Abstract
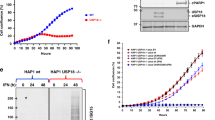
The presentation of human leukocyte antigens (HLA) class I requires the coordinated expression of numerous components involved in antigen presentation. Tumor cells may alter the antigen presentation by HLA class I, allowing them to evade antitumor immunity. In many cases, the lack of antigen presentation can be attributed to the downregulation of genes needed for antigen processing, such as the transporters associated with antigen processing (TAP) 1, and the proteasomal component, low molecular weight proteins (LMP) 2. The TAP1 and LMP2 genes are transcribed from a shared bidirectional promoter containing an interferon (IFN)-γ-response factor element; thus, the IFN-γ-signal strongly induces both TAP1 and LMP2 expression. Low molecular weight proteins2-deficient mice exhibited the development of uterine leiomyosarcomas. Here, the differential responsiveness to IFN-γ of the SKN human uterine leiomyosarcomas cell line was investigated. We now identify the G871E mutation in the ATP-binding region of Janus kinases 1, suggesting that the loss of TAP1 and LMP2 induction is a defect in the earliest steps of the IFN-γ-signal pathway, resulting in the inability of SKN cells to upregulate the antigen-processing pathway. Understanding the mechanisms by which these tumors circumvent cytokine signalling, thereby evading antitumor-specific immunity, would greatly aid the efficacy of immunotherapy for treating uterine leiomyosarcomas.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HLA:
-
human leukocyte antigens
- TAP:
-
transporters associated with antigen processing
- LMP:
-
low molecular weight proteins
- IRF-E:
-
IFN response factor element
- IRF-1:
-
IFN-regulatory factor 1
- GAS:
-
IFN-activated sequence
- Jak1:
-
Janus kinases 1
- CTL:
-
cytotoxic T lymphocyte
- STAT1:
-
signal transducer and activator of transcription 1
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor κB
References
Atkins D, Breuckmann A, Schmahl GE, Binner P, Ferrone S, Krummenauer F et al. (2004). Int J Cancer 109: 265–273.
Belich MP, Glynne RJ, Senger G, Sheer D, Trowsdale J . (1994). Curr Biol 4: 769–776.
Brucet M, Marques L, Sebastian C, Lloberas J, Celada A . (2004). Genes Immun 5: 26–35.
Cabrera CM, Jimenez P, Cabrera T, Esparza C, Ruiz-Cabello F, Garrido F . (2003). Tissue Antigens 61: 211–219.
Chatterjee-Kishore M, Wright KL, Ting JP, Stark GR . (2000). EMBO J 19: 4111–4122.
Dovhey SE, Ghosh NS, Wright KL . (2000). Cancer Res 60: 5789–5796.
Driscoll J, Brown MG, Finley D, Schreiber RD . (1993). Nature 365: 262–264.
Dunn GP, Bruce AT, Ikeda H, Old LJ, Schreiber RD . (2002). Nat Immunol 3: 991–998.
Gaczynska M, Rock KL, Goldberg AL . (1993). Nature 365: 264–267.
Garrido F, Ruiz-Cabello F, Cabrera T, Cozar JM, Pedrinaci S, Tallada M et al. (1997). Immunol Today 18: 89–95.
Groettrup M, Standera S, Stohwasser R, Kloetzel PM . (1997). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 8970–8975.
Harada H, Kitagawa M, Tanaka N, Yamamoto H, Harada K, Ishihara M et al. (1993). Science 259: 971–974.
Hayashi T, Faustman DL . (2002). Cancer Res 62: 24–27.
Hayashi T, Sekine T, Okamoto T . (1993). J Biol Chem 268: 26790–26795.
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H . (1981). J Histochem Cytochem 29: 577–580.
Ihle JN . (2001). Curr Opin Cell Biol 13: 211–217.
Kaplan DH, Shankaran V, Dighe AS, Stockert E, Aguet M, Old LJ et al. (1998). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 7556–7561.
Leiser AL, Anderson SE, Nonaka D, Chuai S, Olshen AB, Chi DS et al. (2005). Gynecol Oncol (Epub ahead of print).
Leitao MM, Soslow RA, Nonaka D, Olshen AB, Aghajanian C, Sabbatini P et al. (2004). Cancer 101: 1455–1462.
Maniatis T . (1999). Genes Dev 13: 505–510.
Miyagi T, Tatsumi T, Takehara T, Kanto T, Kuzushita N, Sugimoto Y et al. (2003). J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18: 32–40.
Momburg F, Neefjes JJ, Hammerling GJ . (1994a). Curr Opin Immunol 6: 32–37.
Momburg F, Roelse J, Howard JC, Butcher GW, Hammerling GJ, Neefjes JJ . (1994b). Nature 367: 648–651.
O'Shea JJ, Gadina M, Schreiber RD . (2002). Cell 109: 121–131.
Platanias LC . (2005). Nat Rev Immunol 5: 375–386.
Ramana CV, Gil MP, Schreiber RD, Stark GR . (2002). Trends Immunol 23: 96–101.
Raspollini MR, Pinzani P, Simi L, Amunni G, Villanucci A, Paglierani M et al. (2005). Gynecol Oncol 98: 334–335.
Seliger B, Maeurer MJ, Ferrone S . (2000). Immunol Today 21: 455–464.
Sexl V, Kovacic B, Piekorz R, Moriggl R, Stoiber D, Hoffmeyer A et al. (2003). Blood 101: 4937–4943.
Shankaran V, Ikeda H, Bruce AT, White JM, Swanson PE, Old LJ et al. (2001). Nature 410: 1107–1111.
Singal DP, Ye M, Ni J, Snider DP . (1996). Immunol Lett 50: 149–154.
Van Kaer L, Ashton-Rickardt PG, Eichelberger M, Gaczynska M, Nagashima K, Rock KL et al. (1994). Immunity 1: 533–541.
White LC, Wright KL, Felix NJ, Ruffner H, Reis LF, Pine R et al. (1996). Immunity 5: 365–376.
Wright KL, White LC, Kelly A, Beck S, Trowsdale J, Ting JP . (1995). J Exp Med 181: 1459–1471.
Acknowledgements
We thank Isamu Ishiwata for his generous gift of the SKN cell lines, and Robert Schreiber for his generous gift of the JAK1−/− MEFs, respectively. We are grateful to Kenneth L Wright for his generous gift of the LMP2 and TAP1 reporter genes, and Jim Ihle for his generous gift of the Jak1 wt expression vectors. We appreciate Dr Toshiaki Saida and the laboratory members of Shinshu University Graduate School of Medicine and Dr S Ferrone, Department of Immunology, Roswell Park Cancer Institute for the critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Science and Technology, from Kanzawa Medical Research Foundation, and from The Ichiro Kanehara Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary information accompanies the paper on Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, T., Kobayashi, Y., Kohsaka, S. et al. The mutation in the ATP-binding region of JAK1, identified in human uterine leiomyosarcomas, results in defective interferon-γ inducibility of TAP1 and LMP2. Oncogene 25, 4016–4026 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209434
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209434
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Novel insights into the molecular mechanisms of HLA class I abnormalities
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2012)
-
Deficiency of activated STAT1 in head and neck cancer cells mediates TAP1-dependent escape from cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2011)
-
Mice-lacking LMP2, immuno-proteasome subunit, as an animal model of spontaneous uterine leiomyosarcoma
Protein & Cell (2010)