young RP, Hopkins RJ, Christmas T, Black PN, Metcalf P, Gamble GD . COPD prevalence is increased in lung cancer, independent of age, sex and smoking history. Eur Respir J 2009; 34: 380–386.
Zulueta JJ, Wisnivesky JP, Henschke CI, Yip R, Farooqi AO, McCauley DI et al. Emphysema scores predict death from COPD and lung cancer. Chest 2012; 141: 1216–1223.
Hoenderdos K, Condliffe A . The neutrophil in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2013; 48: 531–539.
Roos AB, Sethi S, Nikota J, Wrona CT, Dorrington MG, Sanden C et al. IL-17 A and the promotion of neutrophilia in acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2015; 192: 428–437.
Sethi S . Infection as a comorbidity of COPD. Eur Respir J 2010; 35: 1209–1215.
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M . Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 2010; 140: 883–899.
Kim S, Takahashi H, Lin WW, Descargues P, Grivennikov S, Kim Y et al. Carcinoma-produced factors activate myeloid cells through TLR2 to stimulate metastasis. Nature 2009; 457: 102–106.
Li D, Beisswenger C, Herr C, Hellberg J, Han G, Zakharkina T et al. Myeloid cell RelA/p65 promotes lung cancer proliferation through Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in murine and human tumor cells. Oncogene 2013; 33: 1239–1248.
Li D, Beisswenger C, Herr C, Schmid RM, Gallo RL, Han G et al. Expression of the antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin in myeloid cells is required for lung tumor growth. Oncogene 2013; 33: 2709–2716.
Takahashi H, Ogata H, Nishigaki R, Broide DH, Karin M . Tobacco smoke promotes lung tumorigenesis by triggering IKKbeta- and JNK1-dependent inflammation. Cancer Cell 2010; 17: 89–97.
Chang SH, Mirabolfathinejad SG, Katta H, Cumpian AM, Gong L, Caetano MS et al. T helper 17 cells play a critical pathogenic role in lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014; 111: 5664–5669.
Jungnickel C, Wonnenberg B, Karabiber O, Wolf A, Voss M, Wolf L et al. Cigarette smoke induced disruption of pulmonary barrier and bacterial translocation drive tumor associated inflammation and growth. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2015; 309: L605–L613; ajplung 00116 02015.
Moghaddam SJ, Li H, Cho SN, Dishop MK, Wistuba II, Ji L et al. Promotion of lung carcinogenesis by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease-like airway inflammation in a K-ras-induced mouse model. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2009; 40: 443–453.
Kusagaya H, Fujisawa T, Yamanaka K, Mori K, Hashimoto D, Enomoto N et al. Toll-like receptor-mediated airway IL-17C enhances epithelial host defense in an autocrine/paracrine manner. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2014; 50: 30–39.
Pfeifer P, Voss M, Wonnenberg B, Hellberg J, Seiler F, Lepper PM et al. IL-17C is a mediator of respiratory epithelial innate immune response. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2013; 48: 415–421.
Ramirez-Carrozzi V, Sambandam A, Luis E, Lin Z, Jeet S, Lesch J et al. IL-17C regulates the innate immune function of epithelial cells in an autocrine manner. Nat Immunol 2011; 12: 1159–1166.
Song X, Zhu S, Shi P, Liu Y, Shi Y, Levin SD et al. IL-17RE is the functional receptor for IL-17C and mediates mucosal immunity to infection with intestinal pathogens. Nat Immunol 2011; 12: 1151–1158.
Wolf L, Sapich S, Honecker A, Jungnickel C, Seiler F, Bischoff M et al. IL-17 A-mediated expression of epithelial IL-17C promotes inflammation during acute Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2016; 311: L1015–L1022.
Johansen C, Riis JL, Gedebjerg A, Kragballe K, Iversen L . Tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated induction of interleukin 17C in human keratinocytes is controlled by nuclear factor kappaB. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 25487–25494.
Gaffen SL . Structure and signalling in the IL-17 receptor family. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9: 556–567.
Hurst SD, Muchamuel T, Gorman DM, Gilbert JM, Clifford T, Kwan S et al. New IL-17 family members promote Th1 or Th2 responses in the lung: in vivo function of the novel cytokine IL-25. J Immunol 2002; 169: 443–453.
Li D, Beisswenger C, Herr C, Schmid RM, Gallo RL, Han G et al. Expression of the antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin in myeloid cells is required for lung tumor growth. Oncogene 2014; 33: 2709–2716.
Voss M, Wolf L, Kamyschnikow A, Wonnenberg B, Honecker A, Herr C et al. IL-17A contributes to maintenance of pulmonary homeostasis in a murine model of cigarette smoke-induced emphysema. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2015; 309: L188–L195.
Li D, Beisswenger C, Herr C, Hellberg J, Han G, Zakharkina T et al. Myeloid cell RelA/p65 promotes lung cancer proliferation through Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in murine and human tumor cells. Oncogene 2014; 33: 1239–1248.
Pfeifer P, Voss M, Wonnenberg B, Hellberg J, Seiler F, Lepper PM et al. IL-17C is a mediator of respiratory epithelial innate immune response. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2012; 48: 415–421.
Marsland BJ, Gollwitzer ES . Host–microorganism interactions in lung diseases. Nat Rev Immunol 2014; 14: 827–835.
Yadava K, Pattaroni C, Sichelstiel AK, Trompette A, Gollwitzer ES, Salami O et al. Microbiota promotes chronic pulmonary inflammation by enhancing IL-17 A and autoantibodies. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2016; 193: 975–987.
Karin M, Greten FR . NF-kappaB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat Rev Immunol 2005; 5: 749–759.
Papi A, Casoni G, Caramori G, Guzzinati I, Boschetto P, Ravenna F et al. COPD increases the risk of squamous histological subtype in smokers who develop non-small cell lung carcinoma. Thorax 2004; 59: 679–681.
Friedrich M, Diegelmann J, Schauber J, Auernhammer CJ, Brand S . Intestinal neuroendocrine cells and goblet cells are mediators of IL-17 A-amplified epithelial IL-17C production in human inflammatory bowel disease. Mucosal Immunol 2015; 8: 943–958.
Bellocq A, Antoine M, Flahault A, Philippe C, Crestani B, Bernaudin JF et al. Neutrophil alveolitis in bronchioloalveolar carcinoma: induction by tumor-derived interleukin-8 and relation to clinical outcome. Am J Pathol 1998; 152: 83–92.
Teramukai S, Kitano T, Kishida Y, Kawahara M, Kubota K, Komuta K et al. Pretreatment neutrophil count as an independent prognostic factor in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: an analysis of Japan Multinational Trial Organisation LC00-03. Eur J Cancer 2009; 45: 1950–1958.
Coffelt SB, Kersten K, Doornebal CW, Weiden J, Vrijland K, Hau CS et al. IL-17-producing gammadelta T cells and neutrophils conspire to promote breast cancer metastasis. Nature 2015; 522: 345–348.
El Rayes T, Catena R, Lee S, Stawowczyk M, Joshi N, Fischbach C et al. Lung inflammation promotes metastasis through neutrophil protease-mediated degradation of Tsp-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2015; 112: 16000–16005.
Kowanetz M, Wu X, Lee J, Tan M, Hagenbeek T, Qu X et al. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor promotes lung metastasis through mobilization of Ly6G+Ly6C+ granulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 21248–21255.
Wculek SK, Malanchi I . Neutrophils support lung colonization of metastasis-initiating breast cancer cells. Nature 2015; 528: 413–417.
Houghton AM, Rzymkiewicz DM, Ji H, Gregory AD, Egea EE, Metz HE et al. Neutrophil elastase-mediated degradation of IRS-1 accelerates lung tumor growth. Nat Med 2010; 16: 219–223.
Hattar K, Savai R, Subtil FS, Wilhelm J, Schmall A, Lang DS et al. Endotoxin induces proliferation of NSCLC in vitro and in vivo: role of COX-2 and EGFR activation. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2013; 62: 309–320.
Song X, Gao H, Lin Y, Yao Y, Zhu S, Wang J et al. Alterations in the microbiota drive interleukin-17C production from intestinal epithelial cells to promote tumorigenesis. Immunity 2014; 40: 140–152.
Klein M, Obermaier B, Angele B, Pfister HW, Wagner H, Koedel U et al. Innate immunity to pneumococcal infection of the central nervous system depends on toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 and TLR4. J Infect Dis 2008; 198: 1028–1036.
Koedel U, Merbt UM, Schmidt C, Angele B, Popp B, Wagner H et al. Acute brain injury triggers MyD88-dependent, TLR2/4-independent inflammatory responses. Am J Pathol 2007; 171: 200–213.
Rad R, Ballhorn W, Voland P, Eisenacher K, Mages J, Rad L et al. Extracellular and intracellular pattern recognition receptors cooperate in the recognition of Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology 2009; 136: 2247–2257.
Herr C, Han G, Li D, Tschernig T, Dinh QT, Beisswenger C et al. Combined exposure to bacteria and cigarette smoke resembles characteristic phenotypes of human COPD in a murine disease model. Exp Toxicol Pathol 2015; 67: 261–269.
Chang SH, Reynolds JM, Pappu BP, Chen G, Martinez GJ, Dong C . Interleukin-17C promotes Th17 cell responses and autoimmune disease via interleukin-17 receptor E. Immunity 2011; 35: 611–621.
Pfaffl MW . A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 2001; 29: e45.
Remmele W, Stegner HE . Recommendation for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast cancer tissue. Pathologe 1987; 8: 138–140.
Schmidt LH, Gorlich D, Spieker T, Rohde C, Schuler M, Mohr M et al. Prognostic impact of Bcl-2 depends on tumor histology and expression of MALAT-1 lncRNA in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2014; 9: 1294–1304.
Hess C, Herr C, Beisswenger C, Zakharkina T, Schmid RM, Bals R . Myeloid RelA regulates pulmonary host defense networks. Eur Respir J 2010; 35: 343–352.
Gyorffy B, Surowiak P, Budczies J, Lanczky A . Online survival analysis software to assess the prognostic value of biomarkers using transcriptomic data in non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS One 2013; 8: e82241.
Acknowledgements
We thank Anja Honecker for excellent technical assistance. This study was supported by grants from the Wilhelm-Sander-Stiftung to Christoph Beisswenger and Robert Bals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jungnickel, C., Schmidt, L., Bittigkoffer, L. et al. IL-17C mediates the recruitment of tumor-associated neutrophils and lung tumor growth. Oncogene 36, 4182–4190 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.28
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.28
This article is cited by
-
Intratumoural microbiota: a new frontier in cancer development and therapy
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2024)
-
The IL-17 family in diseases: from bench to bedside
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
The Microbiome’s Influence on Head and Neck Cancers
Current Oncology Reports (2023)
-
Immunosuppressive cells in cancer: mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2022)
-
Interleukins in cancer: from biology to therapy
Nature Reviews Cancer (2021)